Introduction
The concept of career success is interchangeably used as career satisfaction (CS) in both past and the contemporary literature. A growing body of theoretical and empirical work has provided a good understanding about CS and its significance among the employees and for the business organizations as well (Ndung’u, 2016). The factors like salary and career promotion are also used to reflect the concept of CS. However, both in past and the recent studies, CS is used as a subjective tool to evaluate the satisfaction of the employees with their professionals. For this reason, it is claimed that career success is psychological success which is primarily reflected through personal achievements with its priority over the objective measures of success like getting a position in management hierarchy
Although the concept of CS is reasonably analyzed both in theoretical and empirical perspective, However, its regional implications in both public and private sector is very limited. In the contemporary career landscape, it is assumed that being employable is also among the core sources of CS (Onyishi et al., 2015). Meanwhile, such perception in the mindset of the individuals impacts on their behavior, thoughts and reactions as well. With the passage of time, when a person is employed, the beliefs about getting new employment opportunity with higher pay or scale is also relatively high (Berntson, Näswall, & Sverke, 2008). It means that the perception of being employed serves as an anchor in the changing workplace. In this regard, the emotional attachment of the employee to its organization is of utmost significance. It is believed that those employees having higher level of affective organizational commitment have higher level of career satisfaction (Lumley et al,, 2011).
Both the economic and social changes have significantly increased the volatility about the complexity of career development. At the same time, many challenges are also observed in the labor market regarding the job opportunity and career development A lot of employees are found who have reported negatively about their job because of insecurity and poor working condition However, at the same time, limited research studies are observed examining the underlying process by which the issue of dissatisfaction in a career by the employees can be revealed (Yen,et al., 2019).
Another notion in the field of career-related outcomes is observed regarding the career adaptability as it is positive linked with the former Job success and career adaptability are higher linked to each other. Meanwhile, good career adaptability may lead towards positive sense in life, career decision making, self-efficacy, and career optimism It is believed that career adaptability is also positively associated with the job-performance rating, hope, and overall wellbeing (Hirschi et al, 2016). However, CS and its relationship with the career adaptability is not something very simple to determine.
For survival and progress of any organization, the role of leaders is significantly vital. In developing organizational objectives, vision and mission, leadership helps the business firms both in short-term and long-term. It is believed that organizational culture is developed through leadership style, hence it is widely affected by the leadership. The effectiveness and performance of the organization is directly associated with the leadership behavior and its level of competence Leaders involve in influencing the employees to persuade their efforts towards organizational objectives. Meanwhile, it is supposed that leadership style is a pivotal component which further stimulates the organization as a whole. Leadership keeps on being a center of discussion for the researches and receives notable investigation. Various approaches are provided by the researchers and similar experts to characterize leadership. Different specialists from a range of economies conclude that leadership management is all about propelling, affecting, and finally empowering other individuals (Stollberger et al., 2019) in the business to contribute for the accomplishment of business objectives. More specifically, leadership is about to influence others as it is very critical factor to uplift the performance of the organization.
The concept of motivation is explained as an internal factor which can impel the one’s action towards some external factors It is believed that the factors like direction, intensity and duration are the three main actions as influenced by the motivation Different employees within the organization reflects different behavior patterns along with different motivational styles. It is believed that motivation is all about the common inclusion of the words like desire, want, wishes, aims and goals. Some authors have explained the factor of motivation as an inner driving force of the employees through which some both personal and organizational level goals can be achieved (Erven & Milligan, 2001).
In existing literature, different theoretical assumptions are also provided covering the title of motivation either directly or indirectly. The first one is entitled as need theory which points out those factors which can play their role in energizing the behavior of the individuals However, the term need may be defined in terms of physiological or psychological deficiencies that arouse the individual’s behavior . Meanwhile, these need can be strong or weak in nature and are influenced by environmental factors. Besides, the human needs vary over time and with the change in the places too
A range of studies are provided by the researchers while exploring the concept of innovative work behavior. During the start of recent decade, researchers like (Abudaqa et al., 2022) has provider his view about innovative work behavior. He claims that there are three interrelated behavior which are under the shadow of generation of idea, promotion of idea, and finally the realization of idea. Whereas authors like (Jonson, 2005) have explained the fact that ideas are surrounding the concept of ideation leadership. While explain that idea generation is something like a creative process which is associated with the generating, developing and finally the communication of new ideas. Some researchers have shown the fact that ideation is like something about thought cycle as linked with the innovation, development and no doubt the actualization or implementation.
