Mi SciELO
Servicios Personalizados
Articulo
Indicadores
-
 Citado por SciELO
Citado por SciELO
Links relacionados
-
 Similares en
SciELO
Similares en
SciELO
Compartir
Revista de Ciencias Médicas de Pinar del Río
versión On-line ISSN 1561-3194
Rev Ciencias Médicas vol.27 no.3 Pinar del Río mayo.-jun. 2023 Epub 01-Mayo-2023
Articles
Characterization of the process of professional orientation for the entrance to the careers of the Medical Sciences
1University of Medical Sciences of Pinar del Río. Faculty of Medical Sciences "Dr. Ernesto Che Guevara de la Serna". Pinar del Río. Cuba.
2University of Medical Sciences of Pinar del Río General Teaching Hospital Abel Santamaría Cuadrado. Pinar del Río, Cuba.
Introduction:
choosing the professional area where a person is going to develop his whole life is not easy, especially when the individual does not have the tools to make an accurate and well-founded choice. Vocational discernment is a process that generates contradictions in young people, visibly affecting their attitudes, who often do not immediately pursue higher education, or decide to change careers due to lack of vocational guidance.
Objective:
to characterize the process of Professional Orientation towards the careers of Medical Sciences in the Pre-university Institutes of the municipality of Pinar del Río.
Methods:
the work is based on the Marxist-Leninist conception and its dialectical-materialist method, it has been supported by the use of different methods of the theoretical, empirical and mathematical-statistical level, which, being closely related to each other, allow obtaining the necessary information which, when ordered, processed and analyzed, make it possible to give an answer to the stated objective.
Results:
the process of Professional Orientation towards the careers of Medical Sciences is asystemic since it reveals a scarce knowledge about those careers that are part of the Medical Sciences and the labor scenarios of the future graduate.
Conclusions:
the theoretical analysis carried out reveals that in the process of Vocational Guidance towards careers in the Medical Sciences there is an inadequate correlation between the career selected in twelfth grade and the motivational interest of the future graduate as a way of continuity and improvement of man throughout his life.
Key words: VOCATIONAL ORIENTATION; STUDENTS; CHOICE.
INTRODUCTION
Since the triumph of the Cuban Revolution, attention to vocational guidance has been of utmost importance; since 1959, projects were drawn up in response to this activity, due to the need, in the most varied specialties, to train workers, technicians and professionals. All this determined the emergence of plans aimed at the development of interests in the different specialties. It has been, since then until today, the responsibility of the school to carry out activities of Professional Orientation.
Vocational Guidance has been treated by Educational Psychology as the result of advances in the theoretical and methodological plane of psychological and pedagogical sciences.1 The National Hero José Martí addresses the subject when referring to the need to prepare man for life, in his book "Ideario Pedagógico" he manifests, in accordance with the concrete conditions of the moment, how this preparation should be, emphasizing the responsibility of preparing them for those jobs for which they could perform in their localities.
The Revolution, as a historical continuity of the legacy of our best thinkers, from the beginning, sets specific tasks on Professional Orientation. These tasks became of the first order when they were reflected in the theses of the Communist Party of Cuba on educational policy. Fundamental importance was given to the work of Vocational Training and Professional Orientation in children and young people, giving the school the leading role in this work; therefore, it is the responsibility of the educational centers at different levels to carry out work aimed at guaranteeing an adequate Vocational Training and Orientation of their students in correspondence with the needs demanded by the development of the society that is being built.
Therefore, when young people really need to be oriented towards certain professions, it is necessary to provide them with detailed information on both the content of the profession and its necessity for the country, and to develop an educational work that stimulates their political-moral motives. When the young person chooses a profession, because of his sensitivity to its importance for the country, he develops it with much more responsibility.
