Mi SciELO
Servicios Personalizados
Articulo
Indicadores
-
 Citado por SciELO
Citado por SciELO
Links relacionados
-
 Similares en
SciELO
Similares en
SciELO
Compartir
Revista Habanera de Ciencias Médicas
versión On-line ISSN 1729-519X
Rev haban cienc méd v.6 n.3 Ciudad de La Habana jul.-sep. 2007
Instituto Superior de Ciencias Médicas de La Habana (ISCM-H)
Facultad de Ciencias Médicas Dr. Salvador Allende.
PHARMACOLOGICAL GLOSSARY
*Lic. Mercedes Sotolongo Montero. Martí 626. Apto. 10 entre Rubiera y Perdomo. Regla. Ciudad de La Habana.Teléfono: 7942568. mercysot@fallende.sld.cu
**Lic. Luis Pérez Pérez. Martí 626. Apto. 10 entre Rubiera y Perdomo. Regla. Ciudad de La Habana.Teléfono: 7942568. lperez@fallende.sld.cu
***Dr. Eduardo Fernández Manchón. Consulado 165 entre Colón y Trocadero. Centro Habana. Ciudad de La Habana. eddy@infomed.sld.cu
****Lic. Rita M. Matías Crespo. Falgueras 557 entre Tulipán y Concepción. Cerro. Ciudad de La Habana.Teléfono 6402833. ritam.matias@infomed.sld.cu
*Asistente.
**Asistente.
***Profesor Auxiliar. Especialista Segundo Grado Farmacología.
****Profesora Auxiliar. Master en Ciencias de la Educación Superior.
ABSTRACT
This glossary has been made mainly to be worked with medical students who are dealing with English with Medical Purposes. It compiles the most common medications ns used in the treatment of several diseases with the medical treatment for each disease, which appears in the book: Practical Medicine used in 4 th year of the medical career. The medications compiled are classified into different groups according to their functions
It is intended to be used in class as a complementary material in order to provide the students with some pharmacological terms necessary for them as future professionals, but it may also be used by all the professionals interested in the theme.This work is just the beginning of what we can do in this field. We recommend its use in all the medical career courses as well as in specialized courses.
Key words: Medications, treatment, functions.
INTRODUCTION
It is well known that in our CEMS the teaching of English is based on the teaching of General English in the first three years and Medical English in 4 th and 5 th year of the medical career. In the English-medical field the students deal mainly with medical language, which will help them to develop as future professionals of the Health Care System.
Medication is one of the aspects students should be acquainted with in order to treat and assist the patients efficiently; but this theme is not very well treated in the text books they use to study in their syllabus.
So, as we consider this, an important element for the development of our future doctors and nurses, we decided to work on this glossary to familiarize them with some pharmacological terms in English and to develop their knowledge in English with Medical Purposes.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
To make this glossary we consulted several pharmacological books 1, 2, 3 as well as medical books 4, 5, 6 and medical dictionaries 7, 8. We selected the medications used in the diseases treated in class and listed them in the same order they are studied in the book.
The medications listed here respond to all the possible medical treatments of these diseases and they are classified into different groups according to their function in the organism.
Then we digitalized the entire glossary and gave it to the students to be used in class. We also placed it in the intranet of our faculty for all the people interested in the subject, because it will not only be very useful for students but also for teachers as well.
CONCLUSIONS
To conclude we can say that this manual is very helpful for students and teachers, who use medical English since it will help them to discuss in class about the medical treatments, make case reports and do the training of the job.
It can also be very useful for the professionals involved in the Health Care System.
We recommend its use in English- Medical courses so as to improve their knowledge in E.M.P.
RESUMEN: Glosario farmacológico.
Este glosario ha sido confeccionado fundamentalmente para ser trabajado por estudiantes que tienen que ver con el Inglés para propósitos médicos. Este compila la mayoría de los medicamentos utilizados en e tratamiento de algunas enfermedades, con el tratamiento médico para cada enfermedad, lo cual aparece en el libro "Medicina Práctica", utilizado en el 4to año de la carrera médica. Los medicamentos compilados se clasifican en diferentes grupos de acuerdo con sus funciones.
Se trata de utilizar en clases como material complementario para proveer a los estudiantes con algunos términos farmacológicos necesarios para ellos como futuros profesionales, pero también puede ser utilizado por todos los profesionales interesados en el tema. Este trabajo es sólo el comienzo de lo que podemos hacer en este campo. Recomendamos su uso en todas las carreras médicas así como en cursos especializados.
