Mi SciELO
Servicios Personalizados
Articulo
Indicadores
-
 Citado por SciELO
Citado por SciELO
Links relacionados
-
 Similares en
SciELO
Similares en
SciELO
Compartir
Podium. Revista de Ciencia y Tecnología en la Cultura Física
versión On-line ISSN 1996-2452
Rev Podium vol.19 no.1 Pinar del Río ene.-abr. 2024 Epub 18-Abr-2024
Original article
Self-exercise of physical exercise in Physical Education students of Higher Education
1Universidad Agraria de La Habana "Fructuoso Rodríguez Pérez ". La Habana, Cuba.
2Universidad de Ciencias de la Cultura Física y el Deporte "Manuel Fajardo". La Habana, Cuba.
Attention to the self-exercise skill of physical exercise constitutes a point of reference for the fulfillment of the strategic objectives set by Cuban universities, particularly in the Physical Education discipline of Study Plan E, as a content of the curriculum that favors the student's protagonism in his/her own learning process, constitutes a necessity in the face of the changes that are taking place in the Cuban Higher Education system, given fundamentally by conditions that arose from physical isolation caused by COVID 19, coupled with the lack of skills to perform physical activity and to guarantee inclusive, equitable and quality education. The objective of this work is to develop a didactic strategy for the training of the self-exercise skill of physical exercise; qualitative and quantitative methods are used in the research. It begins with the diagnosis, using different methods and techniques, such as surveys and interviews. In addition, tests are applied to evaluate the physical condition and insufficiencies presented by Physical Education students of the Veterinary Medicine career at the Agrarian University of Havana. The systematization and the theoretical and methodological foundations analyzed allowed the design of a didactic strategy, which has four stages, each of them with its objective and system of actions, which are offered as a result for the formation of the self-exercise skill of the physical exercise in the students studied. The evidence of the learning acquired by the students, the assessment of specialists indicates an improvement in physical fitness levels, the proposed actions respond to the purpose for which the strategy was conceived.
Key words: training; skill; self- physical exercise; Physical Education.
INTRODUCTION
The training of professionals prepared to competently provide solutions to social problems that are increasingly becoming more complex; it constitutes a matter of essential concern for universities. The 2030 Agenda, although it does not establish particular requirements for higher education, aims in its objective 4: to guarantee inclusive, equitable and quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all, an issue that must be addressed from that educational level (United Nations Organization [UN], 2015), and in section 4.7, incorporated in 2020, it states: "ensure that all students acquire the theoretical and practical knowledge necessary to promote sustainable development, among other things", through education for sustainable development and sustainable lifestyles" (UN, 2020, s/p).
The strategic objectives proposed by Cuban universities reflect indicators that respond to this purpose, and in particular, the Physical Education discipline of Study Plan E projects the formation of skills for the exercise of physical activity and physical exercise as a content of the curriculum that It promotes the student's protagonism in their own learning process, which allows them to acquire tools related to the practice of physical exercise during student, professional and social life on a permanent basis.
The research background shows that in Physical Education, in the Veterinary Medicine career, its only purpose was to increase the level of physical preparation, and not to promote the formation of the habit of practicing physical exercises and the appropriation of methods for self- physical exercise. In a physical diagnosis and the insufficiencies presented by the students of the Veterinary Medicine career, it was identified a low level of physical condition, lack of skills in formation of skills for self-physical exercise, which limits the development of the practice of physical activity.
According to Hernández (2019), which refers to Morales (2015); Barcelán (2016); Yanes (2017); Brito (2017) and Bosque (2018), who use in their research foundations on the conceptions of strategies and their importance for the formation of skills.
Otero (2019) refers to the indissoluble unity with the activity of teachers and students to learn.
According to Montes de Oca and Machado (2011), today the need for a Didactics centered on the subject who learns is recognized, which requires focusing on teaching as a learning orientation process, where conditions are created so that students not only not appropriate knowledge, but develop skills, form values and acquire strategies that allow them to act independently, committed and creative, to solve the problems they will have to face in their personal and professional future.
All education has the double function of human development and responding to social needs. According to Gaeta (2023), this complex task implies an education in continuous search for the dignity of the person, which contemplates a deep knowledge of the students and an acceptance of individual differences.