Throughout the revolutionary process, different plans have been created for the professional orientation of students. The responsibility of professionally orienting young people to their own possibilities and the needs of the country was established at the First Congress of the Communist Party of Cuba (PCC) in its Theses and Resolutions, in which it is stated: "The organization of vocational training and professional orientation of the student should have the full support of state agencies on the fronts of science, culture, production and services, and political and mass organizations, in order to harmonize, on the one hand, the student's choice of professional studies or specialties based on their vocational abilities and interests, and on the other hand, the satisfaction of social needs arising from state planning".2
At the graduation ceremony of the Manuel Ascunce Domenech University Pedagogical Detachment, held on July 7, 1981, in the Ciudad Libertad polygon, Commander in Chief Fidel Castro Ruz said: "In the basic secondary schools and pre-university institutes we must continue to improve the work of vocational training and professional orientation so that young people increasingly better select their studies in accordance with their attitudes and personal and social interests."3
All the ideas in this regard were summarized in the Master Program for Vocational Guidance issued by the Ministry of Education (MINED) in 1990 as part of the improvement of higher education in Cuba.
The 1990s marked a higher stage in the development of Vocational Guidance, starting with the implementation of the Regulation on Vocational Training and Vocational Guidance, where it was established that: "(...) it is a task of teachers and professors of all subjects to guarantee the student the level of generalization of the acquired knowledge, to create interest in the possible application of each knowledge to future working life and on this basis to guide children, adolescents and young people towards the most necessary professions."4
In 2000, the Ministry of Education (MINED) issued Resolution 700 which administratively regulates the guiding role of the school in Vocational Guidance and Vocational Training activities, demanding a hierarchical character of this social institution.5
It is the teaching institutions, through the work of the teaching staff, which are in charge, from the time children start school and even during their professional training, of giving them the tools to face their future, which is materialized thanks to the Cuban educational system and the facilities provided in a general sense by the Revolution.
The characteristics of the contemporary world require a permanent orientation, in order to allow the person to make decisions appropriate to the context in which he/she develops. This situation is especially important in adolescence and youth, since students must decide about their professional future and the direction their lives will take, issues in which the health professional has an important role in the performance of the professional orientation function towards the careers of the Medical Sciences that help them to define an adequate choice of their university career that match their nature with the qualities that are developed in a socialist society, which is a concern and occupation of the Cuban State.
DEVELOPMENT
Cuba demands an education that instructs students about their future profession where they link theory and practice as the basis for the necessary development, an aspect from which the university is a cornerstone in the training for life and work.
Professional orientation has been prioritized since the triumph of the Revolution as one of the most important objectives of the educational task, and is aimed at preparing students for their incorporation into the complex world of production and services, so that they are able to make a conscious choice, based on their interests and real possibilities in accordance with the needs of the country.
The formation of the professional is "...a complex phenomenon that expresses the potential of the person to guide his or her performance in the exercise of the profession with initiative, flexibility and autonomy in heterogeneous and diverse scenarios, from the integration of knowledge, skills, motives and values that are expressed in an efficient, ethical and socially committed professional performance."6
Cuba has important figures such as F. González Rey and V. González Maura, among others, who have directed their studies towards a personological and motivational approach. For V. González Maura, the main figure of the guidance work should be the teacher, seeking the student's self-determination by improving the quality of his professional motivation.
Currently, there are two important concepts issued by Matos Colombié:7 vocational-vocational orientation and integrative methodology. The first is directed "to the education of vocation, of vocational interests to establish a helping relationship through which the student is offered ways, methods, procedures and techniques for the search and finding of an adequate place within the system of professions and learns to choose one in a self-determined and conscious way". This definition presupposes that it is the school that should lead this process and is the one that prepares, coordinates and systematizes the work with the family, community, social, political and student organizations, so that they can participate in the career guidance process.
