Introduction
Comprehensive banking is a term used for financial institutions and banks. It provides clients with extensive options for banking services. Comprehensive banking is mostly formed when the focus is on special client groups; that is, when banks tailor their functions to the needs of their client groups, they have to learn and employ new specializations from wider fields of financial markets (Abtahi, 1996). For instance, a number of German banks which had initially started as business or corporate banks later turned into private banks. Also, retail and corporate banking in Asia shifted towards investment banking with their presence in international competition and the growing global commerce. As such, it can be said that universal banking is in line with human progress and social welfare (Athanassopoulou & John, 2004). Four major client groups of comprehensive baking are retail clients, business clients, corporate clients, and private clients. Different banks have different standards for this classification; however, in most banks, the classification mainly relies on the average deposit of the client accounts. According to each client group, the related banking fields are established to manage the affairs of that client group.
The three main steps of comprehensive banking implementation are client identification, market segmentation, and identification of the needs of each segment. Client identification is the first and most important implementation step of universal banking.Moreover, creative and committed human resources and employees are nowadays considered to be among the primary assets of a banking system and in a sense, the human workforce is the fundamental capital of a banking system (Fornell & Larcker, 1981). Traditional banking focused on the physical activities of the staff and the tasks were carried out within predefined frameworks.However, the circumstances of the human workforce and employees will definitely changein new banking systems such as comprehensive banking. New banking environments require employees that make sound, timely decisions and provide solutions for their problems. This requires capable employees and human workforce.
Empowerment based on educational content is a comprehensive, relatively time-consuming process that requires actions such as sharing the information with the staff, providing adequate autonomy with defined boundaries, and replacing hierarchies with task teams.This, in turn, leads to a flexible and dynamic organization where employees feel a sense of belonging and thus work with enthusiasm and pride (Fornell & Larker, 1981). Marl and Mordis define empowerment based on educational content based on one’s ability to accept responsibility and power via training, trust, and support. Ginned defines empowerment based on educational content as problem-solving by the managers, while Blanchard, in Three Keys to Empowerment based on educational content argues that empowerment based on educational content is based on the knowledge, practice, and motivational ability of individuals (Mohaqeqnia, et al., 2014).
There are certain requirements for the successful implementation of universal banking the most important of which is the employment of competent and capable human resources. Hasangholipoor, et al. (2013), reported that according to directive 90/40024 dated May 14, 2011,issued by the Central Bank of the Islamic Republic of Iran, banks are mandated to group their clients according to various criteria and tailortheir services to each client group. This has led to movements and efforts in the banking system to adapt to the new banking system. International researches have also addressed this subject. Genliterl conducted a study on developing a model for comprehensive banking and staff capability and showed that employees need to be capable in this regard for the targeted implementation of comprehensive banking (Bentler, 1990). Monorsitininvestigated the effect of leadership styles and bank directors’ relationships on job satisfaction among the employees of Turkish banks (Fornell & Larker, 1981).
Considering the competitive atmosphere of Iran’s banking industry and the increasing growth of private banks, implementing and proposing a model for universal banking has been addressed by the banking authorities and the new strategy has found a good position in domestic and foreign areas in both practical and research fields (Hasanqolipoor, Hashemzehi & Sajedifar, 2013). Davari, et al. (2014), investigated the competencies required for comprehensive banking implementation. The research identified the required competencies using exploratory methods and expert opinions. The result indicated the importance of decision making and delegation of authority, competency-based evaluation, technological skills, updated knowledge, flexibility, considering the staff as human assets, and learning. Mazinani, et al. (Khajesalehani, 2014), investigated the relationship between employee communication skills and customer satisfaction, finding that better communicator skills by employees also improves customer satisfaction. Danai & Qaribtarze (2012), investigated the relationship between the decision-making style of the heads of Islamic Azad Universities and their organizational performance, concluding that there was a direct, significant correlation between their directive decision-making and organizational performance.
Considering the overall movement of the national banking system towards comprehensive banking and the role of bank employees and human resources as the chief executives of universal banking, empowerment based on educational content and skills development the staff of Tejarat bank, as an efficient bank, are highly important for creating a competitive edge and increasing staff efficiency. Most banking studiesadopt an objective approach to the subject based on structuralism and functionalism. Therefore, objective and humanist views still require further research. Moreover, one of the beneficial features of management studies is aiding the improved management practices as well as increasing the knowledge on the subject. The current work can improve management practices and provide an opportunity for rethinking the organization’s activity and obtaining practical solutions for improved management performance. As such, this study aims to create a model of comprehensive banking focusing on empowerment based on educational content and skills development of employees. The main question of the research addresses the quality of a comprehensive banking model based on employee empowerment based on educational content and skills development. Accordingly, this brings about three questions:
Materials and methods
This is an applied studyaiming to develop applied knowledge in a specific field. Considering the nature of the subject, exploratory-descriptive research method was selectedand surveys and field studies were used for data collection.
