Meu SciELO
Serviços Personalizados
Artigo
Indicadores
-
 Citado por SciELO
Citado por SciELO
Links relacionados
-
 Similares em
SciELO
Similares em
SciELO
Compartilhar
Mendive. Revista de Educación
versão On-line ISSN 1815-7696
Rev. Mendive vol.21 no.4 Pinar del Río oct.-dez. 2023 Epub 30-Dez-2023
Original article
Advanced professional from distance of the faculty of academic virtual master's programs. Case study
1 Universidad de Matanzas. Cuba.
In Cuban universities, the design of virtual master's degree academic programs from the implementation of the Distance Education Model for Higher Education is today one of the strategic objectives oriented towards the virtualization of professional training. Hence, the objective of the article is to present the results of the practical validation of a methodological conception for the professional improvement at a distance of the faculty of these programs, based on active methodologies from collaborative practices mediated by interaction and socialization in a digital ecosystem such as technological support for its applicability. From predominantly qualitative research with a descriptive approach, scientific methods of the theoretical level such as inductive-deductive, analytical-synthetic and modeling were used; and from the empirical level, the case study with complementary methods such as participatory observation, the survey, and the analysis of the products of the activity. The results are expressed in the transformations of the traditional improvement process, in the suitability of the teacher and his pedagogical practice, by measuring the impact of the transfer of new knowledge in real time to the design of master's programs for their virtual offer. It is concluded that remote professional improvement from the validated conception demonstrates its relevance, viability and adaptability to similar scenarios at the University of Matanzas.
Key words: academic training; digital ecosystem; distance education; higher education; professional improvement
Introduction
Virtual education is one of the most used study modalities for the improvement of professionals in many countries based on the internationalization and democratization of knowledge at a global level. Currently, virtual distance training programs are offered, coordinated by organizations and centers associated with postgraduate education projects, some for commercial purposes, and others for solidarity purposes. Among them are the virtual offers via the Internet of Atlantic International University (AIU), KEYSTONE MASTERSTUDIES , Latin American and Caribbean Institute of Quality in Distance Higher Education (CALED), PUCRS online in Brazil, Loopian Argentina, Consorcio de RED de Educación a Distance (CREA), Ibero-American Association of Distance Higher Education (AIESAD) among others.
In Cuba, the University of Computer Sciences (UCI) stands out, with its offers of virtual postgraduate courses of international scope, and the academic virtual distance master's programs: "Project Management" and "Virtual Education", as well as three others distance programs approved by the Advisory Commission for Postgraduate Education (COPEP), according to the statistical guide of the Ministry of Higher Education (MES): Master's Degree in International Relations; Master of Educational Sciences; and Master in Mathematics Education. All of them under the implementation of the Distance Education Model of Cuban Higher Education (CENED, 2016 cited in Hernández, Ruiz Y Sepúlveda, 2022).
In the Cuban educational field, to promote the development of postgraduate education in this modality, a distinction is made between the important regulatory elements, the Strategic Project 2021-2030, whose objective No. 4 is aimed at guaranteeing scientific and technological development, the introduction of the results of science and the satisfaction of the training, improvement and postgraduate needs of professionals, cadres and reserves in correspondence with the demands of local, territorial and country sustainable development.
Among those that regulate distance postgraduate education are Instruction No.1: Manual for postgraduate management in force since 2020, which explains how to implement the current Postgraduate Education Regulations Res. No.140/19, where includes for the first time in both documents, a chapter that provides the standards and procedures for the management of distance postgraduate courses for Cuban universities.
Likewise, educational policies have outlined computerization guidelines so that universities have digital ecosystems to support distance and virtual education, which is identified as a strength in this study, based on its use as technological support of the distance improvement mediated by Information and Communications Technologies (ICT), in correspondence with the following description based on the conceptualizations in this regard by Pineda Y Orozco (2017) and Cárdenas (2021): a digital learning ecosystem represents an architecture of services, from the integration of computer tools as supports for learning environments, collaboration and nodes that are interconnected to give life to a dynamic educational and social context in which interaction, communication and collaboration occur, information is accessed and produced. new knowledge.
These guidelines cement the intention of the Ministry of Higher Education to implement virtualization in postgraduate education, with emphasis on accredited academic master's programs of Excellence, promoting the transition towards virtual education in some, and designing new programs in virtual mode.
