Mi SciELO
Servicios Personalizados
Articulo
Indicadores
-
 Citado por SciELO
Citado por SciELO
Links relacionados
-
 Similares en
SciELO
Similares en
SciELO
Compartir
Ciencia y Deporte
versión On-line ISSN 2223-1773
Ciencia y Deporte vol.9 no.1 Camagüey ene.-abr. 2024 Epub 04-Abr-2024
http://dx.doi.org/10.34982/2223.1773.2024.v9.no1.004
Original article
Assigning Independent Work with an Interdisciplinary Approach
1Universidad de Guantánamo, Guantánamo, Cuba.
Introduction:
Assigning homework using an interdisciplinary approach constitutes a working priority of Cuban universities' methodological work. The search for objective and effective solutions for teaching optimization, as part of Cuban higher education, has turned into an inescapable reality to train competent professionals committed to their social projects.
Aim:
To design a didactic model that leads to an independent work assignment methodology using an interdisciplinary approach throughout the academic year in the Physical Culture bachelor's degree.
Materials and methods:
Several theoretical, empirical, mathematical, and/or statistical methods were used in this study. The population consisted of 14 faculty members part of the staff.
Results:
There was consensus among the teachers in relation to assigning homework based on an interdisciplinary approach, with the introduction of the didactic model and the relationships created in the category system, which is then realized in the methodology suggested.
Conclusions:
The didactic model implemented through an assigning corrective method based on procedures and didactic resources, contributes to improvements in independent work assignments, using an interdisciplinary approach in the Physical Culture bachelor's degree.
Key words: Didactic model; assigning base; assigning context; in-context assigning procedure.
INTRODUCTION
The search for objective and effective solutions for the optimization of teaching, as part of Cuban higher education, has turned into an inescapable reality to train competent professionals. In that sense, the national efforts are based on the deep transformations introduced in Cuban universities, so that students acquire a general and comprehensive culture, one of the major objectives of professionals.
Considering the brevity humanity reproduces knowledge, the extent of the problem of today's pedagogy can be understood, in coping with the contradiction between their information possibilities and the necessity to maintain updated teaching levels. This lack of proportionality is partly solved by independent homework assignments. Therefore, teachers must perform proper assigning, planning, effective control, and assessment of homework for the acquisition of knowledge by the students.
Several authors have dealt with methodological work, including Martínez Hernández, S., Massip Acosta, A., & Pérez González, F. J. (2021), who said that one of the main work directions in education is the diversification of ways for the optimization of the methodological work, including homework assignments.
Their remarks match the purpose of this study since independent work is a priority in higher education. Therefore, the methodological efforts should be directed at optimizing the teaching-learning process, which has been analyzed by various researchers, with discrete results. It demands further study, being a necessity of the didactic sciences given to university students, who perform and think based on that approach, as mentioned by Valencia (2019) & Addine (2019).
In that sense, the methodological work designed to deal with the implicit contents of interdisciplinary approaches is a relevant aspect of student learning. This integration favors the creation of a much deeper relationship among the subjects within a particular discipline, as well as the comprehension of relationships among them, coinciding with Asencio Cabot, E., Évora Larios. E, and Ibarra N. (2021), who referred to orienting and controlling independent work for continuous teacher education based on an integrating approach, though lacking interdisciplinary relationships within the staff of the same academic year.
Today, quite a few specialists, such as Fragoso, J., Garcés, B., Molina, A., Caminero, V., Roque, L., and Espinosa, I. (2019), consider that one of the ways teachers can strengthen their labor in universities, with a significant impact on comprehensive professional education, is interdisciplinary methodological work. It has an integrating and systemic character in which planning, organization, design, assessment, control, and proper preparation, are critical factors for the integration of didactic components in the teaching-learning process.
Various research studies showed that the least studied aspects within the methodological structure include independent work in the different disciplines and academic year staffs, particularly in assigning and following up an interdisciplinary approach to achieve better results in learning. Hence, such direction should be given greater importance internally in the disciplines.