Palabras Clave: Medicamentos, Tratamiento, Funciones.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
1. Colectivo de autores. Libro de texto de Farmacología 2. Editorial Ciencias Médicas; 1990.
2. Flores, J. A. Farmacología Humana. 2da. Edición. S. A; 1992.
3. Velázquez. Farmacología. 16 th edition. Editorial Mc Graw–Hill Interamericana; 1995.
4. Berman, S. H. et al. Libro de texto de inglés Practical Medicine. Edición Revolucionaria; 1988.
5. Goodman & Gilman's. The Pharmacological basis of Thera peutics. 9 th Edition. International edition Mc Graw–Hill; 1996.
6. Rang H. P. Dale MM Ritter J.M. Pharmacology. 4 th edition. Editorial Churchill Livingstone; 1999.
7. Stedman's Concise Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions. Illustrated - 4 th Edition. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. A Wolters Kluwer Company; 2001.
8. World Heath Organization. International Nonproprietary Names ( INN ) for Pharmaceutical Substances; 1992.
GLOSSARY
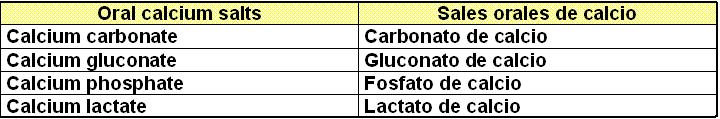
1 . Antihypertensive drugs. - Fármacos Antihipertensivos
I.
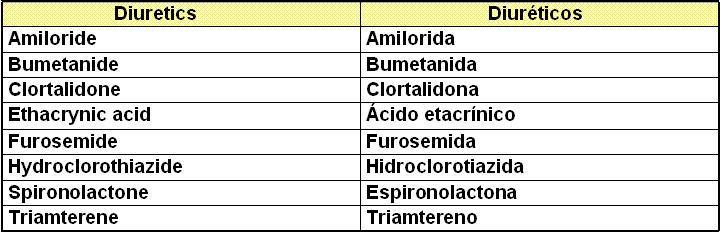
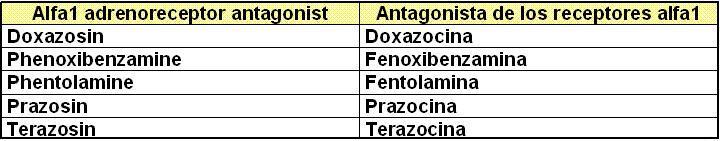
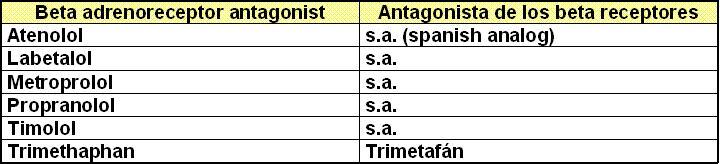
II. Symphaticolitic drugs
II. a)
II. b)
II. c)
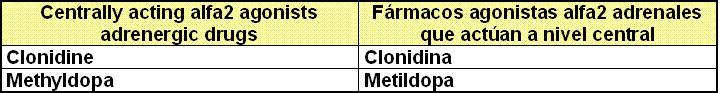
II. d)
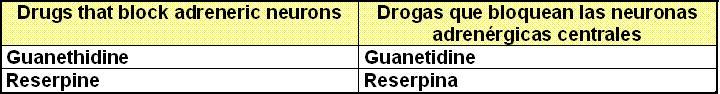
III.
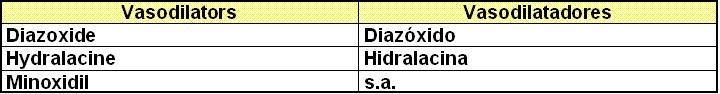
IV. Calcium channel blockers: Bloqueadores de los canales de calcio
IV. a)
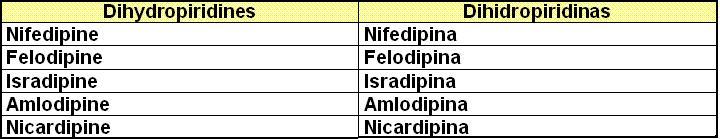
IV. b)
![]()
IV. c)
![]()
V.
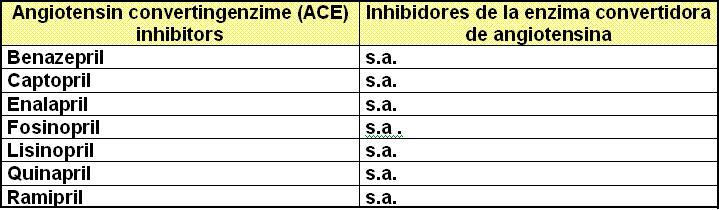
VI.