The bibliographic review carried out reaffirms the authors' criteria in relation to the characteristics that digital technologies have in relation to instantaneity, interactivity, interconnection, diversity, among others; where the variety of services that these provide acquire greater relevance in the postgraduate program due to its high degree of scope, levels of socialization, demands for updating, lifelong learning and the need to develop parallel to work activity, as Álvarez asserts, Fernández, García, Grandoli Y Pérez (2020) when addressing teaching at the postgraduate level in the context of emergency virtualization in the period of social isolation due to the Covid-19 Pandemic.
To this criterion, the authors add that the distance postgraduate program contributes to the digital transformation of society from the development in subjects of digital skills, skills of learning to learn in the self-management of information and knowledge for research, innovation and the disciplinary knowledge of each profession. However, in the context of Cuban higher education, there is a lack of a national strategy for initial teacher training for distance and virtual education, which takes advantage of the technological potential of university institutions for their performance in these modalities of study. as well as the lack of a conceptual framework to refer to the profile of virtual education teachers, which allows the projection of relevant professional improvement, limitations identified by the author Hernández (2022), as a critical element that persists in the delivery. of professional improvement courses to these teachers in a traditional way.
In the opinion of the authors, from their experiences as distance trainers at the University of Matanzas, and from other research carried out (Hernández Y Pentón, 2019), Hernández, Peñate y Hernández, 2023) and (Hernández y Álvarez, 2022), the professional improvement of teachers for the integration of technologies presents a tendency to develop in an emergent, heterogeneous, dispersed, atomized, and reactive way in the face of certain circumstances of the emergence of technologies or emergency contexts, with preeminence to the technological-instrumental approach.
Mostly it is carried out from traditional training scenarios and methodologies, that is, in person and through the transmission-reception of information and knowledge, without conceiving the teacher as a learning subject in the distance modality and its autonomous management from active methodologies and collaborative practices. for the social construction of knowledge.
With the desire to mitigate the weaknesses previously exposed, this study exposes the results achieved in the practical validation of a methodological conception for distance professional improvement mediated by technologies, based on the formation of virtual communities of collaborative practice for individual digital management. and collective of the faculty of academic master's programs of their professional improvement. The validation was carried out using the case study method that integrated a system of complementary scientific methods that also allowed us to measure its impact on virtual pedagogical practice and consider its results as good practices to be generalized in the improvement system of the University of Matanzas.
Materials and methods
To achieve the objective of this work, the qualitative scientific methodology was assumed with a descriptive approach, and the methods of the inductive-deductive, analytical-synthetic theoretical level, document review and modeling for the design of the conception that was applied in the system of institutional improvement. The case study was used as a general method, assumed in the field of scientific methodology of research in education as a method that, in turn, is composed of a system of methods, which in a logical and coordinated way complement each other. with the purpose of carrying out an in-depth study about a particular problem previously determined, according to what was proposed by Soto and Escribano (2019) in their study on the use of the case study method and its meaning in educational research.
In its application, the basic steps of the methodological procedure that are declared in the previously cited source were implemented. 1. Case study design; 2. Collection of information; 3. Application of methods to obtain relevant information, data and evidence; 4. Analysis of the information obtained; 5. Writing the report. For its implementation, the faculty of the master's academic training program "PHYSICAL EDUCATION, SPORTS AND RECREATION SCIENCES" was selected as a study unit, taking into account the following selection criteria:
accredited program of Excellence year 2014 and 2019;
great national and international demand;
faculty with experience in 19 editions, with attitudes towards innovation (pioneers in the institution in new forms of evaluation: digital portfolio technique);
include in the strategic objectives and internationalization strategy of the Faculty of Physical Culture the projection of the virtualization of the academic program.
The 10 full-time teachers made up the research population, taking into account the characterization of the faculty shown in the following table 1.
Table 1 - Composition of the faculty.
| Teachers | Assistant P. | P. Head | Dr. C. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full time | 4 | 9 | 13 |
| Part time | 5 | 1 | 6 |
| Collaborators | - | 2 | 2 |
| Total | 9 | 12 | 21 |
The intentional sample was made up of 10 teachers who represent 47% of the population, under the selection criteria of those responsible for the courses that make up the basic module, and the coordinators of the elective modules of this program. To measure the transfer of learning, the courses to be virtualized by the teachers of the study sample were selected.