These shortcomings evidence that the teacher training process lacks projection that offers proper independent work assignment based on an interdisciplinary approach, which requires a higher integration level among all the actors, thus modifying the current performance mode and changes in the conception of methodological work, particularly the discipline Analysis and Research Methods in Physical Culture, considering that the interdisciplinary approach suits the present demands and new contexts.
The previous was corroborated by a preliminary factual diagnostic performed as part of the research, as well as by the author's experience as the principal teacher of subject Research Methodology at the Faculty of Physical Culture, the University of Guantanamo, Cuba, which was useful for the design and performance of a diagnostic that revealed the following flaws:
Theoretical and practical shortcomings in assigning independent work with an interdisciplinary approach.
Absence of methods and procedures for the independent work assignment using an interdisciplinary approach.
Inappropriate student attitude in coping with independent work with a practical interdisciplinary approach.
Accordingly, this study found shortcomings in the methodological work and the need for establishing integrating and contextualized tools for teachers to conceive proper assignment of independent work with an interdisciplinary approach that produces appropriate professional performances in particular situations.
Hence, this paper aims to design a methodology based on a systemic, integrating, and participatory didactic model that contributes to the proper assignment of independent work with an interdisciplinary approach throughout the academic year in the Physical Culture bachelor's degree.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The research study relied on methods and techniques that enabled a theoretical rationale for the didactic model, its design, and practical data processing. A non-probabilistic intentional population made up of 14 teachers in the first year of the Physical Culture bachelor's degree, was selected.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The current state of the problem was reviewed and characterized, while several dimensions and indicators were set concerning the dependent variable: independent work assignment with an interdisciplinary approach in the first year of the Physical Culture bachelor's degree at the University of Guantanamo, which produced the following results:
Concerning potentialities:
The academic year was acknowledged as the fundamental basic element for independent work assignments with an interdisciplinary approach.
Teachers referred to their willingness to cope with the new changes stated in the interdisciplinary methodological work in the academic year.
Concerning shortcomings:
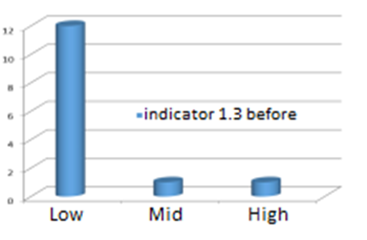
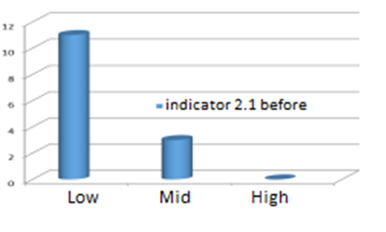
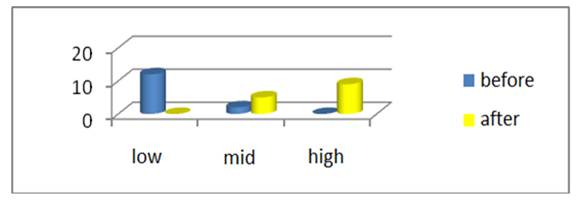
Poor independent work assignment quality by teachers with an interdisciplinary approach (85.7 %), in terms of professional performance in Physical Culture.
Insufficient teacher use of procedures (78.5 %), as evidenced in addressing independent work with an interdisciplinary approach by students.
Figure 1 and Figure 2 show the most affected indicators and dimensions, according to the initial diagnostic.
It was useful to identify the main breach: insufficient teacher training in the development of theoretical-interdisciplinary procedures for assigning knowledge for independent work assignments with an interdisciplinary approach in the first academic year of the Physical Culture bachelor's degree at the University of Guantanamo.
