My SciELO
Services on Demand
Journal
Article
Indicators
-
 Cited by SciELO
Cited by SciELO
Related links
-
 Similars in
SciELO
Similars in
SciELO
Share
Mendive. Revista de Educación
On-line version ISSN 1815-7696
Rev. Mendive vol.18 no.4 Pinar del Río Oct.-Dec. 2020 Epub Dec 02, 2020
Original article
A new look: system for methodological work in complex teaching disciplines
1 Centro Universitario Municipal San Luis. Universidad de Pinar del Río "Hermanos Saiz Montes de Oca”. Cuba
2 Centro de Estudio de Ciencias de la Educación Superior de la Universidad de Pinar del Río "Hermanos Saiz Montes de Oca”. Cuba
Methodological preparation is the essential way in which methodological work materializes, with the purpose of raising the quality of teacher performance and improving the development of the teaching-learning process. Overcoming the insufficiencies associated with the integration of the typology of professors, the modalities of study and the teaching subjects constitutes an urgent challenge. The following question is then presented: How to contribute, so that the methodological work process in the Complex Teaching Disciplines develops with a systemic character and from the integration of the typologies of professors, the modalities of study and intermaterial relations, a methodological preparation process that contributes to an efficient management of the teaching learning process? This work pursues the objective of exposing the experiences of how to conceive, organize and develop methodological work in the DDC. The methods used: analysis and synthesis for the study of the different theoretical and methodological positions about the methodological work process in the Complex Teaching Disciplines; historical - logical in the characterization of teaching disciplines and methodological work and induction - deduction during the process of systematization of categories and essential concepts of the methodological work process in the Complex Teaching Disciplines. Thus, it is revealed the need to structure the methodological work of the Complex Teaching Disciplines based on theoretical and methodological foundations, which allows solving the contradiction between the need to perform methodological work at all levels and the intent to perfect this process, from disciplinary methodological work.
Keywords: Teaching Disciplines; Complex Teaching Disciplines; Methodological work; Teachers; Subjects
Introduction
The very improvement that has taken place in Higher Education in Cuba has forced a re-dimensioning of the methodological work. In what refers to Higher Education, the necessary transformations are already in sight to assume the mission of the university in the face of the demands of the new century.Mena, Silva & Hernandez (2019) state:
These changes are related to the search for solutions to problems such as: the distance between what is taught and the real needs of social development and what is learned; the increase and increasing complexity of contemporary information, its interdisciplinary and transdisciplinary nature; insufficiency of current educational practice to take on the tasks of scientific work; the place that the student and the teacher currently occupy against the one that is truly claimed, the methodological preparation of the teachers (as an essential way in the self-learning of the students) in which the integration of all the teachers to this process (p. 2).
Overcoming the shortcomings associated with the integration of the type of teachers, the study modalities and the teaching subjects constitutes an urgent challenge.
This has meant that at the University of Pinar of the Rio "Hermanos Saiz Montes de Oca" after diagnosis applied, it is found that there are irregularities, that due to their consequences they will not impact:
In the preparation of the subject, from the teaching, the scientific, the investigative and the political - ideological, based on the relationships between subjects.
In the participation of part-time teachers in career and discipline meetings.
In the application of the methodology of the class encounter.
In that the methodological work of the subject groups has not behaved at the desired level, especially the methodological attention to the subjects that are taught in the municipalities.
If it starts from considering that the methodological preparation is the essential way in which the methodological work is materialized, then the need arises that this must be coordinated in the career, discipline, subject and year groups, with the aim of raising the quality of teacher performance and perform it to improve or perfect the development of the teaching - learning process. But the reality prevailing in the current pedagogical practice states that it does not manage to improve the teaching - learning process from the methodological work discipline, because although it is true that the subjects taught in the classroom in the face to face and blended learning mode relate, It is still not possible to integrate part-time teachers with full-time teachers, study modalities and teaching subjects.
The following is then in the pedagogical reality the following question as a research problem: How to contribute that the process of methodological work in Complex Teacher disciplines (DDC) develop itself with a systemic nature from the integration of the types of teachers, the study modalities and inter-subject relationships, a methodological preparation process that contributes to an efficient management of the teaching - learning process?