Physical education and motor games
Prescription of physical exercise
Knowledge Management for Physical Culture
Applied Scientific Research
Inclusive Physical Education
Motor education
Biochemical and physiological responses of the body to physical exercise
Medical control and rehabilitation
The system of methods used at the empirical level as a complement to the case study was made up of the survey with the self-diagnosis questionnaire technique and the satisfaction survey, participatory observation, digital portfolio of evidence and the analysis of products of the activity for the data Collect; as well as mathematical procedures and descriptive statistics techniques for processing and analysis using the program (SPSS) version 22.0.
A survey was applied by interactive digital self-diagnosis questionnaire; as a digital instrument that collects, in addition to the weaknesses in the order of virtual distance pedagogical practice, the general professional data that allows the initial analysis of the teacher in terms of certifications, qualifications, previous professional improvement received; which has made it possible to adapt the relevance of the knowledge system to the postgraduate organizational forms that were designed. The conception uses as a driving axis the profile of the virtual teacher in academic master's programs, a research result published by the author (Hernández, 2022) that forms the basis of the self-diagnosis questionnaire.
The instrument prepared for the satisfaction survey was subjected to a procedure to calculate its reliability which, according to the criteria of Toro, Peña, Avendaño, Mejía and Bernal (2021), provides the degree to which an instrument produces consistent and coherent results. According to these authors, one of the most used reliability coefficients is Cronbach's Alpha; which propose: that values of 0.25 indicate low reliability; If the result is 0.50, the reliability is average or regular; however, if it exceeds 0.75 it is acceptable, and if it is greater than 0.90 it is redundant. Assuming these criteria, Cronbach's Alpha was calculated, which obtained a result of 0.927, which indicates a good degree of reliability of the instrument, since it is higher than 0.7 as shown in Table 2.
Table 2 - Reliability of the satisfaction survey instrument.
| Cronbach's alpha | No. Elements Items |
|---|---|
| 0.927 | 13 |
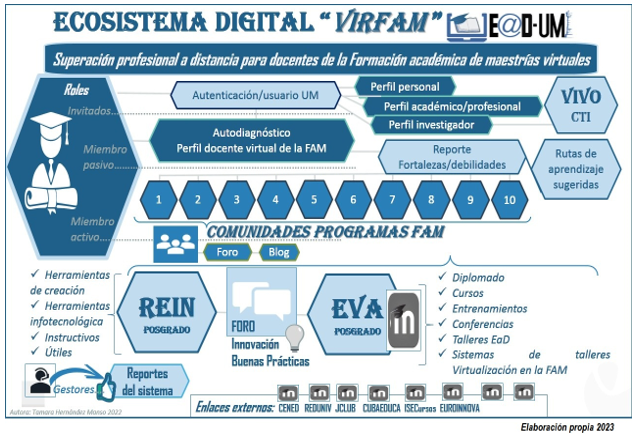
For the practical validation of the methodological conception, a digital ecosystem was designed and implemented as technological support that responds to the application of active participation and interaction methodologies with an open, flexible, online nature; which allowed the autonomous, individual and collective digital management of the faculty, constituted in communities of virtual collaborative practices as shown in figure 1.
Results
The modeling of the methodological conception expresses the application of active methodologies that are implemented both in the development of its curricular component and in the individual and collective autonomous management of improvement as a collective pedagogical process, in virtual collaborative communities of practice, which are exposed next.
In the participatory and interactive management component they are expressed through:
Problem-based learning as a general methodology (need for virtualization of the academic program) (implementation of the Distance Education Model in its Virtual Education variant) (improvement of the faculty for the task). (Scenario: Virtual FORUM as a discussion channel in virtual workshops to collect alerts or needs)
Learning based on thinking, collaborative and cooperative work techniques mediated by ICT and information and knowledge management. (Scenario: virtual FORUM as a discussion channel, virtual workshops, brainstorming, collective formation of the virtualization strategy of the academic program and the improvement of the faculty, analysis, consensus)
Project-based learning (shaping the design of each virtual course of the program in projects, from the instructional design, development of content and digital educational resources, didactic design of didactic activities, assembly and configuration in Moodle of the monitoring of learning management). (Scenario: virtual learning environment and repositories of digital educational resources)
Learning contract (commitment of each teacher to the various organizational forms of training designed for their improvement and the achievement of their objectives based on self-diagnosis based on the profile of the virtual teacher in academic master's programs). (Scenario: Digital portfolio for evidence)
For their part, in the design of the curricular component, they express active methodologies mediated by digital technologies, applied in problem-based learning, project-based learning, flipped learning, collaborative practices, and gamification strategies in the various organizational forms of the activities. designed for distance learning; as well as they are included as objects of study as teaching aids in their knowledge systems.
