Meu SciELO
Serviços Personalizados
Artigo
Indicadores
-
 Citado por SciELO
Citado por SciELO
Links relacionados
-
 Similares em
SciELO
Similares em
SciELO
Compartilhar
Podium. Revista de Ciencia y Tecnología en la Cultura Física
versão On-line ISSN 1996-2452
Rev Podium vol.19 no.1 Pinar del Río jan.-abr. 2024 Epub 02-Abr-2024
Original article
Life Task in Physical Education from Sports for All
1Universidad Central "Marta Abreu" de Las Villas. Facultad de Cultura Física. Villa Clara. Cuba.
2Escuela "Rolando Morales Sanabria Cifuentes". Villa Clara. Cuba
The growth and development of human communities have given rise to the emergence of so-called environmental problems that influence natural resources and human health. In this presentation, it is reflected the reality found in the work with the Life Task from the second cycle of the "Rolando Morales Sanabria" primary school in the Cifuentes municipality, a vital stage in the training of new generations for the conservation of the environment, the maintenance of ethical and moral values of a social project with a humanist foundation. Taking into account these concepts, the objective was to characterize the work with the Life Task from Sports for All as part of Physical Education, in the context described above. This work was carried out with the help of methods and techniques such as document review, observation, survey and interview. The results reveal insufficiencies in this work, from the lack of consultation of official documents, clarifications and regulations, through poor intentionality, to the lack of internalization and carrying out activities in this sense. As conclusions, the foundations for the development of work with the Life Task in the selected context were determined, the current state was characterized, where the casual and irrational use of sports spaces, poor use of the potential of the context, little intention and limited knowledge of the Life Task, as well as the failure to take advantage of the will, desire and disposition of the students to carry out physical-recreational activities related to it stood out.
Key words: Sports for All; Physical Education and Life Task.
INTRODUCTION
The environmental problems of the contemporary world are, for the most part, caused by the direct and indirect action of anthropological factors. This is how the role of man has acquired, especially in recent decades, an essential function in terms of impacts on the environment, which currently constitutes, in many ways, a real concern for humanity.
Such a situation requires a change in man's attitude, so knowledge and convictions in this sense must be translated into actions that favor his environment, from strictly local levels to those of globalized significance. A project of this nature is directly and objectively related to the system of environmental values demanded by contemporary society, which is why no efforts must be spared in this important direction.
This situation, increasingly serious, is conditioned by the irrational attitude of man with his environment, so it is necessary to modify behaviors that have prevailed in historical development, and form new patterns of behavior based on the conception of sustainable development, by be conceived this:
"as a process of creating the material, cultural and spiritual conditions that promote the elevation of the quality of life of society, with a character of equity and sustained social justice and based on a harmonious relationship between natural and social processes, having as its objective both current and future generations." (CITMA, 2016/2020, p.5)
"Climate change is recognized as one of the most complex global environmental problems that presents the greatest challenges to society, the scientific and technical community, and political authorities" (Hernández et al. 2022).
To achieve the difficult goal of working based on a true environmental understanding, for the sake of sustainable development, the Cuban school can and must become the essential center for its promotion. This important endeavor needs to be conceived and carried out as a true component of the comprehensive education of all citizens, in order to promote the orientation of economic, social and cultural processes towards a true culture based on sustainable development.
From this vision, Cuba has prioritized Environmental Education as a state objective. In 2007, scientific-technological research was prioritized through the macroproject on coastal hazards and vulnerability for the years 2050-2100, directed by the Ministry of Science, Technology and Environment and with the participation of 16 institutions from five agencies of the Central State Administration. On February 25, 2011, the Council of Ministers approved directives prepared from the scientific results and recommendations of this Macroproject. (Castro, 2018). (p.2)
In 2015, under the coordination of the Ministry of Science, Technology and Environment, a process began to update the documents already approved by the Consejo de ministros (2022) to confront climate change. The country saw the need to create an alternative to solve this problem. The Life Task emerges as a State Plan to Confront Climate Change, approved by the Council of Ministers on April 25, 2017, the Physical Recreation project, as part of the monitoring of the National Institute of Sports Physical Education and Recreation (Inder) Management System (2023) where the objectives, goals and actions are set in the implementation of the Environmental Strategy, Resolution 134/22.