From Addine (2007), strategies are assumed as "a set of interrelated tactics, a tactic is a specific procedure which is applied and contributed to the entire process, to the strategy in general" (p. 25), as well as the system character of Álvarez (1999).
Álvarez (1999), recognizes the educational teaching process as:
"The essential path of training and its formative nature, where the student acquires his fullness, from the instructive, educational and developmental dimensions. Furthermore, they are considered prepared when they achieve a general and comprehensive culture, which prepares them to solve problems and transform the reality they face." (p.27)
According to Martínez Morales et al. (2022), higher education in Cuba currently faces challenges in relation to the development of different study modalities in times of Covid-19. In this sense, the role of the teacher in directing the teaching-learning process takes on special significance, given the need to develop new methods that guarantee self-management of knowledge by students. This requires the teacher to promote individual and collective responsibility, the development of imagination, creativity and innovative capacity from non-presence.
In this sense, Fierro and Valadez (2022) mention the importance of the physical education strategies implemented in the confinement period, which have laid the foundations for students and school communities to understand the benefits it provides in comprehensive training. of the individual, in addition to having a positive impact on their health.
Morales et al. (2021) assumes that strategies can be evaluated and proposes the ATJ Matrices based on estimating four fundamental dimensions with their corresponding indicators, distributed in each of the matrices, aligned to the context and the objective of the evaluation of the proposed didactics strategy.
For Conde-Williams and Valdez (2023) the teacher, at the individual level, must have adequate development of socio-emotional skills to guide work, guide student performance in both environments (in-person and virtual) and maintain a proactive attitude to find solutions to different situations in the teaching process.
Addine (2007) considers strategies: "a set of interrelated tactics, a tactic is a specific procedure which is applied and contributed to the entire process, to the strategy in general" (p. 25).
De Armas (2011) states that:
"the teaching strategy is the projection of a system of actions in the short, medium and long term that allows the transformation of the teaching-learning process in a subject, level or institution, based on the components of it and that allows the achievement of the proposed objectives in a specific time" (p.20).
According to Hernández et al. (2021), the formation of the skill is achieved when the student consciously appropriates the operations, for which he/she needs adequate guidance on how to proceed, under the timely direction of the teacher, to guarantee correctness in the execution.
When addressing the process of training the skill of self- physical exercise, it is identified that this appears in the Study Plan E of the Physical Education Discipline of university careers. The objectives of this discipline specify the purpose of contributing to the development of physical culture in university students in an organized manner through Physical Education. They guide the systematic practice of physical exercises; in this sense the objective of the research is to develop a strategy to improve the training of skills for self-exercise physical exercise in students of the Veterinary Medicine career.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The research was carried out between the months of September 2020 and July 2022 in the Veterinary Medicine career of the "Fructuoso Rodríguez Pérez" Agrarian University of Havana, in charge of the professional training of Veterinary Doctors, the governing center for this career in Cuba. The study was carried out on students from the first and second years of the degree, 77 students and 15 Physical Education teachers were selected, who develop their teaching in the degree under study. The characteristics that were taken into account for the selection of teachers were:
Have at least five years of experience as a teacher in Higher Education.
Possess teaching category of Assistant, Auxiliary or Full.
Have worked for at least one academic year in the Veterinarian Medicine degree.
For more than two consecutive years.
Have constant improvement tempered with the current demands of Physical Education in Higher Education in Cuba.
Be in the country at the time of application of the instrument.
Show willingness to participate.
For the selection of students, the following inclusion criteria were considered:
Be a first- and second-year student of the Veterinary Medicine degree.
Having participated in the activities of the teaching-learning process of Physical Education that were carried out at the Agrarian University of Havana as part of the diagnosis.
These criteria allowed the selection of all the teachers and students of the indicated years.
Different methods and techniques were used to design and evaluate the strategy, such as surveys, interviews and mathematical statistics. It begins with the physical diagnosis; tests are used to evaluate the physical condition indicated in the program of the University Physical Education Discipline Plan E. In addition, quantitative methods, document analysis and class observation.
The research strategy used was determined from the needs demanded by the study, for this reason, it was organized in three phases. In each of them, methods and techniques are applied that allow the research objectives to be met.
Scientific techniques and methods used
Analytical-synthetic: made possible the systematization of the theoretical and methodological foundations that support the development of professional skills in the professional training process and in particular the way in which the training of skills for the exercise of physical activity in the students of the Veterinary Medicine career at the Agrarian University of Havana "Fructuoso Rodríguez Pérez".