The results shown by the diagnostic confirm that many of the shortcomings in methodological work done in the first year of the Physical Culture bachelor's degree related to independent work assignment using an interdisciplinary approach are linked to the limited teacher training to develop theoretical-methodological and procedures for assigning knowledge in the different areas of Physical Culture performance.
Accordingly, a didactic model was designed to address the weaknesses observed, based on the findings of Giraldo Gutiérrez, F. L., Ortiz-clavijo, L. F. & Zuñiga-Miranda, S. (2020).
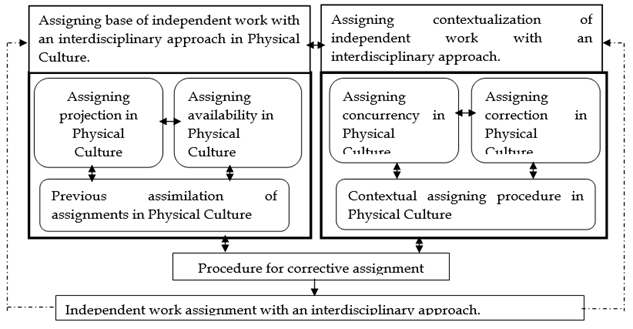
The structuring of the didactic model was conceived as an independent work assignment with an interdisciplinary approach as a process made by two subsystems with internal movements: the assigning character of independent work and the assigning contextualization of independent work, which are put into practice by the corrective method.
The assigning base of independent work with an interdisciplinary approach is a subsystem that results from relationships established between the assigning projection and assigning setting components, which are synthesized in the previous interdisciplinary assignment in the Physical Culture bachelor's degree.
Likewise, it enables the assigning projection of independent work with an interdisciplinary approach in the bachelor's degree, and therefore, in the academic year. It integrates cognitive aspects of disciplines and subjects, along with procedural and attitudinal aspects, among others.
It is an expression of the projection made by teachers so that integrating tasks have an interdisciplinary approach, reflected in student performance modes resulting from learning assimilated through methods and procedures. It manifests in the four spheres of Physical Culture performance.
This subsystem is set by an arrangement of pedagogical tools that favor independent work planning with an interdisciplinary approach, following the identification of professional problems in any of the professional performance contexts in Physical Culture.
Figure 3 shows the first subsystem.
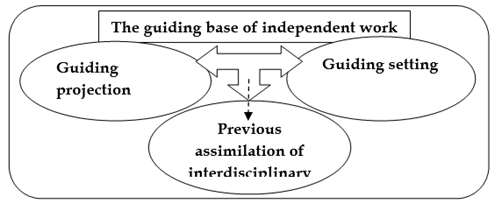
Fig. 3. - Representation of the internal relationships of the subsystem: The assigning base of independent work
The subsystem assigning base of independent work is defined as the process of interaction and assistance between teachers and students to facilitate independent work assignments with an interdisciplinary approach, which permits coherent and systemic articulation of cognitive nodes that make up the discipline of the academic year (Beltrán, 2022).
The assigning base of independent work for Physical Culture permits the determination of assistance and projection levels required by students, their needs, demands, expectations, and possibilities of the degree and inside it, as well as the academic year for independent work assignment using an interdisciplinary approach in methodological work.
This subsystem favors and projects student homework from a perspective that helps understand, interpret, and transform the educational reality to articulate attitudes and values that favor their prolongation, derivation, and consequent generalization to promote a professional culture within the previously mentioned context in the university community.
The practical realization of the components of the subsystem assigning base of independent work with an interdisciplinary approach in Physical Culture takes place through the interrelation with the subsystem assigning contextualization of independent work with an interdisciplinary approach, resulting from the relationships established among the components assigning concurrence in Physical Culture and interdisciplinary assigning correction, which produce a contextual assigning procedure in Physical Culture.
The subsystem assigning contextualization of independent work with an interdisciplinary approach is defined as the process that assigns the contents of different disciplines and subjects integrally and contextualized, according to the formative and interdisciplinary sides, leading to better teacher training for independent work assignment with an interdisciplinary approach in the academic year, favoring their performances in all the different professional performance spheres in Physical Culture (Beltrán, 2022).