The purpose of this study is to analyze the trend in career satisfaction among the government employees as working in the region of UAE through leadership, motivation and innovative work behavior. The rest of the paper is designed as follows. Section two provides the discussion about the literature. Section three analyze the key variables and their operational definition. Section four covers the research methods, while section five provides the discussion of the results. Last section concludes the study.
Research Methodology
Various authors have provided their view about the research design. However, the most widely accepted definition is covered by (Zikmund,et al., 2013) who explain that research design as a dominant plan which explains the procedure for assessing the relevant information for the future analysis. Research design is quite necessary for the researchers to analyze the collected data while answering the key issues as highlighted through applied or a basic research. Therefore, the significance of research design under present study cannot be ignored. Overall, there are two main approaches in research design. One is known as qualitative while other is accepted as quantitative. Researchers have widely explained the two approaches of qualitative and quantitative. For instance, Antwi & Hamza, (2015) added a significant description about both of these approaches and explain the fact that quantitative research design is more appropriate when the paradigm is positivism. On the other side, qualitative research is applied when the paradigm is interpretive epistemology. During the last decade, Yauch & Steudel (2003) have provided their view about qualitative research and specify that data is collected through individual words. While quantitative research collects the data through surveys and other measurements which were in the form of numerals. It is also inferred that survey instrument is frequently coming under the title of positivist approach as explained by (Creswell et al., 2003). In present study, data is collected through a survey, therefore, it is founded under positivist approach. In addition, this research has also utilized the quantitative research design for analyzing the relationship between the leadership motivation, innovative work behavior, and career satisfaction.
Present study considers the government entities which are working under the supervision of United Arab Emirates (UAE) government. At present, UAE has more than 4,000 federal and local e-services on their portal (UAE, 2020). More specifically, the federal level covers the 2445 e-services, 1983 transactional e-services, 177 informational in nature, 70 related to commercial activities, 129 social, and 86 seizural respectively (UAE, 2020). After describing the study population, unit of analysis is under observation. Unit of analysis consists of individuals, work groups, and even the organizations. In present study, the unit of analysis is based on the individuals who are working in different government entities. At the time of conducting this study, there were more than 100,00 employees which are working in different government entities of UAE having different age groups, gender, qualification and working background.
This research defines the following variables
Career Satisfaction The idea of career satisfaction is something like a response by the individuals towards their career and work related events. It normally examines the extent to which individual believe that their progress towards their career is consistent along with their goals, preferences and values It means that career satisfaction is related to the level of happiness as experienced through selecting a career. In addition, job satisfaction is related to situation with the current work. Researchers also claim that career success can also be operationalized in terms of career satisfaction or job satisfaction In this regard, career satisfaction is regarded as “ overall I am satisfied with the choice of my career” Meanwhile, both the demographic and success criteria are to be considered as best indicator of objective success towards a career and its satisfaction However, the role of organizational culture is also very much significant to analyze the while determining the factor of career satisfaction (Jabeen & Isakovic, 2018).