In this sense, results are obtained from scientific activity such as Castillo (2021) which states the possibilities that Physical Education offers to promote responsible behavior in terms of environmental protection; Posso et al. (2022) that present a student mitigation strategy on the causes and effects of climate change through Physical Education, taking into account the sustainable development objectives of the environmental protection pillar and its goals; research consulted on the Life Task , Valladares-Fuente, (2022) refers in a scientific article: the proposal of environmental education indicators for sports professionals and Rodríguez et al. (2022) carried out a trend study of environmental education in the integration of the sociocultural context in primary education.
Although issues related to the environment are addressed in primary school, it is not always possible to achieve a clear understanding of the responsibilities that the school institution has in this regard, so efficient work in this direction does not constitute a practice in the daily school performance of teaching.
As can be seen in the comments and guidelines set out above, work in this regard in primary education is of great importance as part of the comprehensive training of new generations and raising awareness of the phenomenon of climate change. These are aspects that from Physical Education, specifically Sport for All, the possibilities for the development of this activity are not fully used, the difference being clearly marked between what is expected to be done and what is done.
As previously stated, the present research reveals the problematic situation referred to the insufficiencies in the work of the Life Task from Sports for All that is carried out in the second cycle of the "Rolando Morales Sanabria" primary school, in the municipality of Cifuentes; which leads to declaring the following scientific problem: what characterizes the educational work of Physical Education for the Life Task from Sports for All in the second cycle of the "Rolando Morales Sanabria" primary school in the Cifuentes municipality?
From the point of view of science, it is important to raise awareness and delve into the theoretical concepts that support the scientific rigor of the investigative process, which in this case is the educational work of Physical Education. In addition, it is specified for the Life Task from Sports for All and is contextualized in the second cycle of the "Rolando Morales Sanabria" primary school in the Cifuentes municipality.
Finally, the study aims, as a goal or objective, to characterize the educational work in Physical Education for the Life Task from Sports for All in the second cycle of the "Rolando Morales Sanabria" primary school, in the municipality of Cifuentes.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
In relation to the investigative methods to be used, there are the theoretical and empirical methods of science, highlighting among the theoretical methods: the analytical-synthetic, the inductive-deductive, from the transition from the abstract to the concrete and the historical-logical.
Likewise, when delving into the problem posed and to achieve the proposed objectives, the application of the following empirical methods is required: document analysis, interview, survey and observation.
The review of documents focused on obtaining information in relation to the guidelines related to the Life Task in Physical Education, for which the following documents were taken into account.
Brochure of the State Plan to confront Climate Change of the Republic of Cuba (Task Life).
Life Task of the Provincial Sports Directorate in Villa Clara 2020.
Inder National Program 2020 (Management by objectives).
Resolution No, 58/2017.
Methodological Precisions of Physical Education and Sports for All. 2020-2021 academic year.
Actions for the implementation of the State Plan to confront climate change (Life Task) in the Municipal Directorate of Education, Cifuentes de Villa Clara. 2020-2021 academic year.
Brochure of the Ministry of Higher Education. Task Life: for and from Cuba, preserving humanity. (2018)
The analysis categories taken into account were:
Conceptions about the Task of Life.
Treatment and guidelines for the Life Task in Physical Education.
Particularities of the treatment of the Life in Sports for All Task.
Attention to educational work and the Life Task from physical-recreational activities.
Place given to the Life Task in the educational work of working with Sport for All of Physical Education.
To what extent the guidelines satisfy the needs of working with the Life Task from Sports for All as part of the educational work of Physical Education.
The interview carried out to find out the criteria and opinions of teachers and directors about the educational work with the Life Task from Sports for All that takes place in the current conditions of the school; the survey, to verify the level of knowledge of the students regarding the Life Task and its actions in the educational institution in general and particularly in Sports for All and the observation that was carried out on 36 activities, at a rate of four activities per week for nine weeks and based on a guide made for this purpose. In all cases, depending on the dimensions and indicators resulting from the operationalization of the variables, as expressed below (Table 1).