Emergence, evolution and trends of the teaching discipline in Cuba
In Cuba, the educational disciplines have not always existed; these were evolving at the same time the process of teaching - learning in higher education.
As of the University Reform of 1962, great changes were originated; consequently, new careers were created and curricula were modified, in addition to the establishment of new branches and university headquarters, which with the passage of time became new universities. It is in the 1962-1976 stage, considered as a conceptual and preparatory foundation for major qualitative changes in the teaching - learning process, that the need for the emergence of teaching disciplines is evident, since there were: diversity of programs; the content of the subjects very encyclopedic; expository reproductive teaching methods; lack of articulation between the contents of the different subjects; lack of a methodological and didactic work strategy in universities; little didactic preparation of teachers (Cruz y Fuentes, 2020, p.39).
There is then, a complexity in the teaching disciplines, when it is noted that the same teaching subject has to be prepared for different modalities or disciplines, since at present there are disciplines that only have one subject and it is taught in one study modality, but There are others in which more than one subject is interrelated and are taught in all study modalities. Thus, the main subject teacher has to be able to prepare the as often as modalities have to attend and also serving with these same (as) subject (as) to other careers. That is, a new type of teaching discipline is manifested that is projected differently, taking into account the relationships that are established in its structure.
Different conceptualizations of the term teaching discipline
From a pedagogical perspective the teachings discipline:
It is a subsystem of the process of training of professionals whose peculiarities are the selection and systematic integration of those contents taxed to achieving the objectives of the career, ensuring a proper pedagogical sequence, from the existence of the unit of the internal logic of science with the logic of the teaching - learning process, guaranteeing a theoretical training within its field of knowledge and an application of this knowledge in solving problems in the context that surrounds it in the social field(MES, 2018a, p.16).
It is considered teaching or academic as it incorporates not only aspects of a didactic nature, but also because it ensures certain modes of action for professionals in training. Other authors argue that it can be understood by discipline: the organized body of knowledge about a set of things or events (facts, data, observation, sensations and perceptions...), for which basic rules or definitions are formulated that delimit the boundaries of its domain (Sandín, 2020, p.3).
Classification of disciplines
For some authors:
… They are classified in general, basic, basic-specific and the exercise of the profession, according to the contents that characterize it. Thus, the basic ones are aimed at mastering the essential contents for understanding the object of the profession; general to comprehensive cultural education of students so that they can perform successfully in our society; the basic-specific to the domain of the most general contents of the work object of the profession; and those of the exercise of the profession to the particular aspects, typical of that object and that are manifested in the different spheres of action(Horruitiner, 2011, p-8).
The first two (general and basic) are distinguished from the last two since their object is different from that of the profession. Another classification that could be made of the teaching disciplines would be in relation to their link with the study modalities in which they work, according to their degree of relationships and services provided within the institution itself and the relationships that are established between the typology of teachers who interact in it.
Materials and methods
The investigation is performed using as methodological platform the dialectical - materialistic method, which served as starting point for the use of other methods and determine the contradictions that exist between the characteristics required process methodological work in Complex Teaching Disciplines in higher education (systemic, from the integration of teacher typologies, study modalities and inter-subject relationships), which contributes to efficient management of the teaching - learning process and the present reality. The research was carried out on the basis of the documents and resolutions issued by the Ministry of Higher Education, documents, audiovisuals and academic programs of the Center for the Study of Higher Education Sciences (CECE- PRI) and the searches carried out in internet, the Study Plans of the existing careers at the University of Pinar de Rio "Hermanos Saiz Montes de Oca" in the period between 2008 and 2019. For this, theoretical methods (historical-logical, modeling, systemic- structural) and empirical (documentary review, interviews, group interviews, surveys, participatory observation) were applied. The research carried out was of explanatory type and leaned against a quasi experiment developed in the school year 201 8-2019, which allowed the realization of the need for the implementation of the system, as taxed to the efficient management of the teaching - learning process. In the research, the population of teachers in the department where it was carried out is 33; of them 18 are at full time and 15 part - time and is sampled for all 100 %. The population of trainees is two and there are 10 assistant students, of which the totality is also taken as a sample for 100 % in both cases. On the other hand, the population of heads of discipline is six and the totality is taken as a sample for 100 %. Simple random selection criteria were followed.