The following table 3 shows the organizational forms that were developed in the curricular component of the conception, and the number of participating teachers in the study sample who interacted as active members in each of them.
Table 3 - List of training activities developed from the methodological conception.
| Training activity | Participants |
|---|---|
| Distance course “The distance education model of Cuban higher education in the context of the University of Matanzas” | 5 |
| Distance course “Digital innovation in university teaching, Current Trends in Educational Technology” | 10 |
| Distance diploma: Course: Didactic treatment of content for distance education Training: Audiovisual digital treatment for the creation of learning objects such as NETWORK Training: Design, creation and management of learning in Moodle | 4 |
| 3 Conferences on the distance modality. (Capsule format of contents to download) | 10 |
| 7 virtual workshops “For quality and relevant distance education” | 5 |
| 5 virtual workshops “The virtualization of master's academic training programs” | 10 |
In the implementation to validate the conception, the measurement of the impact of professional improvement was carried out in three stages.
Initial: self-diagnostic questionnaire for entry and analysis of the product of the activity. Characterization of the initial organizational, pedagogical and technological state of the teacher for a virtual pedagogical practice
During: participatory observation and satisfaction surveys. Feedback on the effectiveness of the use of selected virtual scenarios, facilitating decision-making to improve their development and resolve barriers.
Final: exit self-diagnostic questionnaire and analysis of the activity product. Identify, record and analyze early results.
The research focused attention on the result indicator, understood for the purposes of this study as the short-term achievements that contribute to solving the needs and problems related to the teacher's distance professional development for the virtualization of the master's program; measurable through three fundamental parameters, which are the following:
Satisfaction: with the objective of obtaining information from the teacher during and at the end of a specific improvement action, such as criteria on the design of activities, the selection of content, methodologies, means and resources, understanding, relevance and applicability; as well as the monitoring and support of teaching and support staff. (Satisfaction survey)
Teacher suitability: with the objective of knowing the effectiveness of the use of the selected environments in the teacher's preparation for pedagogical practice in virtual education based on some essential conditions related to the individual being trained: interest in changing and knowing how to do and certifications and degrees. (Exit diagnostic questionnaire and digital portfolio of evidence)
Transfer of learning: when carrying out the evaluation on the application of what was learned, analyzes are carried out in the immediate environment of tangible results, and results in terms of quality of the virtualization process of the teaching provided and the intensive use of digital technologies. This level requires a period of time after the completion action is completed. (Participatory observation and Analysis of the activity product).
The information obtained has allowed us to carry out the impact analysis shown in table 4.
Table 4 - Impact measurement.
| Impact measurement: Satisfaction direction | |
|---|---|
| Initial and during | Final |
| A total of 17 satisfaction survey instruments were applied in correspondence with the diversity of organizational forms of the training activities developed. | The comprehensive analysis report carried out by the Moodle system shows a high degree of teacher satisfaction, with suggestions on adjusting the orientation and time of the interactive communication and social interaction activities in the virtual workshops. |
| The use of the social and academic interaction space began through Chat, FORUM and social networks (telegram and WhatsApp) in each of the organizational forms of the training activities developed. | The exercise of its use recorded in the diary, demonstrated the use of a single space on social networks and a centralized FORUM at the program level as the most effective way for the collective socialization of good practices, creating the Virtual+EducPosgrado WhatsApp group https/ /chat.whatsapp.com/FCdGB24Y2F6T17m4rxY |
| The use of the REIN space began with basic tools, and in the dynamics of its use, recorded in the diary, others were increased, based on emerging needs for individual and collective professional improvement. | To date, four folders have been registered that include the instructional and didactic materials as results of the methodological component of the scientific result of the research. The directory for NETWORK and Learning Objects is implemented in the institutional REIN, beginning the population of the folder destined for this master's program, which to date has 26 Shared Resources under Creative Commons License. rein.umcc.cu |
| Impact measurement: direction Teacher suitability | |
| Qualified teachers (who have achieved certification in some EaD improvement) 0% | Qualified teachers (who have achieved certification in mandatory workshops) 100% |