Career Guidance has been treated with much emphasis within educational psychology. Society imposes a challenge and psychologically it is necessary to know the driving forces that explain the actions of man, for this it is necessary to analyze the role of internal motivational factors in the regulation of behavior and motivational formations of personality. In this sense, Dr. Viviana González Maura emphasizes:
"The basic motivational formations constitute, by their character, components of all motivational formation to the extent that through them the regulatory potential of the specific and generalizing motivational formations is expressed, they are: the system of objectives, the system of affective experiences, the system of personal meanings."8
In the emergence of Professional Guidance as a process throughout the subject's life, the fundamental emphasis of guidance is made in the stages prior to the student's entrance to a higher education center, so that the work of Professional Guidance is limited to carrying out actions in the preparation of the subject for the choice of profession in Higher Secondary Education and very few continue to provide professional guidance in Higher Education. That is why we agree with Dr. González Maura, when she points out that: "only from a historical-cultural perspective of human development is it possible to understand how personality has at the same time an objective and subjective nature, has an active and autonomous character in the regulation of action and is determined historico-socially in its origin and development..."9
The student needs other people to guide and support him/her in the elaboration of his/her life project, where the young person will accumulate both internal and external information. The student must learn to recognize his/her interests, aptitudes and dominant university areas, so that he/she has elements for a better vocational choice. (10 By virtue of Vigotsky's Historical-Cultural Approach, according to González, V., cited by Torres Domínguez, J.,11 it can be understood how the subject reaches higher levels of functional autonomy, that is, self-determination, only if the social environment creates the conditions and situations conducive to the stimulation of independent and autonomous action, since this is formed in the activity".
Recently, Dr. Jorge Luis del Pino,12 has proposed the so-called problematizing approach, which proposes to place the student in conflicting situations at times of transition between educational stages, highlighting that they are unaware of the destination institutions, the superficiality in the knowledge of the chosen studies, lack of knowledge of professional opportunities.
At the same time, an aspect to be taken into account are the means and techniques with which career guidance is currently being developed and with which academic and labor information is transmitted. This is the main reason why we have been able to verify in integral visits summoned by the Provincial Entrance Commission that in the Pre-university Institutes of the municipality of Pinar del Río, students show a scarce information of professional orientation towards the careers in the Medical Sciences that provide them with tools in making firm, consistent and responsible decisions, learning to recognize their interests, aptitudes and dominant university areas for a better choice of each career in the health branch.
METHODS
The work presented is based on the Marxist-Leninist conception and its dialectical-materialist method, it was supported by the use of different methods of theoretical, empirical and mathematical-statistical level, the statistical methods were used for the processing of information and the analysis by percent was used, which allowed to interpret, summarize and present the information through the analysis of the data, The statistical methods were used to process the information and percent analysis was used to interpret, summarize and present the information through tables and graphs which, being closely related to each other, made it possible to obtain the necessary information which, when ordered, processed and analyzed, made it possible to respond to the objective set out in the empirical methods, which included content analysis, observation and the survey.
The population was constituted by the total number of students in the twelfth grade of the Carlos Marx, Isabel Rubio and Federico Engels Pre-university Institute of the Pinar del Río Municipality in the 2020-2021 academic year. The sample was constituted by 50 students from each Pre-university selected for a total of 150 corresponding to the 2020-2021 school year in the municipality of Pinar del Río. As for the teachers, a total of 16 teachers were part of the universe, those who were directly linked to the teaching process of the twelfth grade of the three previously mentioned Pre-universities, these in turn constituted the sample.
The determination of both the population and the sample was based on feasibility criteria, taking into account the teaching scenario where the research was carried out by the subjects involved. A survey and an observation guide were applied to both groups, which allowed us to obtain the necessary information for the characterization of the professional orientation process of students who aspire to enter Medical Sciences careers.
The descriptive statistical method was used to present the results in tables and graphs. The inclusion criteria for students, professors and experts were taken into account, with the voluntary participation in the research. The topicality of the subject is manifested in the diagnosis of the problems regarding students' professional orientation and the development of activities aimed at achieving it.
RESULTS
Within the sample studied, it was found that there was a preference for the studies of the careers of Medical Sciences but a scarce knowledge of the skills that will be part of the study plans, as well as of the particularities of each career, in addition to the labor scenarios to which they will later be inserted, evidenced in the lack of activities that promote an enriching exchange and that lead to the clarification of all their concerns.