Results
Complex teaching discipline
From the theory of curriculum design, it is known that the curriculum selects and organizes certain learning under certain didactic conceptions, according to methodological criteria, and it structures them accordingly.
Curriculum work is a scientific-technical activity. The curriculum has an objective nature as it responds to: theories, regularities, scientific subjects, a specific historical-social context, the particular characteristics of the student and the social group. Working with the same teaching subject, for the same student, in the same location, two teachers can conceive different programs, still supported by common didactic theories. The human factor, the subjective character of the designer and executor of the curriculum, puts its personal, creative and divergent stamp on it (Konstantinov, 1976, p.133). More complex it is made when these same teachers have to work the same teaching subjects for other types of students and even in other careers. Thus, the curricular object is presented to us in all its complexity: objectively-subjectively and warns us of the need for a rigorous and careful treatment.
This becomes evident when in educational practice it is observed, from the incorporation into the teaching process of new types of students (Social Workers, Comprehensive Improvement Course for Young People, Art Instructors, among others), grouped into two modalities, face-to-face and semi-face-to-face (continuity of studies, courses by meeting, distance education), that there is an increase in the participation of part-time teachers in the teaching process, as there are teachers, both part-time and full-time, who work at all frequencies and with all study modalities, this means that the preparation of these teachers has to be greater, since they must prepare their subject, as many times, as classes have with all the types of students.
Thus, the same teaching subject is derived in itself, on as many occasions as it has to be taught in the two study modes, so it would no longer be the same program, nor the same class system that the teacher would have to prepare, because the difference in this preparation should not only attend to the number of hours that the teacher has in front of the student, but he has also to keep in mind, what "type" of student is "facing". It should not be forgotten that not all the students who enter our classrooms today are recent graduates of a pre-university or polytechnic, but that many of them (especially in Distance Education), can be considered "professionals of the practice", and they come to our classrooms searching for the necessary "theory" to make their productive practice more efficient.
It is necessary, then, that the preparation of the programs of the same subject should take into account, from the same content, which differentiated part of it needs one and which the other, taking into account not the time spent in the classroom, but to the skills that need to be formed in these students, what methods to use and with what means can this work be facilitated.
It happens that these same teachers must teach this same subject, already derived, in other careers, because the profile of the professional that is formed needs the knowledge, skills and values that this teaching subject can provide; It is necessary that the same teacher who has already prepared his subject for the two study modalities, taking into account their peculiarities, has to prepare his subject again, but now not only taking into account what has been explained above, but also considering the professional model and the objectives of the year that student is going through.
Then you are in the presence of a discipline that becomes more complex in its actions as it converges, interacts and interrelates different types of teachers (let's call it typology of teachers), study modalities and teaching subjects, becoming more complex when they are interrelated again when providing service to another career.
From the dialectical - materialist theory it is known that everything that makes an object precisely this particular object and not another, which differentiates it from an innumerable set of diverse objects, is quality. The quality is closely linked to the structure of the thing, that is, to a certain form of organization of the elements and properties that compose it, as a result of which it is not simply a set of these, but their unity and integrity. The structure of a thing allows us to understand why the modification of that thing does not lead directly to the change of its quality(Álvarez, 2019, p.189).
Thus, this teaching discipline acquires a new quality, which is to be complex. It is not complex in it as a subsystem of a larger system, which is the career in the process of training professionals, but complex in its structure, based on the relationships that are manifested in it. Well, remember that quality is expressed in properties.
Hernández & Aguilar (2020) state:
For several years the Theory of Complexity is gaining strength , which is based on certain historical and scientific background such as the principle of uncertainly or indeterminacy and the Theory of Relativity of Albert Einstein, along with other theories such as: general system, chaos, and fractals, among others; extrapolating to a certain extent and with different nuances and utilities to other fields of knowledge, it is conceived by Edgar Morín (1976, 1997, 1999, 2000), as a web of events, actions, interactions, feedback and determinations that constitute our phenomenal world . It pays attention to the study of "complex systems" (objects, phenomena and certain processes) (p.3).