Modeling: made it possible to determine the components of the proposed strategy, its structure, as well as the establishment of the corresponding interrelationships.
Structural systemic approach: it was used to develop the strategy; it facilitated the understanding of the interactions that occur between the theoretical-methodological and operational components in line with the characteristics of the context in which the professional training of the students of the degree takes place. Veterinary Medicine from the Agrarian University of Havana "Fructuoso Rodríguez Pérez".
Analysis of documentary sources: The Study Plan "E" of the Veterinary Medicine career was analyzed, as well as the Physical Education Discipline program, the planning documents of the teaching process, the class system and the support teaching materials, with the purpose of interpreting the information provided by the content of these documents related to the training skills for exercising physical activity in students.
In the research, an interview is carried out with Physical Education teachers, in order to verify the state of preparation of the teachers for the training of the ability to exercise physical activity in the students during their passage through the degree. Which allowed to assess the impact of teachers on students with the formation of the skill.
Student survey: applied to students, with the objective of knowing how they perceive the formation of the ability to exercise physical activity to face Physical Education processes.
Observation of classes: to observe if the activities and actions allow students to develop the ability to self- physical exercise.
Methodological triangulation: as a technique it allowed to contrast the data obtained from different sources: surveys, interviews, analysis of documentary sources and class observations, for the assessment of the development of the training of the ability to self-exercise physical exercise of the students of the Veterinary Medicine career at the Agrarian University of Havana "Fructuoso Rodríguez Pérez".
Statistical-mathematical methods were used to process the information, such as: the empirical frequency distribution for the processing of data obtained from surveys and interviews.
The research was carried out on the basis of a dialectical-materialist conception, the logic of theoretical and empirical investigations, which allowed to understand the object of study.
The theoretical validation of the proposal was carried out using the criteria of specialists, with the objective of predicting the expected effectiveness and validity of the proposal. The ATJ Matrices are first applied, which consists of a filtering process, which establishes a matrix arrangement to predict the validity of the scientific result. Meanwhile, the validity and reliability of the results was verified through the practical effectiveness and the satisfaction index of the applied strategy, which allowed sufficient evidence to be obtained about the scientific value and applicability of the strategy.
RESULTS
The study carried out on the students under investigation during the development of the Physical Education classes made it possible to determine, through the applied survey, how they perceive the formation of the self-exercise skill of physical exercise to face the processes of Physical Education.
100% of those surveyed considered that the skill to self-exercise physical exercise is important for Veterinarians in their professional performance. They stated that they are aware that knowing how to physically exercise themselves can keep them healthy. They also argued that they have the possibility of performing the functions of a Veterinary Doctor physically prepared to fulfill their functions and thus be more useful to society.
The largest number of students surveyed considered that the self-exercise skill of physical exercise is perform physical exercises indicated by the Physical Education teacher. But that number exceeds half of the students (45, out of 77 for 58.44 %). 18.48 % (15 students) assumed the self-exercise skill of physical exercise as mastery of actions to diagnose, plan, organize, perform and control physical exercises and the remaining 17 students (22.07%) value that it is the planned application of content that guarantees the individual practice of physical exercises. Although the percentage of students who are not clear about the concept is higher, it reaches 58.44 % of the sample, which corresponds to the answers provided by the teachers, where 12 of them are not clear about the concept. concept, so they do not transmit it to the student with the accuracy required for understanding.
For 22.07 % of the students (17), only the content received in the subject of Physical Education has been beneficial for the formation of the self-exercise skill of physical exercise. The rest of the students surveyed (60) consider that they have not been beneficial. This negative response represents 77.92 % that cannot be discarded; therefore, its behavior is due to the fact that the activities carried out are insufficient, nor are tasks aimed at preparing the student to physically exercise themselves from the training. degree, which would facilitate your successful professional performance.
Of the students surveyed, 58.44 % rated the level of stimulation and motivation to perform the physical exercises received in Physical Education as good; 17 of them, 22.07 %, are fair and the remaining 15 students, 19.48 %, consider it deficient.
Finally, they were asked if they wanted to add anything more about the formation of the self-exercise skill of physical exercise in the undergraduate training process and among their proposals they suggested carrying out, in classes, activities and tasks that train the student. with a culture of self-exercise, in accordance with the objectives of the subjects. They also pointed out personalized advice from teachers to counteract the individual deficiencies of each student. They recognized the attitude towards the tasks set in the classes for carrying out the physical exercises as positive.