Table 1. - Dimensions and indicators
| Dimension | Indicator |
| Participation | Attendance |
| Disposition for the fulfillment of activities related to the Life Task. | |
| Involvement in the preparation, development and control of activities. | |
| Satisfaction of physical-recreational motives | Preferred times for carrying out physical-recreational activities. |
| The design of the Sports for All activities makes explicit the relationship between the physical-sports-recreational needs with the Life Task. | |
| Preferred times for carrying out physical-recreational activities. | |
| Level of knowledge of the Life Task that allow its relationship with the practice of Physical Recreation | Identification of the Life Task. Relationship Task Life and Physical Recreation. Identification of actions of the Life Task in physical-recreational activities. Recognition of spaces or moments that work on the Life Task Potentials of the Life Task to conserve natural conditions. |
| The conditions of the context are taken into account to enhance the work with the Life Task from Sports for All in Physical Recreation. | |
| The teacher's intention is appreciated for starting the Life Task from Sports for All as a component of Physical Recreation. | |
| Use, enjoyment and conservation of the environment. | |
| Sustainable transformations of the environment | Identification of areas for Physical Recreation. |
| Use, enjoyment and conservation of the environment. | |
| Man-nature relationship for sustainable physical activity | Quality of interpersonal relationships. |
| Attitudes consistent with the Life Task in carrying out physical-recreational activities | |
| Integration of community factors. |
In addition, statistical-mathematical methods are used with descriptive statistics (frequency tables) with the empirical distribution of frequencies.
The population included the directors (2), teachers (3) and second cycle students (85) of the "Rolando Morales Sanabria" primary school, in the municipality of Cifuentes, during the 2021 academic year.
The research acquires a practical methodological value, focused on the work on environmental problems and contradictions, declared and oriented from the Life Task that turn out to be generators of a developing teaching-educational process, which transcends the teaching work, to encompass the extra-teaching and the extracurricular; it can also be used as an example of possible actions to rigorously address different themes of the Life Task during the teaching-educational process, which is why it constitutes important material for the performance of teachers with the purpose of achieving a higher level of scientific and systematicity in the performance of the comprehensive training of students.
In relation to the investigative methods to be used, there are the theoretical and empirical methods of science.
Regarding the study aimed at offering all the theoretical support of the research, including the postulates of the theory of knowledge, the historicity of the research problem and the conceptual basis that bases the work developed, the following theoretical methods stand out:
Analytical-synthetic method: to penetrate the essence of the phenomenon under study and systematize the information necessary for the development of the methodological alternative.
Inductive-deductive method: for the study of particular elements in the elaboration of general conclusions and vice versa, during the process of structuring and verifying the methodological alternative.
Method of transition from the abstract to the concrete: starting from the foundations of the theoretical principles of the educational work of Physical Education that support the work to be developed with the Life Task from Sport for All, arrive at the precise definition of the actions to take.
Historical-logical method: to explain the historical evolution of the educational work of Physical Education that supports the work to be developed with the Life Task from Sports for All and its foundations.
Based on the review of all official provisions that regulate work in teaching and taking into account the demands of the diagnostic-research work in this work, the following empirical methods are required:
The review of documents, to achieve an adequate understanding of the guidelines and provisions of the Ministry of Education at its different levels in general and the particularity of the primary level that corresponds to the field of research development, as well as those of the Ministry of Science, Technology and Environment, in relation to programs, resolutions and laws in force in the country.
Scientific observation: to verify in practice the performance of Physical Education teachers in the work of educational work with the Life Task from Sports for All in the second cycle of the "Rolando Morales Sanabria" primary school, in the municipality of Cifuentes.
In addition, statistical-mathematical methods are used with descriptive statistics (frequency tables) with the empirical distribution of frequencies.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The review of documents showed that the conceptions of the Life Task appear homogeneously in all the documents and with an adequate derivation for each of these and the sectors they deal with. Furthermore, in all cases it is conceptually recognized the need for work in this sense and its coherence in the integration of community factors and the recognition of the teaching institution as the cultural center of the community and axis of comprehensive training is conceptually recognized of the individual, consequently, with the social project that is built.
The role of transversality of work is recognized, in this sense, within the educational teaching process and its importance in the use of different spaces and scenarios for the sake of the much-needed comprehensive training. Now, the use of Sport for All, nor the characteristics of Physical Education, nor how to proceed in these cases are made explicit in any case, that is, there is a general indication of the work aimed at the internalization and development of this activity, but the guidelines do not specify in this sense.