| Teachers certified in some improvement over EaD 0% | Certified teachers in: Diploma 40% Distance course “The distance education model of Cuban higher education in the context of the University of Matanzas” 50% Distance course “Digital innovation in university teaching, Current Trends in Educational Technology” 100% |
| Impact measurement: direction Learning transfer | |
| In the initial phase, there were 5 virtual Moodle courses, where the interactive learning platform was used for the distribution of digitized content with traditional face-to-face and meeting teaching methodology. | The design of eight postgraduate programs based on COPEP guidelines is available for approval in the distance modality mediated by ICT. The technical opinion and approval of the institutional Distance Education group of the 8 postgraduate programs is available based on the policies and procedures for their approval in the distance modality mediated by ICT. The instructional design for distance learning graduate courses is available for the production of the 8 graduate programs. In the 8 postgraduate courses, digital content is available in hypertextual resources under the micro-content technique based on the structure approved by the program and the institutional policies for the distance modality mediated by ICT in postgraduate education: Schedule of training activities Distance course dynamics Teacher profile Study guides Basic material for micro-contents Supplementary materials The RED and OA are produced from the instructional design of 8 postgraduate courses in coordination between teachers and DRPA, for the REIN and Moodle The contents, NETWORK and learning situations are updated in response to the professional improvement received in 10 postgraduate courses in coordination between teachers and DRPA at the EVA |
In this order of idea, other evidence of the transformation of improvement in distance modality was collected in the diary formed through the case study that shows favorable results achieved as a virtual community of collaborative practices manifested in:
development of the short, medium and long-range master's program virtualization strategy for its virtual distance offering;
the inclusion of the virtualization point of the program in the agenda of the master's faculty based on the monitoring of the implementation of the distance education model of Cuban higher education;
the inclusion of quality management of its virtual courses systematically in the work system of the Vice Dean of Research and Postgraduate Studies;
the design of the website as the official site of the master's degree;
the design and implementation of the social and academic network on Facebook.
inclusion in the sectoral research project "Management of Physical Culture processes" the sub-task "Teacher preparation for teaching sciences applied to Physical Culture from new learning scenarios with ICT" course 21- 22, which in turn has generated the following results:
design and implementation of five virtual workshops based on the virtualization of academic master's programs;
scientific production related to these results in events and publications at the IX International Workshop "Virtualization in Higher Education". III International Scientific Conference University of Cienfuegos, 2021; XII International Congress Higher Education IX International Workshop "Virtualization in Higher Education", University 2022; Monographs University of Matanzas 2022.
Discussion
It is confirmed in the study carried out, whose relevance is justified by the need expressed in the strategic objectives of the Ministry of Higher Education in Cuba aimed at virtualizing academic training in postgraduate education, that teacher preparation in scenarios mediated by digital technologies takes on another connotation; aspect that is addressed in the policy of perfecting the Cuban distance education model based on the profound transformations that have been assumed in the continuous training of professionals to face contemporary social demands.
Assuming in this study the regularities of distance education mediated by digital technologies, is based on professional improvement with advantages in terms of flexibility of times, spaces, rhythms, itineraries, moments and technological devices, for the self-management of learning. The psychopedagogical characteristics of the adult identified as the majority beneficiary in this modality are concluded (Ruiz Y Pichs, 2020) as addressed by these authors in their research on virtual education as a trend in the development of distance education in Cuba and in the world.
Modality that, in addition to demonstrating the usefulness of new knowledge, promotes the development of technological and digital skills in learning to learn; in such a way that the learning strategies acquired with the use of these technologies facilitate being able to function in other scenarios, where it is vital to start from a heterogeneous variety of experiences and prior knowledge of the teacher, through independent and autonomous active participation, promoting collaborative practices, even from the selection of content, ways and ways of obtaining improvement.
The determination of achievement indicators to measure impact on training and professional improvement is based on the scientific literature consulted in this regard (Mestre, Quiroz y Zambrano, 2015) and (Aveiga, Rodríguez Y Segovia, 2018) based on the selection between the three prevailing indicators; effect, result and product. Selecting impact parameters to measure results.