The interview carried out with teachers allowed to assess the impact of teachers on students with the training of the self-exercise skill of physical exercise.
100 % of those interviewed agreed that the formation of the self-exercise skill of physical exercise has not been taken into account in the development of the discipline and the subjects that comprise it.
It was found that the teacher is only governed by the program of the Physical Education discipline, Plan E, as a governing document and from there the adjustments are not made in correspondence with the diagnosis for the formation of the skill of self-exercise of physical exercise, that is, the adaptations are made by the teacher based on his/her experience in practice; therefore, it can be assessed that these require methodological guidelines and updating of theoretical elements for the formation of the skill of self-exercise of physical exercise.
The interviewees agreed that the teacher shows great interest and concern in addressing the specificities of the students, in the same way that they consider that the formation of the self-exercise skill of physical exercise is a generator of physical health and contributes positively to the cognitive, psychological, motor and functional spheres of the organism. They also agreed that through training and skill development, a better level of health for the student is achieved.
The interviewees recognized that the training of the self-exercise skill of physical exercise can be very favorable for students because they learn at the same time as they participate, it allows them to be independent, self-plan, self-evaluate and make decisions on their own.
Observation of classes did not note the orientation for the formation of the self-exercise skill of physical exercise. Likewise, in the class system analyzed, the use of this didactic tool was not evident; it is observed that students are interested in the development of activities in class.
By applying methodological triangulation as a technique, it allowed to contrast the data obtained from different sources such as the survey, the interview, analysis of documentary sources and class observations:
There is motivation and commitment of students in the educational teaching process of Physical Education in the Veterinary Medicine career towards participation in physical activities. 30% of the students surveyed only feel motivated to perform physical exercises. A low level of knowledge that the student has is observed due to the results of the physical condition diagnosis. Limitations are identified such as the orientation of support materials and studies for the development of the skill is not conceived. In the documents of the teaching process, discipline program and in the class system, no treatment is given to how to form the ability to self-exercise physical exercise. The non-existence of teaching support materials for the formation of the skill. There is no didactic strategy on how to proceed with the formation of the skill for self-exercise of physical exercise. Teachers recognize the importance of training the self-exercise skill of physical exercise in the teaching process of Physical Education.
For the training of skills for self-exercise of physical exercise in students of the Veterinary Medicine career of the Agrarian University of Havana "Fructuoso Rodríguez Pérez", a didactic strategy was designed, taking into account different types of strategies that served as a basis for its analysis and projection.
The above constitutes the theoretical-methodological bases for the design of the didactic strategy for the formation of skills for self-exercise of physical exercise in students. in the teaching-learning process of Physical Education.
The didactic strategy presented allows the formation of skills for self-exercise of physical exercise in students of the Veterinary Medicine career. This is developed and implemented in the Physical Education Discipline and its objective is aimed at: perfecting the training of the self-exercise skill of physical exercise in students of the Veterinary Medicine career,
The didactic strategy is designed based on the scientific problem: How to contribute to perfecting the training of the self-exercise skill of physical exercise in students of the Veterinary Medicine career? Which leads, from an initial state, to the application of the diagnosis to design a set of actions and reach an ideal state in terms of the development of the skill, the general objective of the strategy: Contribute to perfecting the formation of the self-exercise skill of physical exercise in the PEA of Physical Education in students of the Veterinary Medicine career.
The designed teaching strategy consists of 4 stages:
Stage 1. Diagnosis.
Stage 2. Planning and organization.
Stage 3. Implementation.
Stage 4. Evaluation.
For an appropriate characterization of the main elements that articulate the action plan of each stage, the following clarifications are made:
Objective: it is what guides the end, the purpose.
Actions: are the activities or tasks that are planned based on the fulfillment of the strategy objective.
Procedures: brief description of how the actions are executed.
Methods and techniques: way of executing the actions (not required for all of them).
Participants: are those who are involved in the development of the action actively or passively.
Responsible: they are the insurers of the development and compliance of the action.
Temporality: specifies the duration in estimated times for the development or fulfillment of the actions; which can be permanent or temporary: short term (up to three months); medium term (four months to a year), long term (more than a year).