The study used secondary sources such as books, papers, journals, and online resources to gather data. After that, it used a field study approach for developing and proposing the target model.
The statistical population of the qualitative phase consisted of a panel of experts who were able to help find the desired comprehensive banking model based on their experience and knowledge. The statistical population at the quantitative phase consisted of the staff of bank system of Iran.
Data analysis was performed using component identification via the Delphi fuzzy method (expert views), identification of component interrelations using the Fgtma -Fdematel method, developing a mathematical model based on large-scale, robust modeling; problem-solving using metaheuristic techniques, and sensitivity analysis via soft operational research techniques. The Delphi fuzzy method was utilized to select the experts and classify their responses and finally integrate them.after designing the types of banking for model design for each of the types of banking product development indicators and services related to human resourcesindicators are studied though study in research literature and expert opinions specified. Then the mathematical model was written using linear programming method and the weight of each of the effective factors is solved by solving the models with lingo software was obtained.The DEMATEL method was used to identify and investigate criteria interrelations and map network relationships. Further, the robust method was used to solve optimization problems with data uncertainty.
Results and discussion
This study investigated various empowerment based on educational content models and the factors influencing the empowerment based on educational content. After reviewing the recent employee empowerment based on educational content models in all levels, the factors identified in the models were submitted to the expert panel who selected 32 factors which they thoughtwould influence the staff empowerment based on educational content in comprehensive banking (Table 1).
Table 1 - Factors influencing employee empowerment based on educational content.
| No. | Factor |
|---|---|
| 1 | Sense of influence |
| 2 | Choice |
| 3 | Sense of competence |
| 4 | Sense of meaningfulness |
| 5 | Information |
| 6 | Rewards |
| 7 | Power to make decisions affecting organizational direction |
| 8 | Power to make decisions affecting organizational performance |
| 9 | Employee self-esteem |
| 10 | Self-efficacy beliefs |
| 11 | Senior management coaching |
| 12 | Training |
| 13 | Participation |
| 14 | Motivation |
| 15 | Job satisfaction |
| 16 | Information technology (IT) |
| 17 | Management strategies |
| 18 | Organizational conditions and factors |
| 19 | Employee self-efficacy sources |
| 20 | Participation in decision-making |
| 21 | Corporate values |
| 22 | Open relationships |
| 23 | Feedback dependent control |
| 24 | Structuring |
| 25 | Facilities |
| 26 | Employee decision-making ability |
| 27 | Staff operational responsibility in implementing the decisions |
| 28 | Access to decision and execution tools |
| 29 | Staff responsibility towards the outcomes of their decisions |
| 30 | Integrations between the senior managers and frontline employees |
| 31 | Involving the staff in planning and operational information of the organization |
| 32 | Involvement of staff unions |
Moreover, having investigated different types of comprehensive banking and the previous models and their implementation methods in Iran according to the banking experts, we selected the following six types of banking to investigate for model development:
Private banking.
Retail banking.
Virtual banking.
Corporate banking.
Investment banking.
Business banking.
In the next step, in order to respond to the first question, the components and function of each banking type were identified using field studies and a questionnaire survey. Then the product development criteria in each banking system were identified and according to the experts, 32 factors influencing comprehensive banking were expertly reviewed and ranked based on their effectiveness.
Private banking
The types of private banking and their components are categorized into two groups: Asset management; financial services and private services and consultations. The development criteria of private banking products were investigated from four perspectives:
Needs assessment: every client;
Relationships: account manager;
Delivery: Offices and special branches
Required information: personal life information.
Afterward, the 32 factors affecting employee empowerment based on educational content in comprehensive banking were submitted to the panel of experts and ranked by their priority (Figure 1).

Fig. 1 - Employee empowerment based on educational content in private banking as perceived by the experts.
Retail banking
The 32 factors affecting employee empowerment based on educational content in retail banking were submitted to the experts and ranked (Figure 2). Different operations in retail banking were determined as follows:
Deposit reception.