It can then be understood that the theory of complexity assumes a philosophy that, based on scientific bases, rejects any simplifying way of approaching the study of learning, teaching and evaluation; these processes are classified as complex, which makes it an important methodological tool when assuming supported positions and procedures.
Mena & López (2017) state:
It is therefore the Complex Teaching Discipline , a curricular structure, a subsystem of the professional training process that has as particularities in the analysis and didactic relationships, interactions of various types: some, given by those that are established between the study modalities, the typology of teachers and teaching subjects and others as well, due to their presence in other careers , aimed at providing subjects with the knowledge, habits, skills, abilities and values to competently solve the problems of their profession (p . 10).
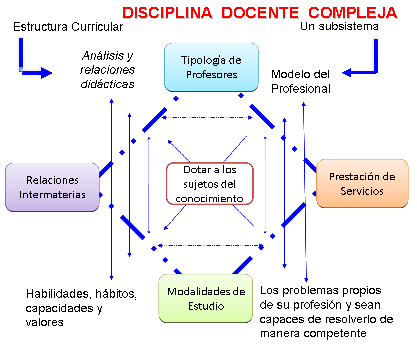
The Complex Teaching Discipline (Figure 1) is present in those careers where disciplines have the following characteristics:
It is conducted by both full- time and part-time teachers.
It is taught in both study modalities.
Contains more than one subject or teaching subject.
They have presence in more than one career.
In addition, they may have another characteristic, which is a specific basic or basic discipline of the career.
Manifests n in it the following degrees of complexity:
It occurs in the disciplines where all the types of teachers, the study modalities and the relationships between subjects are present.
One or more subjects are taught in other careers and other study modalities.
It manifests itself when two or more disciplines or subjects are integrated and make up a new subject or discipline that is taught in other careers and in all study modalities(Mena & López, 2017, p. 10).
Discussion
Given the above, it has been noted that, as much as the part - time teachers as full - time presented methodological difficulties directing the teaching - learning process in this mode; it is proposed, then, the preparation of the faculty belonging to the curricular structure based on blended learning and inter subject relations. This would promote that the teacher, in the same extent that he is teaching, is being prepared, guided and evaluated attending not only to the deficiencies and problems that have been detected in the control of the teaching process of the subject he teaches, but also having taking into account the essential characteristics of the modality to which it belongs and in which it teaches.
It is therefore necessary that the teacher be capable of mastering both the material he teaches as the didactics; it is necessary, therefore, that the teacher must be accompany in this process ensuring domain and application of the methodology of the methods of teaching work in these conditions, which, according to the author, propitiate a continuous approach to work in this mode.
It is necessary for the methodological preparation of teachers in this discipline to imply:
The fundamental forms of methodological teaching work
The fundamental forms of methodological scientific work
The teacher's knowledge of the profile of the professional being trained
The methodological preparation of the group of Complex Teaching Discipline
Fiallo (2012) states:
Teachers have the ability to master the content of various disciplines, and through methodological preparation that is done at cycle or chairs, grade, or self -preparation level, may develop the teaching process (teaching and learning) in a more interdisciplinary way, and although it is precisely at this level of teaching where, from the very content of the disciplines that are taught, it is about achieving interdisciplinary, when students are expected to acquire, develop and apply knowledge, skills, values and forms of action in accordance with the contents that are developed ... (p.13)
This general preparation of the group of Complex Teaching Discipline is the preparation of the group through the forms of methodological work, that is, the forms of teaching - methodological work and scientific - methodological work.
Forms of teaching-methodological work for DDC
Today, one of the most debated issues in the typology of Higher Education institutions is the question of how to methodologically prepare teachers. There are some teachers who consider "very traditional" and "technical" the methodological cycle that is carried out today at the career, teaching discipline and academic year levels and propose the implementation in this preparation of the so-calledblended learningoronlinelearning as It is also called, alleging that the methodological preparation carried out in these groups is inefficient, a compelling reason that implies that one of the shortcomings that today occurs in current pedagogical practice is that the methodological work does not contribute to efficient management of the teaching - learning process.