![]()
2.- Miocardial infarction: Infarto del miocardio
I.
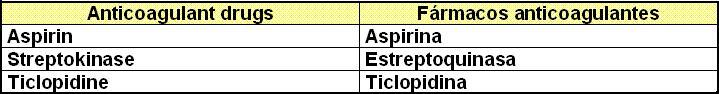
II.
![]()
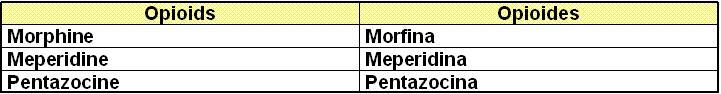
III.
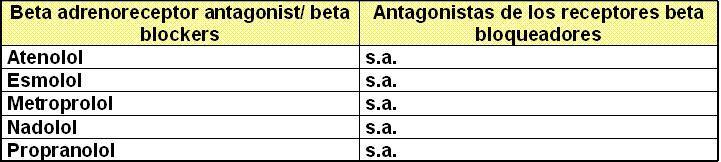
IV.
V. ACE inhibitors. (See Antihypertensive drugs)
VI
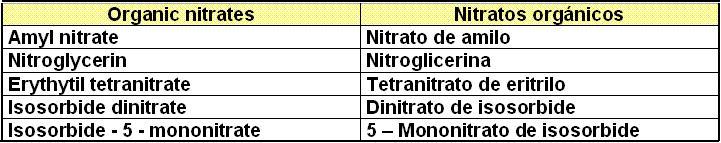
VII. Calcium Channel Blockers. (See Antihypertensive drugs)
3. Pneumonia: Neumonía
I.- Beta lactan antibiotics: Antibióticos beta lactámicos
I. a)
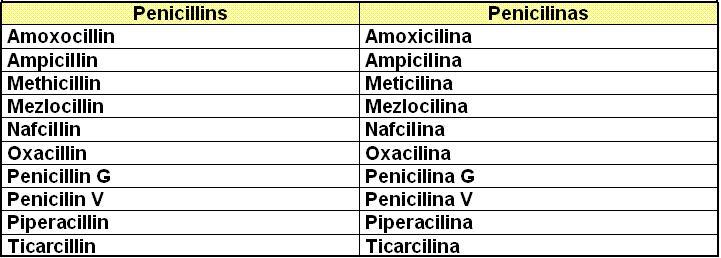
I. b)
 |
 |
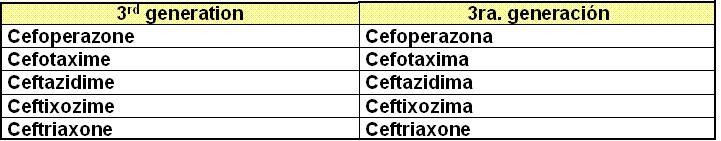 |
III.

IV.
![]()
V.

V. a)
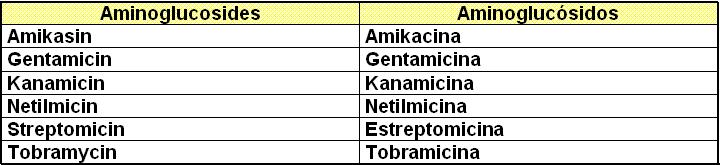
V. b)
V. c)
![]()
V. d)
![]() V. e)
V. e)
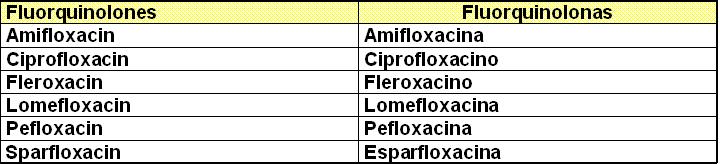
4. Tonsilitis (See Pneumonia)
_ Penicilins
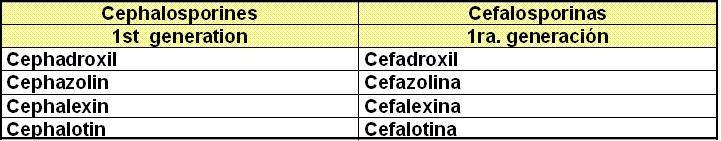
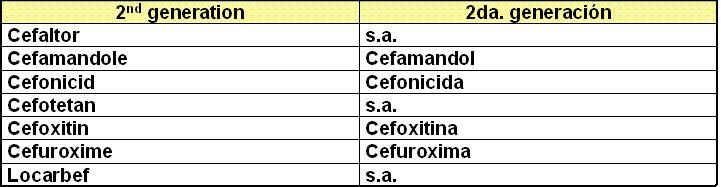
_ Cephalosporines
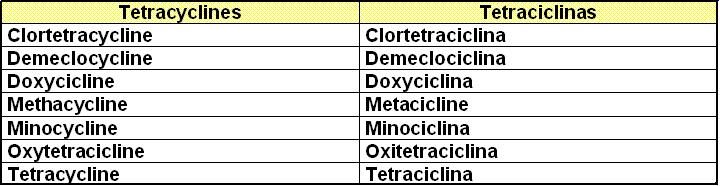
_ Tetracyclines
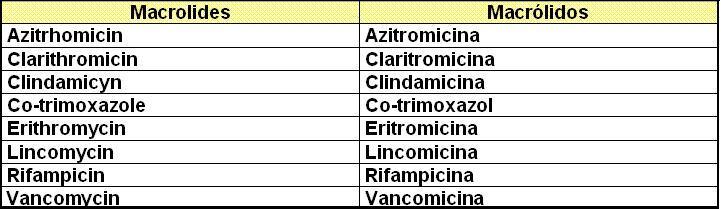
_ Macrolides
5. Drugs used in the treatment of Asthma : Fármacos utilizados en el tratamiento del Asma
