Dear editors:
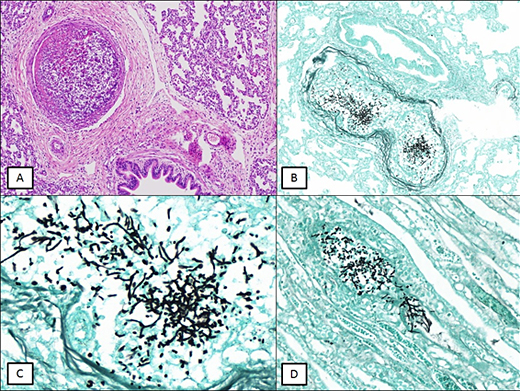
Septic pulmonary embolism (SPE) is rare and represents a real diagnostic challenge regarding the etiology of the process.1 SPE is defined by the pulmonary involvement added to the microbiological culture positive for the etiologic agent. (2,3 The images presented are of a newborn who, on the 43rd postoperative day for correction of gastroschisis, and on his 9th postoperative day for correction of intestinal volvulus, developed sepsis with sudden dyspnea after central venous catheter replacement. The newborn clinical context developed after the surgical procedure, having a close relationship between the intervention and its infectious condition. The patient died and the autopsy found lungs with edema, hemorrhage, areas of infarction and emboli containing fungal structures in the form of hyphae and yeast (Fig. 1, A, B, C y D).
Morphological aspects represented the diagnosis of Candida sp. The same structures were found in vessels of kidney. There are other species besides C. albicans, but morphologically all have a similar aspect: yeasts, thin hyphae and pseudo-hyphae at obtuse angles, unlike Aspergillus sp., in which hyphae are thick and at acute angles. Aspergillus sp. is the main differential etiological diagnosis. This type of fungus has the characteristic of invading organs as observed in this case. Although the definitive diagnosis depends on the microbiological culture, histochemical stains help a lot in the characterization, such as the Grocott-Gomori and the PAS with diastasis. Blood culture, collected in two samples, moments before death, tested positive for Candida albicans.
In the past, drug users and patients with endocarditis represented the main etiological groups for SPE. Currently, catheter or immunocompromised patients should also be considered.2,3,4,5 Regarding catheters, it is important to note that the incorrect manipulation of this invasive instrumental type is the main risk factor that contributes to the establishment of septic fungemia and embolisms.
In our case, it is important to consider major surgery performed with manipulations of organs of the gastrointestinal tract, a topography where the microbiota contains C. albicans. C. albicans is the fourth leading cause of sepsis mortality in intensive care units, being the most common fungus in these infections, deserving special attention from medical assistants, especially for the other species of Candida sp.2,3