Supervising e-payment methods.
Credit services and bank facilities.
Resource and usage assessment.
Claims.
Credit risk of the branches and their performance assessment.
In-person banking services to individuals and companies.
Market analysis and assessment of competition status and services.
Insurance services for clients.
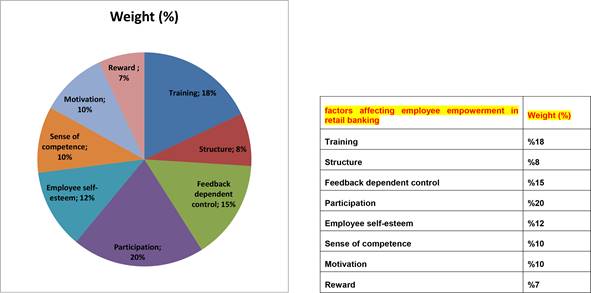
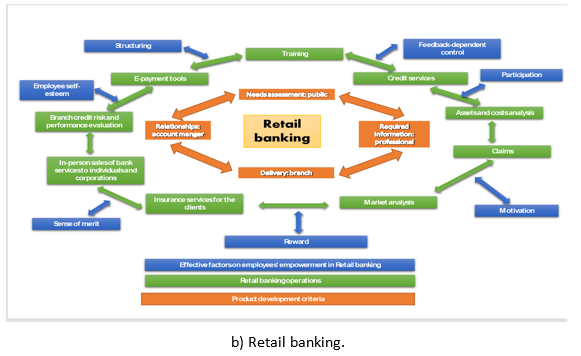
Fig. 2 - Employee empowerment based on educational content in retail banking as perceived by experts.
Virtual banking
Different virtual banking operations were determined as follows:
Moreover, the criteria for virtual banking product development were investigated from four perspectives:
Then, the 32 factors affecting employee empowerment based on educational content in virtual banking were submitted to experts and ranked (Figure 3.

Fig. 3 Employee empowerment based on educational content in virtual banking as perceived by the experts.
Corporate banking
Different corporate banking operations were grouped as follows:
Then, the criteria for corporate banking product development were investigated from four aspects:
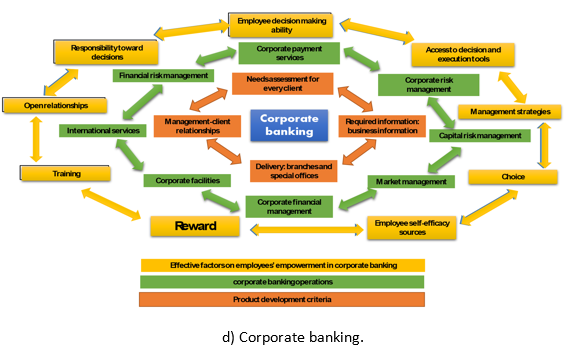
The 32 factors influencing employee empowerment based on educational content in corporate banking were submitted to the experts for ranking (Figure 4).
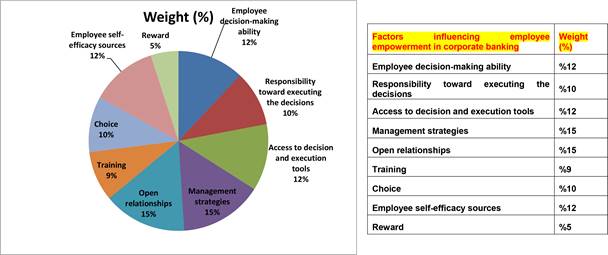
Fig. 4 - Employee empowerment based on educational content in corporate banking as perceived by the experts.
Investment banking
Different operations of investment banking were identified as follows:
Financial studies;
Assessing and supporting business plans;
Developing financial justification plans for projects;
Consultation and leadership in financial resourcefunds for financing businesses;
Assessment of the evaluation and public or private distribution of corporate securities;
Subscription and subscription agreement for securities;
Strategic assessment and operation support for the purchase and merging of companies;
Participating in and financing new and profitable projects;
Consulting for corporate financial restructuring and developing business plans for businesses;
Preparing companies for listing in national and international exchange markets.