Regarding scientific observation, the results are summarized as follows:
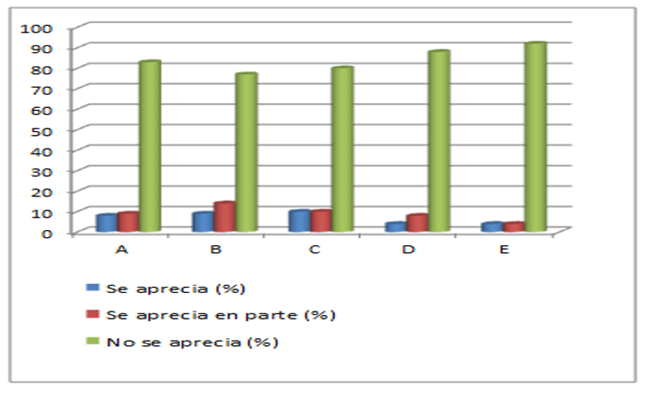
Taking into account the conditions of the context to enhance the work with the Life Task from Sport for All in the educational work of Physical Education is seen in only 6 activities and is evaluated poorly by 16 %.
Regarding the teacher's intention to carry out actions of the Life Task from Sports for All as a component of the educational work of Physical Education, only in five activities for 13 %, which is why it is also evaluated poorly.
The design of the Sports for All activities makes explicit the relationship between the physical-sports-recreational needs and the educational work with the Life Task only in four activities evaluated poorly for 11 %.
The mastery of Physical Education teachers over the Life Task is appreciated through their performance in Sports for All in 16 activities, for which they are evaluated as regular for 44%.
Modes of action consistent with the internalization of the Life Task by the participants in Sport for All are appreciated, only 16 % evaluated poorly in six activities.
Legend
A - Use of contextual conditions to enhance work with the Life Task from Sports for All.
B - Intentionality of the teacher in starting the Life Task from Sports for All.
C - Sports Activities for All, which makes explicit the relationship between the physical-sports-recreational needs and the educational work with the Life Task.
D - Samples, from the teachers, through their performance in Sport for All, of the mastery of the Life Task.
E - Modes of action consistent with the internalization of the Life Task by the participants in Sport for All.
This information can be graphed for a better understanding and allows an assessment of the result obtained in the observations of the activities, which led to the confirmation that the performance of the Life Task in the activities of Sport for All presents serious difficulties, exemplified in Figure 1.
Regarding the results of the interview, it was evident that:
One of the five teachers interviewed (20% of them), has the criterion that he has sufficient knowledge about the environment and the Life Task, to be able to adequately face his teaching work in this direction, the remaining four (80%), considers that his knowledge on the matter turns out to be limited.
Among the main ways to obtain information from teachers about the work of the Life Task in a general sense and in particular for Physical Education, an aspect corresponding to the second question of the interview, the following were indicated, in order of priority: self-improvement, radio and television information. Only one of the teachers (20%) considered the development of postgraduate courses and the methodological preparation carried out in schools to be important, issues that are considered very significant and of high value to undertake consistent work in the field. of environmental education.
In relation to the results corresponding to the third aspect discussed in the interview, all of the teachers consulted (100%) consider that they incorporate Life Task into the activities of Sport for All only on some occasions and without systematicity and rigor. that this type of activity requires.
The ways in which teachers develop actions directed towards the students' Life Task are, fundamentally, excursions, video debates, among others, being very limited on the part of the teachers.
Regarding the limitations that teachers and directors face in developing these actions, 100% of those interviewed allude to the scarcity of teaching resources, as well as the little time available for it. Therefore, teachers and directors propose, in order to effectively develop appropriate actions in schools based on efficient work on the Life Task from Sport for All, the following recommendations:
Develop actions in favor of the creation of teaching aids of all types, which facilitate the objectification of activities where natural teaching aids and nature itself prevail in the different instructive and educational tasks to be carried out.
Use teaching schedules so that a greater number of environmental educational activities can be planned, through work that includes both teaching and extra-teaching and extracurricular activities, in permanent link with community factors. This is done to strengthen capacities in the territories, as well as the formation of a training strategy on issues of risk, vulnerability and environmental danger, adaptation and mitigation of climate change, from a community, participatory, inclusive, gender perspective, and differentiated by vulnerable groups.
Increase the topics of environmental content in the different methodological activities at all levels, offering this type of work all the priority that it requires; so that education, training, awareness and citizen participation are strengthened, generating a change in behavior in the face of climate change.