The methodological conception that is presented for the autonomous professional improvement of faculty formed in communities of virtual collaborative practices, together with the digital ecosystem designed as technological support; as well as the results obtained in the measurement of its impact, allow us to reaffirm that the study responds to the demands for improvement and postgraduate studies of professionals, in correspondence with the sustainable development of the Cuban nation as content addressed from objective No. 4 of the Strategic Project 2021-2030, in the POSCOVID-19 Higher Education Program, being one of those that contributes the most to strengthening the economy to face a prolonged crisis scenario as expressed by Díaz-Canel, Alarcón & Saborido (2020) and Díaz-Canel y Núñez (2020), as well as included in the National Economic and Social Development Plan until 2030.
These scenarios have demonstrated in the educational field the viability of virtual education for the continuity of training processes in higher education, protected by Resolutions No.49/20 and No.51/20 of the MES. The latter aims to promote scientific methodological work in order to perfect the programs of the different forms of improvement, using blended and distance study modalities, and develop professional improvement actions with a minimum of presence, promoting learning from the workplace with the maximum possible use of networking and distance education.
"In line with this reality, improvement is favored, in part, by the rapid insertion of ICT in activities and postgraduate programs as a sign that technological development makes it possible for thousands of people from different geographical areas to receive improvement in their area of professional occupation. Therefore, the massification of higher education is guaranteed and teaching reaches where face-to-face education cannot. (Ruiz Y Luzbet, 2019. p.7)
What is supported by these authors in their article "Virtual education: A viable option for the development of postgraduate programs." Conceiving distance and virtual education in professional improvement, beyond the theoretical approach that accompanies it, generates unprecedented challenges to project it into practice. It implies recognizing the contributions of subject-centered pedagogy as the center of training from active methodologies, the development of the pedagogical-creative thinking exercise of the teacher and, in particular, the paradigmatic rupture of the transfer of knowledge towards its management. from collaborative practices, as a prospective vision of all educational institutions that promote equitable and supportive social transformations in the course of this 21st century.
In this direction, the authors share the criteria of Labrador and Andreu (2008) in understanding active methodologies as the methods, techniques and strategies that the teacher uses to convert the teaching process into activities that encourage the active and leading participation of the student. These same authors frame its application in postgraduate education, from social demands and work environments with the need to train professionals with skills such as autonomy, development of work in small multidisciplinary teams, participatory attitude, communication and cooperation skills, problem solving, creativity, among others.
The assumptions assumed in this study support the viability of distance professional improvement mediated by technologies based on their management from virtual communities of collaborative practices, which share common objectives or problems as guides in the construction of knowledge, experiences, innovations. educational solutions for their solution, and that in its socialization and generalization contributes to forming good pedagogical practices as a collective seal in the virtualization process of each academic master's program.
The validation of the methodological conception, the case study presented and the results presented when measuring the impact of distance professional development, have allowed us to ratify its significance from a guiding function towards the transformation of traditional professional development of the teacher to training scenarios at a distance. distance mediated by technologies, to the professional renewal of the teacher for the viability of the virtualization of academic master's programs, and towards the design of digital transformation routes for the management of human talent from digital ecosystems in university institutions.
The results validated in the study are considered novel, as they present a conception whose elements of methodological value are based on the application of active methodologies mediated by ICT in a group dynamic, which promote collaborative work beyond its curricular component, which contributes to the autonomy and prominence of the master's faculty for the digital self-management of professional improvement in accordance with their needs from virtual communities of practice.