Transformational Leadership The approach of transformational leadership refers to the approach by which leaders in any business organization motivate their followers towards the organizational goals and objectives Such leaders also identify the interests of their followers to perform beyond the expectations. It means that transformational leadership plays a significant role in causing those changes which are necessary for the effective management within the organization. Authors like Kim (2017) believe that “transformational leaders have the ability to transform organizations through their vision for the future, and by clarifying their vision, they can empower the employees to take responsibility for achieving that vision”. Different types of leadership behavior have been reflected by the leaders which are idealized influence, inspirational motivation, intellectual stimulation and individualized consideration
Transactional Leadership The idea of transactional leadership is based on the assumption of marginal improvement. It also considers the factor of maintaining the quantity of performance based on the bargain relationship ). Authors like Bass (1985) defined the transactional leadership as such type of behavior which is based on the factors of reward and punishment. In transactional leadership, there is a clear plan to achieve the goals, focusing the key roles as played by teammates, requirements of the task and core expectorations from the followers by the leader. Through such approach, it is expected that there would be an increase in terms of compliance, reduction of resistance, and support for the mutual dependence too It is further believed that transactional leadership is linked with the creativity of middle-level managers while Öncer (2013) believes that transactional leadership is not linked with the innovativeness or risk taking dimensions.
Motivation As per the research findings of it is explained that there has been more than 140 attempts found in the literature to define the concept of motivation at workplace. However, the research contribution by Latham & Pinder (2005) has defined the term motivation in the following context:
“work motivation is a set of energetic forces that originate both within as well as beyond an individual’s being, to initiate work-related behaviour and to determine its form, direction, intensity, and duration.”. In addition, the literature work on the concept of work motivation explains that an individual is found to be intrinsically motivated in his/ her work at the time when he/she observed enjoyment, interest, self-expression, personal challenges, or/and satisfaction of his curiosity. It is further believed that people within the organization needs to feel intrinsically motivated. Owing to the positive feelings, individuals with intrinsically motivation can become ego-involved with their job, and committed for doing well (Minbaeva, 2008).
Innovative Work Behavior In both current and the past research, individual innovation is explored in terms of personality trait, behavior and output Innovative work behavior or IWB is typically refers to the exploration of opportunities and generation of some new ideas It means IWB is something which is entitled as creatively related behavior. However, it may also claim as individuals’ behavior which directs them towards implementing a change with the help of some new knowledge for improving a process towards personal or organizational performance. Meanwhile the construct of IWB is closely associated to the factor of employee’s creativity (Dul & Ceylan, 2011) which is defined as the production of new ideas regarding the products, services, procedures or the processes too.
Results and discussion
Table 1 provides the information for all the demographic factors covering the title of gender, age, working experience, and educational background respectively. It is believed that for the gender factor, both male and female respondents were targeted. However, male members are reflected a percentage portion of 83.1 % (241 in numbers), while females are covering a sample portion of 16.9 percent of 49 in numbers. Therefore, it is inferred that more than 80 percent of the respondents are the male while the rest of the members are females who are working in UAE government entities but are the local citizens. Secondly, the age distribution of the respondents specifies that total of 71 respondents or 24.5 % were between 20-25 years of age, 61 respondents or 21 % were between 26-30 years, 77 respondents or 26.6 % were between 31-35 years, 81 respondents or 27.9 % were between above 35 years of age. It means that our study has experienced all type of age groups who are working in government entities of UAE. In addition, present research has observed that there were 81 respondents (27.9 %) with 1-2 years of working experience, whereas 69 respondents (23.8 %) were those having a working experience of 3-4 years. Furthermore, 66 respondents or 22.8 % of the sample reflects those individuals who were working with the experience of 5-7 years. Lastly, there were 74 respondents (25.5) who have a working expertise of greater than 7 years. It shows that there is a good diversification among the respondents in terms of working experience in the region of UAE. In terms of educational background, overall five categories were observed and added in the questionnaire. As per the findings under Table 4.3, majority of the respondents were those who are working with the 14 years of qualification (i.e. 78 respondents, 26.9 %), followed by those having an educational background of above 16 years (i.e. 75 respondents, 25.9%). Meanwhile, those who have only 16 years of education been 67 respondents, hence covering sample portion of 23.1 % respectively.