The above authors revealed a teacher-developing process capable of locating students in concrete interdisciplinary relevant situations, which includes assigning concurrency, interdisciplinary assigning correction, and contextual assigning procedures in Physical Culture, as its components. Assigning contextualization becomes the moment when what is taught and learned is integrated and contextualized. This scenario consolidates the interdisciplinary approach among academic disciplines, including the spheres of Physical Culture student performance, namely, Physical Education, sports, physical therapy activities, and recreation.
Consequently, the subsystem favors the growth of integrated subjects suited for the concrete historical conditions of society and identified by their interdisciplinary culture, so engaged as to implement independent work with an interdisciplinary approach through methodological work.
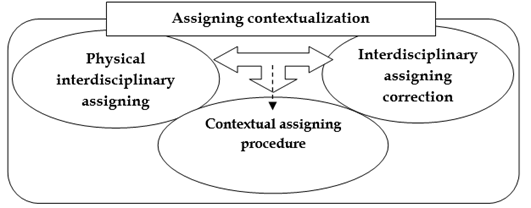
The assigning contextualization is made of components having dialectic and interdependent relationships Figure 4.
Assigning contextualization
This subsystem requires an assignment that involves the context and concrete historical conditions in which a teaching-learning process takes place in the Physical Culture bachelor's degree, depending on its particularities and the need for interdisciplinary methodological work that favors the link among academic disciplines mediated by the socialization it generates.
It allows teachers to self-regulate, and consider their motivations, knowledge, and assessments, based on customization and possible plans and projects conceived for implementation in physical education and sports, recreation, or therapeutic and prophylactic physical culture.
The subjects that intervene or interact (subject-object, subject-subject) play a critical role in the pedagogic process, from the individual to the social, and therefore, create interactions in a complex system of links, and practical life situations with enriching experiences, contents, and goals. They develop and synthesize individual and group relationships that converge in the academic year, and require a diagnostic resulting from previous planning for practical materialization in the students' research and job practices, which shapes professional performance modes.
Another significant element is the relationships established by the academic year teachers and tutors along the research and job practices, as well as in the year's staff. It creates new links and bonds among the students engaged, and within the students themselves, as conditioning aspects for the materialization of independent work with an interdisciplinary approach, based on the main integrating discipline in the Physical Culture bachelor's degree.
Therefore, this process requires mastery of theoretical-methodological knowledge, as well as the assigning procedures at the different spheres of professional performance, as an important condition to conduct methodological work in the academic year.
A resulting component of higher order among all the elements of the didactic model is independent work assignment with an interdisciplinary approach, which is a process and result derived from a fruitful, flexible, and corrective methodological work shaped to the historic-concrete conditions of their participants in different performance contexts in the Physical Culture bachelor's degree.
The structural levels can be figured out in all the system's components of the relationships identified. A first structural level, with a lower complexity, occurs in the subsystem assigning base, which is represented by components assigning project, assigning availability, and previous assimilation of independent work assignment with an interdisciplinary approach, materialized in subsystem assigning contextualization, being the second level of complexity.
In this particular model, the theoretical knowledge from the assigning base of independent work becomes the assigning contextualization. Hence, the hierarchy of different complexity levels in the system modeled is revealed.
First level: the subsystem assigning base of independent work with an interdisciplinary approach for Physical Culture.
Second level: the subsystem assigning contextualization of independent work with an interdisciplinary approach to Physical Culture.
Overall: A process of independent work assignment with an interdisciplinary approach in the Physical Culture bachelor's degree.
The following sketch shows the structure of the model suggested, its subsystems, and their corresponding components for independent work assignments with an interdisciplinary approach.
Figure 5 shows the structure of the proposal.