Then, the criteria for investment banking product development were ranked as follows:
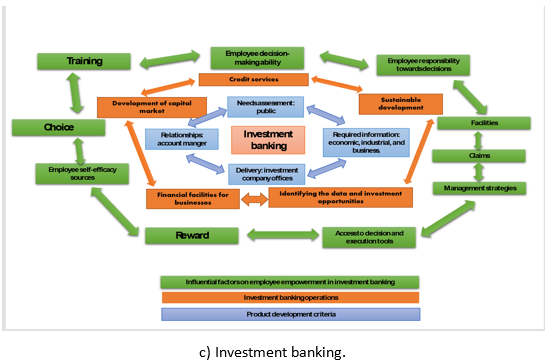
Next, the 32 factors influencing employee empowerment based on educational content in investment banking were ranked by the experts (Figure 5).
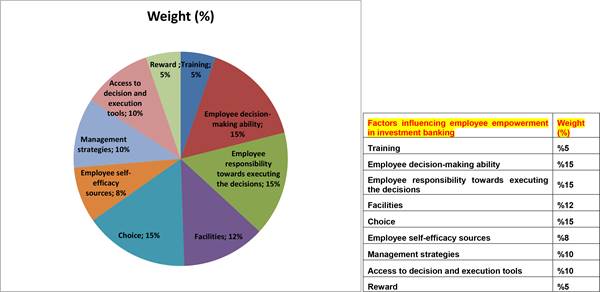
Fig. 5 - Employee empowerment based on educational content in investment banking as perceived by the experts.
Business banking
Different business banking operations were identified as follows:
Then, the criteria for business banking product development were investigated from four aspects:
In the next step, the 32 factors affecting employee empowerment based on educational content in business banking were submitted to the experts for ranking (Figure 6).
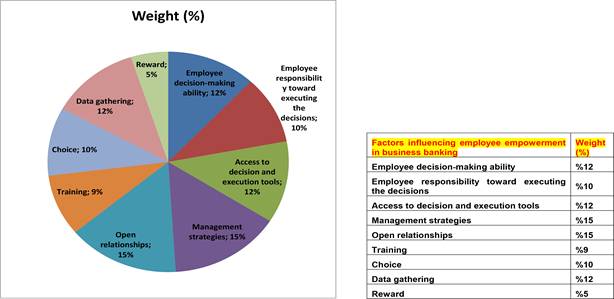
Fig. 6 - Employee empowerment based on educational content in business banking as perceived by the experts.

Fig. 7 - Relationships between variables, parameters, constraints, and coefficients for the proposed universal banking model focused on employee empowerment based on educational content and skills development.
In the last step (Figure 7), based on the component relationships in comprehensive banking focused on employee empowerment based on educational content, the authors used the Linear Programming method (using expert views to extract system parameters and place them in a structure based on graph theory and hierarchical structures) to classify the components of universal banking as follows:
Then, the factors influencing employee empowerment based on educational content were classified based on the weights given by banking experts to each component of universal banking. The results showed that the two factors of training and reward influence all components of universal banking. The remaining components of universal banking were calculated and classified based on their respective banking functions. Figure 8 shows the obtained universal banking model focused on employee empowerment based on educational content.
Conclusions
Considering the proposed universal banking models have always consisted of market segmentation and client classification (i.e. corporate, investment, virtual, business, retail, and private banking, etc.) which are rooted in two of the four paradigms of social sciences (structuralism and functionalism), the present research studied the implementation of universal banking from the humanist and cognitive paradigms. The results indicate that employee empowerment based on educational content and analyzing the factors influencing empowerment based on educational content in each banking component can effectively influence the sound implementation of universal banking.After weighting to each factor influencing the good implementation of universal banking in Group A (private, corporate, business, and investment banking), the Group A factors were identified as follows:
Employee decision-making ability.
Employee responsibility toward implementing the decision.
Access to decision and implementation tools.
Employee self-efficacy sources.
Then factors influencing Group B were identified as follows:
Further, the two factors of training and reward were effective in different types of universal banking. Mashhadi (2010), investigated the relationship between employee communication skills and customer satisfaction. They concluded that verbal communication skills had a direct and significant relationship with customer satisfaction, where higher verbal communication skills were related to higher customer satisfaction. As for listening skills, the findings and the feedback showed that they did not predict customer satisfaction, that is, there was no significant relationship between listening skills and feedback with customer satisfaction.
Therefore, the verbal skills of employees were stronger predictors of customer satisfaction. Momeni & Fa’alqiomi (2007), conducted a study on the results of employee empowerment based on educational content in the health and medicine sector, concluding that organizations can invest on employee training and learning to increase the capacity required for added value, effective performance, and responsibility by the staff.