Mi SciELO
Servicios Personalizados
Articulo
Indicadores
-
 Citado por SciELO
Citado por SciELO
Links relacionados
-
 Similares en
SciELO
Similares en
SciELO
Compartir
Revista Cubana de Medicina Tropical
versión On-line ISSN 1561-3054
Rev Cubana Med Trop v.50 n.3 Ciudad de la Habana sep.-dic. 1998
Presentación de casos
Universidad Central de Venezuela, Sección de inmunoquímica y sección de entomología médica del Instituto de Medicina Tropical "Félix Pifano" Departamento Médico de Exgeo C.A.
Dermatitis causada por Hylesia metabus (Lepidoptera: Hemileucidae) en la región costera del Estado del Delta del Amacuro, Venezuela
Resumen
Se presentan 2 casos de una dermatitis intensa causada por la mariposa Hylesia metabus en un área que hasta el momento, no ha sido descrita como endémica para esta especie. Las dermatitits observadas en estos casos pueden describirse como pápulas generalizadas salientes, muy circunscritas, pruriginosas, comparables con la urticaria, eritematosas, edema de grado variable; así como una erupción monomorfa, consistente en pápulas pequeñas, duras, coronadas por una pequeña vesícula. Las lesiones descritas de los 2 pacientes evolucionaron con pápulas intensamente pruriginosas, durante una semana y al cabo de estos días los pacientes sanaron sin secuelas dermatológicas.
Descriptores DeCS: DERMATITIS/etiología; LEPIDOPTEROS; VENEZUELA.
Lepidopterism by Hylesia may have been restricted mainly to Suramerica, in the French Guayana,1-3 Argentina,4-6 Perú,7 Brazil8 and Venezuela.9,10 Hylesia metabus is the species most common in Venezuela, presents in the swamp zones of the eastern country, particularly in Sucre, Monagas and Delta Amacuro States. These butterflies are extremely prolific, accomplishing ovipositions from 200 to 300 eggs that deposit them in any place, preferably in its host trees which are the mangrove (Rhizophora mangle), merey (Anacardium occidentalis), aguacate (Persea gratissima) and guayaba (Psidium guajava).10 The adult specimens possess a high phototropism and therefore they constitute serious problems for the nearby populations to their breeding-places. The internationally known affection called "Caripito itch" is a dermatitis produced by this genus of Lepidoptera.7,10
Despite the fact that the caterpillar can also produces dermatitis, the most frequent accidents are determined by adults.
The venomous appliance of the butterfly is constituted by hollow thorns disseminated between the hair of the abdomen, communicated with unicellular glands included in the epidermis. The accidents happen by a simple contact with the animal or with the hair detached during the fluttering and it is of high intensity when the butterfly is crushed on the skin. Generally, dermatitis and other manifestations produced by this genus take place in epidemic outbreaks, appearing throughout of the year when Hylesia abound in number.
This report describes two cases of intense dermatitis caused by Hylesia metabus in a non described area of geographical distribution in Venezuela. Puerto Coporito is a place located in the Caño Macareo, north of Delta Amacuro State, Venezuela, At 0 meters of altitude; 85 % of humidity with a rainfall rate of 2 000 mm per year.
Clinical records
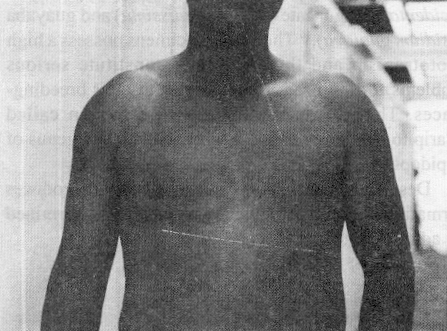
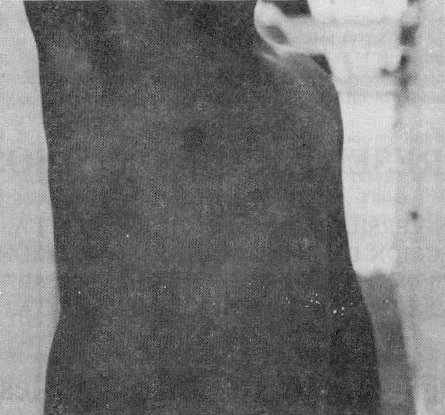
Case 1. On March 9, 1997 a warm calm day in Puerto Coporito, Caño Macareo, north Delta Amacuro, a 32-year-old man was walking across the forest while on a oil exploration expedition. He was wearing only trousers. He had seen a number of butterflies in the trees, but suddenly one moved out quickly from the tree and put up on the chest patient. After 15 minutes he started to complain from burn sensation and itching and then an erythematous and pruriginous lesions appeared. At 24 hours after the contact, the patient consulted to us presenting erythemato, papulous and pruriginous lesions in anterior toraxic region, which covered nearly all skin of the pectoral region (figs. 1 and 2).
Fig. 1. Anterior view of dermatitis produced by butterfly Hylesia metabus.