Regarding the results of the survey, the following procedure is described:
Before proceeding with the application of the survey, it was spoken with the students about some specific situations of the Life Task, so that the topic, the importance and the knowledge of acting accordingly were highlighted. To this end, aspects of the environment, biodiversity, climate change, the meaning of animal protection, problems related to vectors that are responsible for the transmission of diseases and the importance of environmental conservation were addressed; all of this linked to the quality of life of the population.
The survey applied to the students related the dimension, level of knowledge of the Life Task that allows its relationship with the practice of Physical Recreation and the indicators determined in this regard; where the results shown below were manifested (Table 2).
Table 2. - Encuesta
| Indicators collected in the survey | Number of Students who respond positively | % | Number of Students who respond negatively | % | ||
| Knowledge about Life Task | 18 | 21 | 67 | 78 | ||
| Relationship Task Life and Physical Recreation | 31 | 36 | 54 | 63 | ||
| Identification of actions of the Life Task in physical-recreational activities | 12 | 14 | 73 | 85 | ||
| Recognition of spaces or moments that work on the Life Task | Morning session | Classes | Physical education | - | ||
| 51 | 60% | 23 | 27% | 11 | 12% | |
| Acceptance of carrying out physical-recreational activities with contents of the Life Task | 85 | 100 | - | - | ||
| Potentials of the Life Task to conserve natural conditions | 26 | 31 | 59 | 69 | ||
The interpretation of the numerical results shown in the summary of the indicators collected in the survey, express that the knowledge that the students have of the Life Task is insufficient, that there are few physical-recreational activities that they carry out in relation to the Life Task. It is also clear that Physical Education and its system of influences is not a space used to learn about or work on environmental content that is related to the Life Task, despite the fact that there is total acceptance for the practice of physical-recreational activities with content of the Life Task; likewise, deficiencies are evident in the knowledge of the potential of the Life Task to preserve natural conditions.
Based on the results obtained in the application of the research instruments, it was characterized the existing situation regarding the work of the Life Task conceived and carried out in fact in the school with the population selected for the performance of the scientific work. In general sense, in the observed activities, there is no systematicity in the treatment of the Life Task from Sports for All in the educational work of Physical Education, also showing insufficient knowledge that the students have of the Life Task and of its potential to conserve natural conditions.
The main problems that currently exist with the Life Task and Sports for All, according to the criteria of those interviewed, are related to the poor development of an integrative conception in this sense, the lack of adequate overcoming of the teachers and the provision of documents that offer precise methodological guidelines in this regard.
When assessing the results obtained in the observations of the activities, and those obtained through the rest of the research instruments applied, it can be confirmed that the performance of the Life Task in the classrooms of the school under study still presents serious difficulties. There is no doubt that the preparation and adequate self-preparation of teachers to carry out this type of work in a systematic and thorough manner presents insufficiencies.
The results of the work presented manage to surpass the visions and achievements of previous research such as those mentioned by Castillo (2021) and Posso et al. (2022), Valladares-Fuente, (2022) and Rodríguez et al. (2022); since it works in the case of primary education and it is possible to characterize the existing situation with respect to the relationship of the Life Task with Physical Education from the actions of Sport for All, valuing it as vital in the development of new generations and having as a basis the perspective that a better world is possible.
These results highlight the insufficiencies in the entire process that transcends the actions of the students and expose gaps in the teachers' knowledge in both theoretical and methodological aspects. As part of the benefits of this work, it is the fact that it is based on the made characterization; recommendations are offered to direct the work that will improve the situation detected, as well as the dimensions and indicators on which the process of diagnosing the situation for the selected context must be based.
Finally, based on the theoretical elements analyzed and on the characterization of the current situation in the work of the Life Task from Sports for All as part of the educational work of Physical Education in the selected context, the characteristics were determined. where the scope of the solution proposal should be directed. This process is pertinently developed as part of the modes of action that the teacher's work aspires to have based on three spheres of their professional performance, the cognitive, the affective and the attitudinal.
From the cognitive:
Typification of environmental problems in local, national and international contexts.
Influence of the ways that allow solutions and prevention to environmental problems.
Determination of positive and negative influences on the environment.
Mastery of legal regulations linked to environmental problems.
Characterization of the relationship between the environment and the quality of life of human beings.
From the affective:
Support of feelings that demonstrate love and respect for nature and its resources.
Defense of convictions that demonstrate commitment to current and future generations in the conservation of the environmental sphere.