The results found in the present research confirmed the need of young people to have educational spaces that allow them to know and develop a broader vision towards the health field, showing the need to listen and exchange with professionals in this field who are able to provide all the necessary information, as well as their experience in the work environment.
In addition, the study indicates that the students are unaware of the particularities of each career, the academic index required to access them, the number of places offered, the duration, the general content of the study plan to be completed and the future job possibilities.
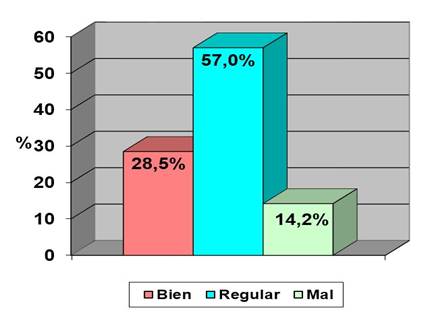
The diagnosis carried out reveals that there are difficulties in the work of professional orientation with a view to the diversification of the 12th grade and the conscious choice of career due to the lack of conscious orientation activities (Fig. 1).
Regarding the percentages that represent the acquisition of knowledge about the careers in the Medical Sciences, it was found that a considerable percentage of students (14,2 %) have little knowledge about the particularities of the careers in the Medical Sciences, as well as the academic index necessary to access each one of them, the duration time, the general content, the study plan and the way of completion of studies in each career.
This data allows us to affirm that the results validate the hypothesis that at the time of their terminal year in the Pre-university Institutes there is a considerable group of students who do not have sufficient information for the choice of a career in the Medical Sciences and in many occasions this information is not received by the Institution but by other means, whether it is the family, the community or friends.
In addition, the study developed found that in the process of Professional Orientation that is developed in the Pre-University Institutes, not always all the educational agents such as teachers, school psychologists, pedagogues, parents, members of the community and representatives of health institutions participate, since their presence is essential for a better clarification of all their concerns, favoring with their work the contribution of knowledge to the teaching activity that is carried out, allowing the student to interact with his or her own characteristics and those of a professional horizon.
The research carried out provided us with information about the role of the counselor, since he/she has the responsibility not only to place the student in an occupational area, but also to train him/her to manage an internal and professional world that is more and more changing and complex, with more stable and efficient instruments. The work of teachers to develop it efficiently is imperative, given the need for students to be well oriented in order to make a conscious choice of their profession. In addition to having a design and planning of the activity to be developed with the students in such a way that their actions guarantee the fulfillment of its purpose and objectives, and in this sense, the planning of the activity according to a method, to an organization of the actions to be developed, plays an important role.
BIBLIOGRAPHICAL REFERENCES
1. Conesa Santos M, Pérez Solano AA, Carbonell Figueroa AC, Vázquez Morell M. “La preparación de los docentes del 2. ciclo en la orientación profesionalhacia carreras pedagógicas en los escolares”, Revista Atlante: Cuadernos de Educación y Desarrollo [Internet]. 2019 [citado 7/3/2022]: 28. Disponible en: Disponible en: https://www.eumed.net/rev/atlante/2019/09/preparacion-docentes-escolares.html 1. [ Links ]