Referencias bibliográficas
Aveiga, V. I., Rodríguez, L. A., y Segovia, S. R. (2018). Superación Profesional y Formación Académica: ¿conceptos iguales o diferentes? Didasc@lia: Didáctica y Educación. 9(3), 205-216. https://revistas.ult.edu.cu/index.php/didascalia/article/view/783/780 [ Links ]
Álvarez, M., Fernández N., García, P., Grandoli, M. E. Y Pérez, C. (2020). La docencia en el nivel de posgrado en el contexto de virtualización de emergencia. Aprendizajes y desafíos para el futuro en la experiencia de la Universidad Nacional Tres de Febrero, Revista Innovaciones Educativas, 22(1), 171-187. ISSN 2215-4132. http://dx.doi.org/10.22458/ie.v22iespecial.3153 [ Links ]
Cárdenas, O. A. (2021). Diseño y construcción de un ecosistema digital: estrategias para articular la información y la formación policial. Revista Logos Ciencia Y Tecnología, 13(3), 71-58. https://doi.org/10.22335/rlct.v13i3.1417 [ Links ]
Díaz-Canel, M. M. y Núñez, J. (2020). Gestión gubernamental y ciencia cubana en el enfrentamiento a la COVID-19. Revista Anales de la Academia de Ciencias de Cuba. 10(2). http//www.revistaccuba.sld.cu/index.php/revacc/article/view/881 [ Links ]
Díaz-Canel, M., Alarcón, R. y Saborido, J. (2020). Potencial humano, innovación y desarrollo en la planificación estratégica de la educación superior cubana 2012-2020. Revista Cubana de Educación Superior, 39(3). http://www.rces.uh.cu/index.php/RCES/article/view/383/422 [ Links ]
Hernández, J. M., Peñate, A. G. y, Hernández, T. (2023). La preparación del docente para la formación en interpretación del patrimonio: virtualización y metodologías activas. Atenas, (61), 1-12 [ Links ]
Hernández, T. (2022). Perfil ocupacional y desempeño docente en la formación académica: maestrías virtuales. Revista REEA. 11(3), 1-15. Centro Latinoamericano de Estudios en Epistemología Pedagógica. http://www.eumed.net/es/revistas/revista-electronica-entrevista-academica [ Links ]
Hernández, T. y Álvarez, Y. (2022). La transcomplejidad del perfil docente de la formación académica: maestrías virtuales. Revista de Ciencias Humanas. 23(3). https://revistas.fw.uri.br/index.php/revistadech/article/view/4495 [ Links ]
Hernández, T. y Pentón, B.H. (2019). La Educación a distancia en el posgrado, experiencias innovadoras de aprendizaje continuo y permanente. Libro III Simposio Internacional Ciencias e Innovación Tecnológica. Vol. XI, Capítulo Educación a Distancia. Editorial Opuntia Brava. https://opuntiabrava.ult.edu.cu [ Links ]
Hernández, Y., Ruiz, L., Sepúlveda, J. C. (2022). Evaluación de la implementación del Modelo de Educación a Distancia de la Educación Superior Cubana.Referencia Pedagógica,10(2),79-93. http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S2308-30422022000200079&lng=es&tlng=es [ Links ]
Mestre, U., Quiroz, L.S, y Zambrano, J.M. (2016). Criterios para la evaluación del impacto académico de programas de maestría en la modalidad semipresencial. Didasc@lia: Didáctica y Educación . 7(5) (Monográfico Especial). ISSN 2224-2643. https://revistas.ult.edu.cu/index.php/didascalia/article/view/538 [ Links ]
Pineda, E. y Orozco, P. (2017). Ecosistemas de aprendizaje con gestión de TIC. Una estrategia de formación desde la pedagogía praxeológica.Revista Docencia Universitaria,17(4), 71-95. [ Links ]
Ruiz, L. y Luzbet, F. (2019). La educación virtual: Una opción viable para el desarrollo de programas de posgrado. En Ciencia e Innovación Tecnológica. Vol. XI. Editorial Académica Universitaria (Edacun) en coedición con la Revista Opuntia Brava. https://biblat.unam.mx/es/revista/opuntia-brava/2 [ Links ]
Soto, E. y Escribano, E. (2019). El método estudio de caso y su significado en la investigación educativa. En Procesos formativos en la investigación educativa. Diálogos, reflexiones, convergencias y divergencias (pp. 203-221). Chihuahua, México: Red de Investigadores Educativos Chihuahua. ISBN: 978-607-98139-1-8 https://rediech.org/inicio/images/k2/libro-2019-arzola-11.pdf [ Links ]
Toro, R., Peña, M., Avendaño, B. L., Mejía, S. y Bernal, A. (2022). Análisis Empírico del Coeficiente Alfa de Cronbach según Opciones de Respuesta, Muestra y Observaciones Atípicas. Revista Iberoamericana de Diagnóstico y Evaluación e Avaliação Psicológica. RIDEP, 63(2), 17-30. ISSN: 1135-3848. https://www.aidep.org/sites/default/files/2022-04/RIDEP63-Art2.pdf [ Links ]
Received: February 24, 2023; Accepted: August 14, 2023











 texto em
texto em