Expression of feelings and positions of disagreement with irresponsible behavior towards the environment.
Disposition to environmental protection.
Manifestation of feelings of belonging to the environment.
Internalization of preferential feelings for the adoption of healthy lifestyles.
From the attitude:
Disciplined participation in activities related to the environment.
Collaboration to disseminate the best experiences and knowledge in favor of environmental conservation.
Adopt critical stances towards people who display irresponsible environmental behavior.
Assume behavior and acceptance of norms at school and in the community aimed at environmental conservation.
Acceptance of abstinent lifestyles in favor of individual and collective health.
CONCLUSIONS
Based on the governing documents such as the Brochure of the State Plan to confront Climate Change of the Republic of Cuba (Task Life) and the Actions for the implementation of the State Plan to confront climate change (Task Life) in the Municipal Directorate of Education in Cifuentes municipality of Villa Clara province, 2020-2021, the theoretical foundations of the educational work in Physical Education were determined for the work to be developed with the Life Task from Sports for All in the "Rolando Morales Sanabria" primary school, in the municipality of Cifuentes, where the conceptions of climate change, ecosystem, sustainability, Physical Recreation, recreational programming, Sports for All and Life Task.
The current situation of the work of the Life Task from Sports for All in the "Rolando Morales Sanabria" primary school, in the municipality of Cifuentes, is characterized by insufficiencies in its development, manifested in the instability and lack of systematicity in the use of spaces and potentialities of the context, little intentional work in relation to the physical-recreational needs or motives of the participants, limitations in the knowledge of the Life Task and its possibilities of transversality in the educational teaching process on the part of the teachers as the main generators of the process and the failure to take advantage of the will, desire and disposition of the students to carry out physical-recreational activities related to the Life Task.
REFERENCIAS BIBLIOGRÁFICAS
Castillo-Escalona, J. (2021). La Cultura Ambiental como núcleo de la Estrategia Educativa de la disciplina Educación Física. Ciencia Y Deporte, 6(3), 15-31. https://doi.org/10.34982/2223.1773.2021.V6.No3.002. [ Links ]
CITMA. Ministerio de Ciencia Tecnología y Medio Ambiente. (2020). Programa Nacional de Educación Ambiental para el Desarrollo Sostenible (2016/2020). CITMA: Cuba. [ Links ]
Consejo de ministros. (2022). Proyecto de Recreación y uso del Tiempo Libre 2022-2030. Ediciones Políticas. La Habana. https://www.moa.gob.cu/es/actualidad/noticias/592-proyecto-recreacion-y-uso-del-tiempo-libre-para-este-verano-2022-en-moa [ Links ]
Hernández Víctor, Y., Almeida Maldonado, E., & Brown Manrique, O. (2022). Indicadores para la evaluación del cambio climático en el municipio de Venezuela en Ciego de Ávila, Cuba. Universidad Y Sociedad, 14(S3), 699-712. https://rus.ucf.edu.cu/index.php/rus/article/view/3004 [ Links ]
Instituto Nacional de Deporte, Educación Física y Recreación. (2019). Plan para el Enfrentamiento al Cambio Climático en el Deporte (2019-2020). INDER. Villa Clara. [ Links ]
Posso Pacheco, R., Lara Chala, L., López Arias, S., & Garces Quilambaqui, G. (2022). Objetivo de desarrollo sostenible acción por el clima: un aporte desde la Educación Física. Ciencia Y Deporte, 7(2), 34 - 45. https://doi.org/10.34982/2223.1773.2022.V7.No2.003. [ Links ]
Rodríguez León, Y. I., Lao Santos, L., Torres Moreno, V. E., Céspedes Gamboa, L. R., & Tamayo Maceo, A. L. (2022). Estudio tendencial de la educación ambiental en la integración del contexto sociocultural en la educación primaria. Universidad Y Sociedad, 14(3), 751-761. https://rus.ucf.edu.cu/index.php/rus/article/view/2923 [ Links ]
Valladares-Fuente, F., & Posso Pacheco, R. (2022). Indicadores de la educación ambiental para el profesional del deporte. Ciencia Y Deporte, 7(1), 45 - 59. https://doi.org/10.34982/2223.1773.2022.V7.No1.004 [ Links ]
Received: October 03, 2023; Accepted: December 15, 2023











 texto em
texto em