Theoretical assessment of the didactic model using expert opinion
A total of 14 experts were consulted. Expert opinion tackled five aspects: the theoretical rationale for the didactic model, organizing and structuring the model of systems and subsystems leading to expected goal accomplishment, level of practical applicability derived from didactic and methodological management that offers a unique didactic model to teachers and directors of the academic year.
Most aspects were regarded as positive by the experts, within categories Very Appropriate (VA), Appropriate (A), and Inappropriate (IA), with a predominance of Very Appropriate in relative frequencies that varied between 80 and 100%. The experts recommended aspects to be considered for adjustment of the general conception of the didactic model.
Processing of aspects provided by the experts produced the following cut-off points: 1.68 3.49
___VA__/___A____/___IA___
Where: VA = Very appropriate; A = Appropriate; IA = Inappropriate.
The analysis of cut-off values helped infer that the experts reached a consensus upon assessing the aspects as Very Appropriate.
A statistical analysis of the results based on expert opinion that relied on the Green method helped determine consensus associated with the level of relevance of aspects evaluated by the experts. These aspects were corroborated through qualitative and quantitative interpretation of the data, considering the didactic model in compliance with its methodology, and appropriate relationships between the subsystems and components, as well as internal component relationships in each subsystem, which favor the conditions for the organization and implementation of the methodology and contribution to teacher training for independent work assignment with an interdisciplinary approach in the academic year in the Physical Culture bachelor's degree, and the dynamic role of the assigning corrective method during such training.
Assessment of the didactic model through a pre-experiment
The indicators evaluated in the pre-experiment showed higher results and better teacher training in mastering the theoretical and methodological knowledge and manifesting assigning powers for the implementation of independent work with an interdisciplinary approach, comprehensive mastery of knowledge about a particular area of a discipline and its different contexts for interdisciplinary professional performance, observed in proper practice for independent work assignment with an interdisciplinary approach in the academic year in the Physical Culture bachelor's degree. This general summary of the pre-experiment is shown in Figure 6.
Main results achieved upon the application of the pre-experiment
Greater teacher mastery (92.8 %) of the theoretical and methodological knowledge evidenced in the reflection of the performance modes during the concrete and accurate assignment of independent work with an interdisciplinary approach, seen in the solutions provided by the students in the teaching-learning process in the first year of the bachelor's degree.
Lessons showed appropriate didactic and methodological conception (76.9 %) that favored independent work assignment with an interdisciplinary approach and the relationship between the subject's contents and the different spheres of professional performance in Physical Culture.
This paper showed several different studies that praise the adjustment of methodological work in higher education, such as Álvarez (2004) and Addine (2019). However, the new social challenges, transformations in education, and influence of science and technology demand a new approach to address the problems that emerge in different knowledge types with an interdisciplinary approach.
Accordingly, other authors have expressed their concerns and offered their contributions in terms of methodological work with a comprehensive approach characterized by an interdisciplinary dynamic of its own. Some of them are the following: Disotuar & Guilarte (2018); Estrada (2019); Figueroa, Pezoa, Godoy & Diaz (2020); Dudina (2020); Jara (2020).
All of them have contributed important theories associated with an interdisciplinary standpoint in science education, skills for scientific thinking with a sociology-critic base for initial teaching education. However, there are shortcomings, whose contextualization is essential in the Physical Culture bachelor's degree. Hence, this proposal includes new ways and procedures to address that problem.
CONCLUSIONS
The diagnostic of the current state of the problem permitted the identification of existing weaknesses for independent work assignments with an interdisciplinary approach, whose causes lie essentially in the insufficient theoretical-methodological knowledge and the assigning procedures.
The didactic model is a way of contributing to assigning independent work with an interdisciplinary approach, which as a result of the relationship between its subsystems, assigning base of independent work with an interdisciplinary approach in Physical Culture and the assigning contextualization of independent work with an interdisciplinary approach, emerges as the assigning corrective method, an alternative to address the scientific problem.