Stage 1. Diagnosis
This stage is the starting point of the strategy, where the object of study is characterized and the problem to be solved is specified. It is important to highlight that an effective diagnosis determines the existing problems and provides clarity in the selection of strategic actions for their solution.
Specific objective of the stage: diagnose the current situation of the training process of the self-exercise skill of physical exercise in the students of the Veterinary Medicine career, determining the state of the physical condition of each student.
Stage 2. Planning and organization
At this stage, the actions and operations were determined for the formation of the self-exercise skill of physical exercise in the students of the Veterinary Medicine career.
The assurance and training actions of Physical Education teachers were planned in the teaching-learning process of Physical Education for the formation of the self-exercise skill of physical exercise.
Specific objective of the stage: plan actions to ensure the process of training the self-exercise skill of physical exercise in students of the Veterinary Medicine career, determine goals to achieve in the short, medium and long term, specific objectives and design actions for the stage.
Phase 3. Implementation
At this stage, the actions are determined for the implementation of the strategy for the formation of the self-exercise skill of physical exercise in the students of the Veterinary Medicine career.
Objective: execute the actions planned in the previous phase. Carry out a system of methodological activities, carrying out training for Physical Education teachers, through workshops and the execution of the postgraduate course planned from the previous phase.
Stage 4. Evaluation
This stage is in charge of controlling and evaluating the functionality of the teaching strategy.
Specific objective of the stage: collection of information, evaluate compliance with the objective of the strategy for the formation of the self-exercise skill of physical exercise in students of the Veterinary Medicine career.
This stage represents the closure of the exposed strategic planning. The integration of all the actions declared in the proposed strategy and their corresponding adjustments demonstrate its contextualized, objective, systemic and flexible nature. Its practical application must enable the achievement of the desired state from the training of the Veterinary Medicine student.
A feedback system must be specified between the diagnosis and the different controls that must be carried out during the performance of physical exercises.
With the partial application of the didactic strategy for the formation of the self-exercise skill of physical exercise, and with the intention of knowing the physical conditions of the students under study in the research, the sets of tests indicated for the Plan E, in which standards proposed by a multidisciplinary team of the Ministry of Higher Education of Cuba are required, such as: Planks and sit-ups, time trial and Cafra test and Navette test, with the aim of knowing the state of physical condition and cardiorespiratory (Table 1).
The average age and weight of the students under investigation are shown in the table below.
Table 1. - Personalization of students, average age, weight and height by sex
| Sex | Size in m | Weight in kg | Age |
| Male 32 | 1.70 | 70 | 17 |
| Female 45 | 1.62 | 60.5 | 17 |
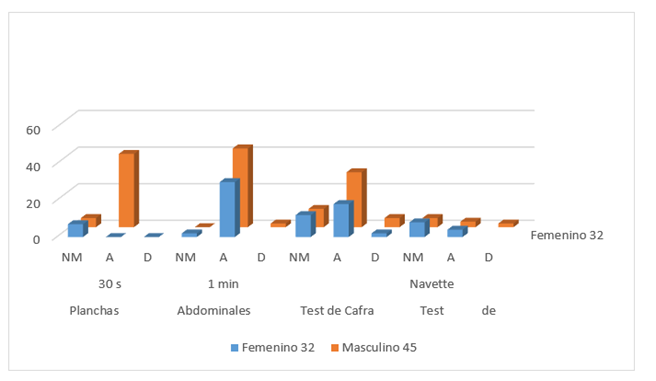
The application of the tests carried out allowed to know that 65% of the sample studied needs to improve their physical condition. As seen in the next table, female students are the ones who most need to improve their physical condition.
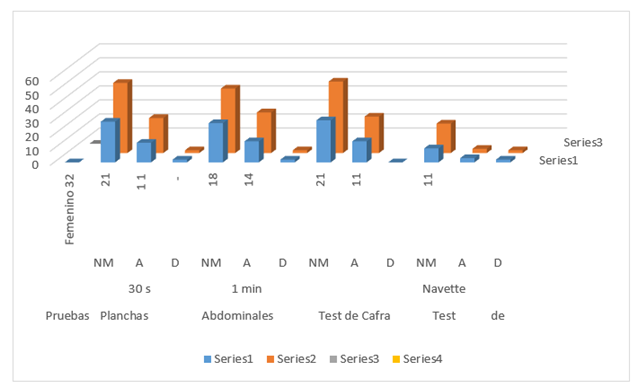
In the applied Cafra test, it must be said that there are 51 students, which represent 66% who are in the Needs Improvement range, which indicates that they are not in a position to take the Navette test, (Table 2), (Figure 1 and Figure 2).