I. Antinflamatory drugs: Fármacos antinflamatorios
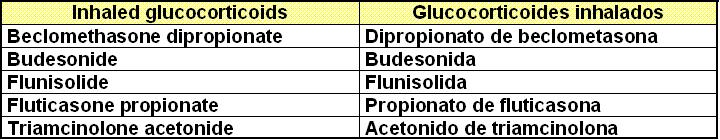
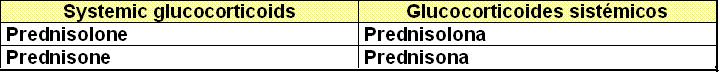
I.I. Glucocorticoids: Glucocorticoides
a)
b)
I.2. Cromolyn sodium : Cromoglicato sódico
I.3. Nedocromil sodium : Nedocromil sódico
II. Broncodilators : Broncodilatadores
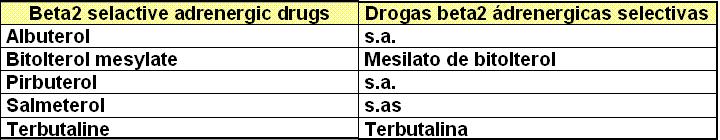
II.2 Theophiline: Teofilina/ Aminofilina
II.3

6. Duodenal ulcer / antiulcer medications : Úlcera duodenal / medicamentos antiulcerosos
I.
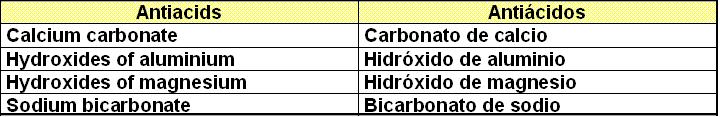
II.

II. a)
![]()
III.

IV.

V.
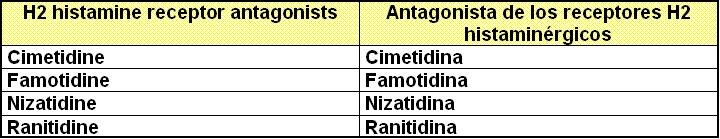
VI.
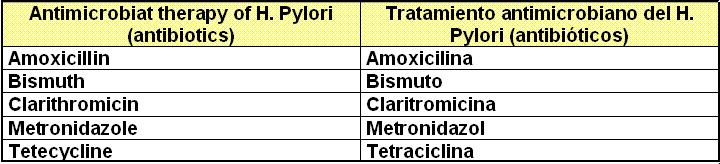
7. Cirrosis of the Liver: Cirrosis Hépatica
I. Diuretics (See antihypertensive drugs)
II. Albuminum: Albúmina
III. Cholestiramine: Colestiramina
IV. Penicillamine: Penicilamina
V. Water soluble vitamins: Vitaminas hidrosolubles
The vitamin b complex: Complejo vitamínico B
VI. Fat soluble vitamins: Vitaminas liposolubles
Vitamins A, D, K
VII.