Table 1 - Demogrpahic Details of the Respondents
| Gender | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Titles | Frequency | Percent | Cumulative Percent | |
| Valid | Male | 241 | 83.1 | 83.1 |
| Female | 49 | 16.9 | 100 | |
| Total | 290 | 100 | ||
| Age | ||||
| Titles | Frequency | Percent | Cumulative Percent | |
| Valid | 20-25 Years | 71 | 24.5 | 24.5 |
| 26-30 Years | 61 | 21 | 45.5 | |
| 31-35 Years | 77 | 26.6 | 72.1 | |
| Above 35 Years | 81 | 27.9 | 100 | |
| Total | 290 | 100 | ||
| Working Experience | ||||
| Titles | Frequency | Percent | Cumulative Percent | |
| Valid | 1-2 Years | 81 | 27.9 | 27.9 |
| 3-4 Years | 69 | 23.8 | 51.7 | |
| 5-7 Years | 66 | 22.8 | 74.5 | |
| >7 Years | 74 | 25.5 | 100 | |
| Total | 290 | 100 | ||
| Educational Background | ||||
| Titles | Frequency | Percent | Cumulative Percent | |
| Valid | 14 Years | 78 | 26.9 | 26.9 |
| 16 Years | 67 | 23.1 | 50 | |
| 16 Years plus Diploma | 70 | 24.1 | 74.1 | |
| above 16 Years | 75 | 25.9 | 100 | |
| Total | 290 | 100 | ||
Source own elaboration
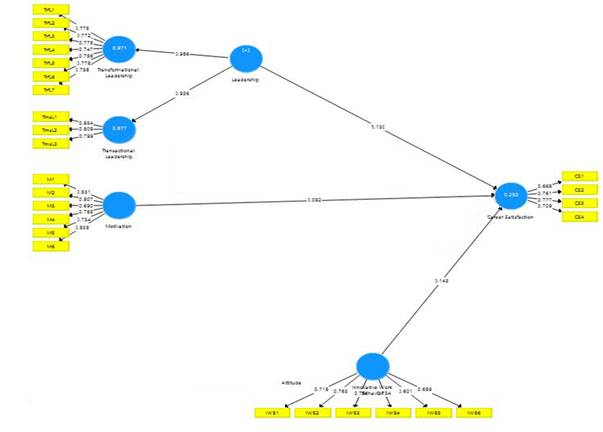
Table 2 indicates that value of α for all the variables is like career satisfaction (0.708), innovative work behavior (0.811), motivation (0.847), and leadership (0.917) respectively. Similarly, the value of CR for all the study variables is as follows; 0.82 for career satisfaction, 0.86 for innovative work behavior,0.87 for motivation, and 0.93 for overall leadership style. Meanwhile, as per the findings under Table 2, variables have the following AVE scores i.e career satisfaction; innovative work behavior; 0.51, and leadership; 0.57 respectively.
Table 2 - Results Summary for Reliability and Validity of the Constructs
| Construct | Items | Loading | Cronbach's Alpha | CR | AVE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Career Satisfaction | CS1 | 0.668 | 0.708 | 0.82 | 0.533 |
| CS2 | 0.761 | ||||
| CS3 | 0.777 | ||||
| CS4 | 0.709 | ||||
| Innovative Work Behavior | IWB1 | 0.718 | 0.811 | 0.861 | 0.51 |
| IWB2 | 0.763 | ||||
| IWB3 | 0.766 | ||||
| IWB4 | 0.734 | ||||
| IWB5 | 0.601 | ||||
| IWB6 | 0.689 | ||||
| Motivation | M1 | 0.531 | 0.847 | 0.875 | 0.544 |
| M2 | 0.807 | ||||
| M3 | 0.690 | ||||
| M4 | 0.785 | ||||
| M5 | 0.734 | ||||
| M6 | 0.835 | ||||
| Leadership* | TRFL | 0.986 | 0.917 | 0.931 | 0.573 |
| TRNSL | 0.936 |
Source own elaboration
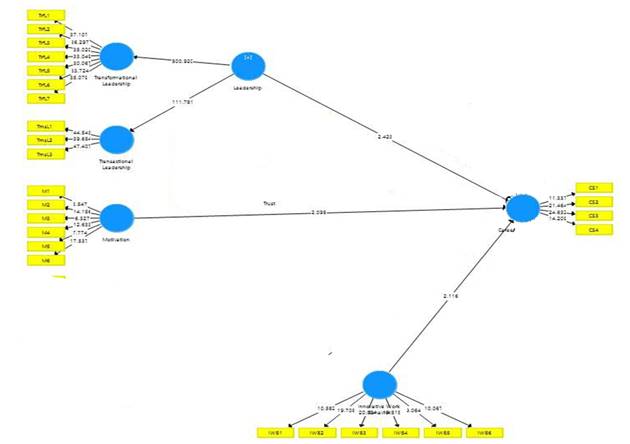
After determining the model fit indices, next step is to analyze the direct relationship between the study variables (Figure 1). The impact of leadership on career satisfaction is also examined through SEM findings are values are provided in Table 3. It shows that leadership is a positive predictor of career satisfaction and overall direct impact is observed. This impact is reflective through a coefficient of 0.133 with the standard deviation of 0.055. This means that overall leadership style is a positive indicator for increasing the career satisfaction among the employees who are working in government entities of UAE. Based on these findings, H5 is also supported. Furthermore, the impact of motivation on career satisfaction is found to be positively significant. This means that employees with the higher motivation tends to enjoy more career satisfaction as observed in the governmental entities of UAE, hence H6 is also supported. As per the observation, innovative work behavior is also observed to a significant exogenous determinant for career satisfaction in current study. As per the findings under Table 3, innovative work behavior is causing more career satisfaction among the selected employees of government entities in UAE region (i.e beta=0.135, standard deviation= 0.055, t-statistics= 2.116, and p-value= 0.0035). This would consider that H3 is supported. (Figure 2)