Table 2 Results of the initial diagnosis carried out on the students with the Plan E tests
| Evidence | Planks 30 s | Abs 1 min | Cafra test | Navette test | ||||||||
| N.M. | TO | d | N.M. | TO | d | N.M. | TO | d | N.M. | TO | d | |
| Female 32 | 21 | 11 | - | 18 | 14 | - | 21 | 11 | - | 11 | - | - |
| Male 45 | 29 | 14 | 2 | 28 | 15 | 2 | 30 | 15 | - | 10 | 3 | 2 |
Legend: NM: Needs Improvement; A: Acceptable; D- Featured
The application of the strategy demonstrated evidence of learning materialized in the increase in the levels of physical condition of the students, this made possible the efficient, adequate work of the teachers in the formation of the self-exercise skill of physical exercise, which allows students perform physical activity and improve their physical fitness (Table 3).
Table 3. - Results obtained after the application of the strategy, carried out on the students with the same tests as Plan E
| Evidence | Planks 30s | ABS 1 min | Cafra test | Test Shuttles of | ||||||||
| NM | A | d | NM | A | d | NM | A | d | NM | A | d | |
| Female 32 | 7 | 2 5 | - | 2 | 30 | - | 12 | 18 | 2 | 8 | 4 | - |
| Male 45 | 5 | 40 | - | 0 | 43 | 2 | 10 | 30 | 5 | 5 | 3 | 2 |
Legend: NM: Needs Improvement; A: Acceptable; D- Featured
DISCUSSION
Learning based on didactic strategies of self-exercise of physical activities applied in the teaching of physical education guarantees that students maintain their state of physical condition and can achieve the expected learning results.
The physical education strategies implemented in the confinement period have laid the foundations for students and school communities to understand the benefits it provides in the comprehensive training of the individual, in addition to having a positive impact on their health.
According to UNESCO (2020), beyond the need to increase levels of Physical Activity in children and youth, Physical Education is a fundamental right that brings benefits for individuals, families, communities and society in general; plays an important role in developing basic knowledge about physical activity, well-being and physical capabilities; improves mental health and psychological abilities; increases social capabilities; contributes to the prevention and rehabilitation of those at risk of falling into addictions, crime, exploitation or poverty; and can bring important benefits on the health, social and economic levels.
For Rivera and Martínez (2023), the teacher must have adequate development of skills to guide the work, guide student performance and maintain a proactive attitude to find solutions to the different situations of the teaching-learning process.
For Conde-Williams and Valdez (2023), the teacher must pay particular attention to the planning of activities, understood not as the delimitation of face-to-face and virtual activities, but rather conceive them as a system from a didactic design that stimulates interactivity, creativity and motivation for learning.
Juanes and Rodríguez (2021) recognize that distance education and virtual physical education have become effective tools that can contribute to the quality of life of people in isolation. The pedagogy of physical education has been oriented towards the discovery of new methods and strategies to reach more people in the best way.
Díaz-Canel (2023) expressed that hybrid education as a teaching-learning modality gained particular relevance during the confinement caused by the COVID-19 epidemic. Currently, it remains a viable option for teaching innovation by combining the face-to-face and virtual modality, in addition to expanding the spectrum of didactic and methodological alternatives in a context of digital transformation characterized by extensive use of Information Technologies. and Communications (ICT) in all areas of society.
When comparing research related to the performance of physical activities and the way in which physical exercises are oriented from the university curriculum in the discipline of Physical Education, the use of strategies for the training of self-exercise of physical exercises in students is not found, which could be applied in conditions of physical isolation caused by the pandemic or other forms of confinement due to economic crises and natural phenomena.
The results obtained with the practical application of the strategy recognized that it contributes to the training of a Veterinary Doctor capable of exercising and maintaining a state of development of physical condition for a better quality of life.
CONCLUSIONS
From the study of the theoretical and methodological foundations of the formation of the self-exercise skill of physical exercise, it was found that there are limitations in proposals aimed at the continuous and permanent training of future Veterinary Doctors, which made it possible to design and apply actions as a basis to carry out the strategy proposal.