The findings of this study using expert opinion and pre-experiment evidenced the feasibility of the didactic model in terms of structure, and the relationship between its subsystems looking for proper independent work assignments with an interdisciplinary approach.
REFERENCIAS BIBLIOGRÁFICAS
Addine, F., Recarey, S., Fuxá, M., Fernández, S. (2020). Didáctica: teoría y práctica Pueblo y Educación. Editorial Pueblo y Educación, ISBN 959133852X. P. 317. https://books.google.com.cu/books/about/Did%C3%A1ctica_teor%C3%ADa_y_pr%C3%A1ctica.html?id=zOUREAAAQBAJ&redir_esc=y [ Links ]
Asencio Cabot, E., Évora Larios, E., y Ibarra, N. (2021). La orientación y control del trabajo independiente en la formación continuada de docentes. Centro de Información y Gestión Tecnológica y Ambiental de Las Tunas, Cuba. ISSN-e: 1025-6504. 26(4). https://revistas.reduc.edu.cu/index.php/transformacion/article/view/e3594 [ Links ]
Cingualbres, R. J. E., Nobal, A. S. G., & Lao, M. D. C. B. (2019). Un abordaje teórico a las relaciones interdisciplinarias desde las Estrategias Curriculares en la Cultura Física (Revisión). Revista científica Olimpia, 16(55), 114-125. https://revistas.udg.co.cu/index.php/olimpia/article/view/828/1549 [ Links ]
Dudina, T. (2020). Enfoque interdisciplinario en la enseñanza. Buenos Aires, Argentina: Editorial Magisterio del Rio de la Plata. [ Links ]
Figueroa Céspedes, I., Pezoa Carrasco, E., Godoy Elías, M., & Diaz Arce, T. (2020). Habilidades de Pensamiento Científico: Una propuesta de abordaje interdisciplinar de base sociocrítica para la formación inicial docente. Revista de Estudios y Experiencias en Educación. http://www.rexe.cl/ojournal/index.php/rexe/article/view/867 [ Links ]
Fragoso, J., Garcés, B., Molina, A., Caminero, V., Roque, L., y Espinosa, I. (2019). Una Aproximación a la Interdisciplinariedad desde la Filosofía. Medisur. 15(1), 6. http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1727-897X2017000100009 [ Links ]
Giraldo Gutiérrez, F. L., Ortiz-clavijo, L. F., & Zuñiga-Miranda, S. (2020). Políticas de Ciencia, Tecnología e Innovación en América Latina y el Caribe y su influencia en la producción y apropiación de la CTI. Revista Linguagem & Ensino, 23(1), 296-316. https://periodicos.ufpel.edu.br/index.php/rle/article /view/17751/11147 [ Links ]
Jara Miguel, A. (2020). El enfoque interdisciplinar en la enseñanza de las Ciencias Sociales y Humanas. Reflexiones epistemológicas y metodológicas. Clio Asociados (30), 75-89. En Memoria Académica. http:/www.memoria.fahce.unlp.edu.ar/artÍrevistas/pr.12141/pr.12141.pdf [ Links ]
Martínez Hernández, S., Massip Acosta, A., & Pérez González, F. J. (2021). El estudio y trabajo independientes en la mira de la educación médica superior cubana. Educación Médica Superior, 35(1). https://ems.sld.cu/index.php/ems/article/view/2175/1216 [ Links ]
Ocampo Ospina, L.F., Valencia Carvajal, S. (2019) Los problemas sociales relevantes: enfoque interdisciplinar para la enseñanza integrada de las ciencias sociales. Dehesa. REIDICS: Revista de Investigación en Didáctica de las Ciencias Sociales, ISSN 2531-0968, 4, 60-75 https://dialnet.unirioja.es/servlet/articulo?codigo=6924882 [ Links ]
Received: September 04, 2023; Accepted: October 24, 2023











 texto en
texto en