Table 3 - Direct Relationship between the Variables.
| Hypotheses | Variables and Directions | Beta | (STDEV) | T Statistics | P Values | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1 | Leadership Career Satisfaction | 0.133 | 0.055 | 2.423 | 0.016 | Supported |
| H2 | Innovative Work Behavior Career Satisfaction | 0.135 | 0.064 | 2.116 | 0.035 | Supported |
| H3 | Motivation Career Satisfaction | 0.111 | 0.053 | 2.095 | 0.037 | Supported |
Source own elaboration
Conclusion
Present study has examined the impact of leadership, motivation, and innovative work behavior on the career satisfaction among the government employees of UAE. To test all the study research hypotheses, structural equal modelling technique was applied for both direct and indirect relationship between the variables. For this purpose, data was collected from the government employees working at UAE. Overall 384 sample questionnaires were distributed among the study respondents where the returned questionnaire were 314. Further investigation of the individual questionnaires had provided the evidence that only 290 copies were found to be good enough for the study results. This sample of 290 questionnaire is observed as a correct final response rate of 75.50 %. Meanwhile for testing the hypotheses, level of significance was less than 0.05 under two tailed test. The findings of the study indicate that there is a significant impact of leadership, motivation, and innovative work behavior on the career satisfaction among the targeted employees of government sector of UAE. In addition, the review of existing literature also provided the evidence that it is lacking with the exploring the trends in career satisfaction among the government employees of UAE. The reason is that most of the studies have been conducted in different regions including developed and developing economies while little research has been done specifically among the government entities of UAE and their employees. Thus, the current research has focused on the government entities of UAE to provide another theoretical contribution in the present body of literature. Furthermore, the trends of the earlier studies have shown that most of them have been conducted on the developed economies with a very little implication for the other regions where different cultural trends and organizational norms are observed. Meanwhile, various limitations as also attached with the study. For example, the focus of present study is only on the employees of government entities as working in the region of UAE. It means that only the public sector employees were under consideration in the present study analysis. This would indicate that employees from the private sector of UAE were not observed which is another study limitation. Additionally, present study was conducted in UAE while observing the government employees and specifically the citizens of UAE. It means that study has a regional as well as a cultural limitations which specifies that findings are only applicable to similar region or the employees with the similar culture at any other place. Future studies are highly suggested to cover these limitations.