The diagnosis on the formation of the self-exercise skill of physical exercise carried out to the students and teachers of Physical Education of the Veterinary Medicine career showed substantial and well-characterized evidence on the problems related to the formation of skills in Physical Education in the didactic procedure, it was found that they lack methodological indications for the training and development of this skill.
The designed strategy, which is presented, allows the formation of the self-exercise skill of physical exercise in students of the Veterinary Medicine career.
REFERENCIAS BIBLIOGRÁFICAS
Addine F. (2007). Didáctica. Teoría y práctica. Playa, Cuba: Editorial Pueblo y Educación. https://isbn.cloud/9789591315243/didactica-teoria-y-practica/ [ Links ]
Álvarez de Zayas, C. M. (1999). Didáctica. La escuela en la vida. Playa, Cuba: Editorial Pueblo y Educación . https://isbn.cloud/9789591306814/didactica-la-escuela-en-la-vida/ [ Links ]
Conde-Williams, A.C., de la Valdés-Sánchez, M, (2023) La educación híbrida, una reflexión desde la preparación del docente universitario. Rev Inf Cient. 2023; 102:4268. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8147700 [ Links ]
Fierro-Rojas, C., & Valadez-Gutiérrez, J. (2022). Gestión institucional en Educación Física por medio de las tecnologías en tiempos de la covid. Pedagogía y Sociedad, 25(63), 89-107. http://revistas.uniss.edu.cu/index.php/pedagogia-y-sociedad/article/view/1453 [ Links ]
Hernández-Echevarría, T. I., Paulas-González, O., Morales- Ferrer, A. M., & Marín- Ramírez, J. R. (2021). Situación actual de la habilidad dirigir en el proceso de formación profesional de Cultura Física y Deportes (parte 1). Revista científica Especializada En Ciencias De La Cultura Física Y Del Deporte, 14(32). https://www.deporvida.uho.edu.cu/index.php/deporvida/article/view/744 [ Links ]
Juanes Giraud, B., y Rodríguez Hernández, C. (2021) Educación física en tiempos de Covid-19. Valoraciones a partir de la utilización de las TIC. Conrado .17(79). Cienfuegos mar.-abr. 2021Epub 02-Abr-2021 http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1990-86442021000200032 [ Links ]
Martínez Morales, Y., Concepción Rodríguez, M. L., & Padilla García, O. (2022). La creatividad: una necesidad para la modalidad no presencial en tiempos de Covid-19. Pedagogía y Sociedad, 25(65), 77-95. https://revistas.uniss.edu.cu/index.php/pedagogia-y-sociedad/article/view/1568 [ Links ]
Montes de Oca Recio, N., & Machado Ramírez, E. (2011). Estrategias docentes y métodos de enseñanza-aprendizaje en la Educación Superior. Humanidades Médicas, 11(3), 475-488. https://humanidadesmedicas.sld.cu/index.php/hm/article/view/127/81 [ Links ]
Morales Ferrer, A., Hernández Echevarría, T., & Otero Brande, J. (2021). Matrices ATJ, herramientas para pronosticar la validez de un resultado científico en la Cultura Física. PODIUM Revista de Ciencia y Tecnología en la Cultura Física, 16(1). http://podium.upr.edu.cu/index.php/podium/article/view/999 [ Links ]
Organización de las Naciones Unidas [ONU], (2015). La Agenda para el Desarrollo Sostenible. ONU. https://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/es/development-agenda [ Links ]
Organización de las Naciones Unidas para la Educación, la Ciencia y la Cultura. (2020). El coronavirus COVID-19 y la educación superior: impacto y recomendaciones. UNESCO. http://www.iesalc.unesco.org/2020/04/02/elcoronavirus-covid-19-y-la-educacion-superior-impacto-y-recomendaciones/ [ Links ]
Rivera Calle, F.M., García Martínez, A. (2023) Aula invertida con tecnologías emergentes en ambientes virtuales en la Universidad Politécnica Salesiana del Ecuador. Rev Cubana Educ Sup 37(1): 108-123. http://scielo.sld.cu/pdf/rces/v37n1/rces08118.pdf [ Links ]
Received: October 01, 2023; Accepted: January 07, 2024











 texto en
texto en