This is true, but in the author's opinion, not the whole problem is the consideration that the methodological cycle applied today is traditional or not, but rather that the problem is centered on the planning, organization and execution of the cycle. Cycle that is done, year after year, semester after semester; However, the reality requires that teachers continue with difficulties in designing the syllabus, in planning the class system (sometimes not manufactures), on the methodology of the class meeting and implementation of the forms of teaching work in blended learning, in the selection of methods and means in direct relation to the content and the skill to be trained. The entire group of teachers is not always present, as long as the participation and permanence of the teachers is not achieved at the time of the meeting, there is no flexibility when selecting which of the ways the methodological treatment should be carried out and not the cycle is carried out according to the individual problems of each teacher.
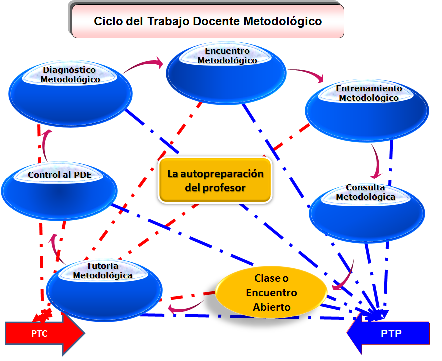
It is known that the current methodology cycle is: Self preparation of the teacher, preparation of the disciplinary subject, methodological meeting, methodological class, open class, test class, control to teaching activity.
You may ask yourself: at what point in the cycle can the head of the DDC determine where the cause of the problems that his group presents today lies?
What forms of methodological work can allow you to determine how to carry out a planning that goes from the general to the individual, taking into account the difficulties detected?
What form of methodological work, from a work that starts from the general to the individual, can integrate full-time teachers with part-time teachers?
Taking into consideration the questions raised, it is proposed as a form of methodological teaching work, which allows the head of the DDC to determine where the cause of the problems that his group presents today from the general to the particular, to the methodological diagnosis lies.
The importance that the diagnosis would have in the methodological work of the CDD, and in particular for the management of the head of the CDD, it is essential since it would allow knowing the particularities of a teacher at a given moment (or period), the causes of their difficulties and insufficiencies, its potentialities and would allow characterizing it from the point of view of its teaching, scientific and general development. In other words, from the methodological point of view, the diagnosis is made to more efficiently manage the teacher's mode of action, and in a broader sense, the teacher's methodological preparation, according to their teaching, scientific and research needs, both general as well as particular. This is its fundamental objective.
It can be considered, then, the methodological diagnosis, as a form of methodological work in the DDC, while, to the mean of theAlvarez (2020): the shape is the operational component that configures and externally organizes a process, P-93, so that the methodological diagnosis or diagnosis of methodological problems is form:
Well, it allows the head of the DDC to configure organize and design the process of methodological preparation of teachers taking into account their results, because he chooses what form of teaching-methodological work, both for general problems and for individual problems, is going to implement in the methodological work cycle. This means that the cycle that is proposed does not have to occur completely, it does not have to be static, but it is attending to the problems of its group that it must be put into practice.
It can be planned, organized and controlled, that is, it is directly related to the management carried out by the head of the Complex Teaching Discipline.
It is done, both individually and collectively.
It can be carried out in a tutorial way, in which a teacher with methodological flaws is attended by both the head of the Complex Teaching Discipline and by an expert, or in a group way when the methodological problem manifests itself in a general way.
It can be carried out, if desired, in two moments or simultaneously, one with full-time teachers and another with part-time teachers or indistinctly, taking into account the particularities and characteristics of the type of teachers that affect CDD and time available to each member of the collective.
It is directly related to the rest of the forms that make up the proposed cycle.
Methodological meetings:It constitutes the orientation of teachers to a discipline theme or in the case of failing, a unity of the program, related not only with a specific discipline, but with other disciplines or sciences; or offering in its development the most recent information related to this science to propose what are the methods, means and forms of the teaching - learning process that will be used in the treatment of these contents.
Aims:
Define the approach that should be given to a discipline theme of to unity of a program.
Guide the class system.
Guide teachers in relation to the most recommended methods and means for the development of classes.