2. TESIS y Resolución. Primer Congreso del PCC [Internet]. La Habana: Editorial DOR del CC del PCC; 1978. [citado 7/3/2022]. Disponible en: Disponible en: https://www.granma.cu/file/pdf/PCC/1congreso/Tesis%20y%20Resoluciones/I-Congreso-del-PCC.Tesis-y-Resoluciones-sobre-pol%C3%ADtica-educacional.pdf 2. [ Links ]
3. DISCURSO PRONUNCIADO POR FIDEL CASTRO RUZ, PRESIDENTE DE LA REPÚBLICA DE CUBA, EN EL ACTO DE GRADUACION DE 10 658 EGRESADOS DEL DESTACAMENTO PEDAGOGICO UNIVERSITARIO "MANUEL ASCUNCE DOMENECH", EN EL POLIGONO DE CIUDAD LIBERTAD, EL 7 DE JULIO DE 1981, "ANO DEL XX ANIVERSARIO DE GIRON" [Internet]. La Habana; 1981. [citado 7/3/2022] Disponible en: Disponible en: http://www.cuba.cu/gobierno/discursos/1981/esp/f070781e.html 3. [ Links ]
4. Ministerio de Educación. Programa Director de Orientación Profesional. Reglamento sobre Formación Vocacional y Orientación Profesional [Internet]. 1990 [citado 7/3/2022]. Disponible en: Disponible en: https://www.mes.gob.cu/es/noticias/proceso-de-ingreso-la-educacion-superior 4. [ Links ]
5. Martínez Rodríguez T, Martínez Castillo V, Copello Janjaque M. El desarrollo de la orientación profesional en Cuba, sus características. EFDeportes.com, Revista Digital5. . Buenos Aires [Internet]. 2013 [citado 7/3/2022]; 18(180). Disponible en: Disponible en: https://efdeportes.com/efd180/el-desarrollo-de-la-orientacion-profesional-en-cuba.htm 5. [ Links ]
6. González Maura V. La orientación profesional como estrategia educativa para el desarrollo de intereses profesionales y del valor responsabilidad en la formación profesional del estudiante universitario. Folleto. La Habana: CEPES; 1999. [ Links ]
7. Matos Columbié Z. La Orientación Profesional Vocacional. Una metodología integradora para su desarrollo en preuniversitarios guantanameros. Tesis de Doctor en Ciencias Pedagógicas. La Habana; 2003. [ Links ]
8. González Maura V, González Tirados RM, López Rodríguez A. "Diseño de situaciones de aprendizaje que potencien competencias profesionales en la enseñanza universitaria. Revista de Formación del Profesorado e Investigación Educativa [Internet]. 2011 [citado 7/3/2022]; 24: 121-134. Disponible en: Disponible en: https://dialnet.unirioja.es/descarga/articulo/3844478.pdf 8. [ Links ]
9. González Maura V. "El profesor universitario:¿un facilitador o un orientador en la educación de valores?." Pedagogía Universitaria [Internet]. 2002 [citado 7/3/2022]; 7(4): 44-51. Disponible en: https://cmapspublic.ihmc.us/rid=1HB69FGK6-6MH7C6-103W/Prof.%20universitario%20facilitador%20u%20orientador.pdf9. [ Links ]
10. Benítez Blanco MC. Elección de carreras universitarias de los egresados del nivel medio del colegio privado subvencionado italiano santo tomás, cohorte 2020. Ciencia Latina Revista Científica Multidisciplinar[Internet]. 2021 [citado 7/3/2022]; 5(6): 12877-12904. Disponible en: Disponible en: https://doi.org/10.37811/cl_rcm.v5i6.1289 10. [ Links ]
11. Torres Domínguez J. El trabajo de orientación profesional: una estrategia metodológica hacia carreras agropecuarias en estudiante de Secundaria Básica. Instituto Superior Pedagógico Rafael María de Mendive; 2003. [ Links ]
12. Quesada Madrigal DM, Armas Simón JL, Castallón Brito Y. LA GEOGRAFÍA DE DÉCIMO GRADO Y SU CONTRIBUCIÓN A LA ORIENTACIÓN PROFESIONAL. Pedagogía 2019 [Internet]. 2019 [citado 7/3/2022]: 14p. Disponible en: Disponible en: https://trabajos.pedagogiacuba.com/trabajos/23Ponencia%20MSc.%20Dania%20Mar%C3%83%C2%ADa%20Quesada%20Madrigal.pdf 12. [ Links ]
Received: July 05, 2022; Accepted: June 15, 2023











 texto en
texto en