Fig. 2. Lateral view of dermatitis produced by butterfly Hylesia metabus.
The lesions evolved to intensely pruriginous papulas and the clinical picture, whose duration was of approximately one week then returned residual lesions. In the treatment systemic antihistamines, topical corticosteroids and cold compresses were used.
Case 2. This case corresponden to a physician from the area, who was working in Mariusa, a palaphitic population in Delta Amacuro. A butterfly grubbed to him and put up on the left arm and hand, presenting a burn sensation, that it was supplanted by an evolution of erythemato, papulous and pruriginous lesions similar to the above case. The physician was treated with systemic antihistamines.
Discussion
The dermatitis produced by Hylesia metabus can be grouped as generalized and projected papulas, very limited, pruriginous, erythematous and edema of variable degree, comparable to the nettle-rash. In other cases, are seen as a monomorphic eruption, consistent of small papulas, hard and crowned by a small vesicle.11 We can see also, located lesions, very similar to contact eczematiform dermatitis, characterized by well delimited plates, in high relief red color. It is observed also rhinopharingitis manifestations, very similar to the allergic vasomotor rhinitis9 and bronchial symptoms of asthmatiform type. It also has been observed ocular forms characterized by palpebral edema, congestion and conjuntival edema in occasions vesiculous that to be opened let ulcerations that heal in a variable time.
Our cases were restricted to a dermatitis symptomatology because the therapy was administrated quickly. However, the rash persisted for a week. The patients reported that these hairlets were detached easily and become airborne in light breezes or other disturbances. On contacting skin they penetrate readily, and their barbs ensure that many of them penetrate further. Therefore, skin entry results in a florid maculopapulovesicular dermatitis (figs. 1 and 2).
Summary
2 cases of acute dermatitis caused by butterfly Hylesia metabus in an area that so far has not been considered as endemic for this species were presented. The dermatitis observed in these individuals may be described as very circumscribed, pruriginous, erythematous generalized protruding papulas that may be compared with urticaria, and with a variable degree oedema. Monomorphic eruption consisting in small hard papulas crowned by a little vesicle was also present. The lesions of these 2 patients evoluted with intensely pruriginous papulas for a week and after that they healed without dermatological sequelae.
Subject headings: DERMATITIS/etiology; LEPIDOPTERA; VENEZUELA.
Referencias Bibliográficas
- Boyé R. La papillonite guyanaise. Bull Soc Pathol Exot 1932;25:1099-2007.
- Leger M, Mouzels P. Dermatoses prurigineuse determinee par des pappilons saturnidae du genre Hylesia. Bull Soc Pathol Exot 1918;11:104-107.
- Tisseuil J. Contribution a létude de la papillonite guyanaise. Bull Soc Pathol Exot 1935;28:719-21.
- Dallas ED. Otro caso de dermitis extendida, producida por un lepidóptero y notas sobre Hylesia nigricans Ber (Lepidoptera: Bombicidade). Anais. Buenos Aires: Universidad de Buenos Aires, 1993:469-74.
- Jorg ME. Nota previa sobre el principio activo urtigante de Hylesia nigricans (Lepidoptera: Hemileucidae) y las dermitis provocadas por el mismo. Anais. Buenos Aires: Universidad de Buenos Aires, 1993:482-95.
- Jorg ME. Dermatosis lepidopterianas (segunda nota). Anais. Jujuy: Universidad de Buenos Aires, 1993:1617-35.
- Allard HF, Allard HA. Venomous moths and butterflies. J Washington Acad Sci 1958;48:18-51.
- Moreno C, Cardoso JL, Carreri-Bruno GC, Domingos MF, Pinto RH, Carvalho, R. Surtos epidemicos de dermatite causada por mariposas do genero Hylesia (Lepidoptera: Hemileucidae) in S. Paulo State, Brazil. Rev Saud Publ 1993;217-220.
- Pifano F. Las dermatozoonosis en el area tropical, especialmente en Venezuela. Tesis de la Cátedra de Medicina Tropical. Universidad Central de Venezuela. Caracas, Venezuela. 1980;s.d:1-20.
- Vasquez LN. Problemática de la palometa Hylesia metabus Crammer en la región nor-oriental venezolana. Mem. VCL. Entomol 1993;27.
- Arias H. Dermatitis por Hylesia nigricans. Arch Argent Dermatol 1981;31:171-80.
Recibido: 12 de mayo de 1997. Aprobado: 15 de septiembre de 1998.
Dr. Alexis Rodríguez-Acosta. Apartado 47423. Caracas 1041. Venezuela.
- Profesor Titular en Medicina Tropical. Instituto de Medicina Tropical de la Universidad Central de Venezuela.
- Médico de la Empresa Exgeo C.A.
- Profesor Instructor. Instituto de Medicina Tropical de la Universidad Central de Venezuela.
- Profesora Instructora. Cátedra de Medicina Tropical de la Universidad Central de Venezuela.