Analyze the scientific approach that the unit should have.
Highlight the content that may present difficulties for students and the treatment required.
Define the convenient means to support the action of the method in development of the class.
Guide the different forms of control that can be applied.
The methodological training set:It is aimed at preparing teachers in the design and organization of the class system, from the preparation of the syllabus, making a diagnosis to determine where the main difficulties in the planning of that system and that it responsibly involves the entire typology of teachers lie.
Managing scientifically means starting from a deep knowledge of the object of management, that is, of the personality and professionalism of each of the members of the system; combine their individual and collective interests with institutional and social ones; be able to reveal the progressive trends of its development; plan, organize, regulate and control its movement in correspondence with such trends; discover its internal contradictions in time and facilitate their solution; overcome obstacles that appear along the way; ensure unity of the targeting system; and guarantee that each of its components fulfills its role in line with the objectives set.
To achieve this, it is proposed to establish a form of management that allows such elements to be systematically combined; which is perfectly achievable today.
Methodological consultation:It is the fundamental way of the methodological work to enable a more direct approach between teacher and head of the Complex Teaching Discipline, while her teachers can clarify the doubts that have emerged in the process of teaching and learning, both of a pedagogical and didactic character and of a specific content of a given discipline.
It encourages, in addition, the possibility of being a means of control over the progress of the implementation of methodological strategy, the methodological work plan of the career, methodological work plan of the Complex Teaching Discipline, the discipline programs, subject programs, among others. That is, they are like a "thermometer" that will enable, with its information, the measures to be taken by the discipline coordinator as well as the determination of generalizing an approach or not.
Methodological tutoring:It must start from the characterization of teachers in order to learn what they need to carry out an efficient teaching - educative work. The domain of the teachers designated as tutors should be taken into account in this tutorial; they must be professors with a higher teaching category and, if possible, a high scientific degree.
This tutoring can be considered optional, that is, it is not an imposition of the group, but an option to consider, and especially for new work instructors' teacher who are inserted in the process.
Methodological open meetings class: It is who completes the cycle of the forms used in the development of methodological preparation; we say cycle by the close relationship between the methodological training, the methodological meeting class and meeting class open - .
Generally, the class meeting open is prepared according to one of the themes or unities treated in the methodological meeting class, but may be the case that because of the needs of the discipline collective, a class of a designed theme or unity not previously analyzed would be designed.
Its objective is to provide assistance to participating teachers, exemplifying the development of the meeting in all its aspects.
Control of the teaching-methodological process: it is the way that closes the cycle of methodological teaching work, it is the way it allows to check and monitor how the methodological guidance on planning, organization and development of the fulfilled process of teaching - learning, and It involves the analysis of the causes of the deviations and the determination of the measures to be taken to rectify them.
It should be noted that monitoring does not only mean discovering defects and problems, but also revealing the best experiences in order to disseminate and generalize them.
The control must be systematic, continuous and dynamic and must cover all spheres of the activity under control. Its strength lies precisely in that it helps to build - up and are advanced experiences, methods and find more efficient ways of improving the work of the collective. It is, moreover, a means of strengthening of the Complex Teaching Discipline
In this cycle, some forms can be combined with others; for example, it can occur in a training as a meeting a query or methodological class, or may be in a meeting or training (Figure 2).
Forms of scientific methodology work of the system for methodological work in the DDC
Scientific work
The methodological work has among its distinctive features the property of reflecting the qualitative changes that are appreciated in the direction of the teaching - learning process and enables, by the group, the assimilation and mastery of the methodology and the most advanced scientific advances in its specialty and in the pedagogy of higher education. This must be, therefore, a particular character and must meet the educational tasks that have in front of it, the group of DDC.
Thus, the work of scientific validation of the programs redesigned by the group, as well as the knowledge and analysis of the study plans, cannot be carried out outside of the methodological work carried out in the group, and that is why it must be integrated to one of its forms: scientific - methodological work.
The scientific - methodological work includes scientific research related to the improvement of the teaching - learning process.
When reflecting on these approaches it shows that it is a set of activities related to research in pedagogy and everything related to a methodology for teaching, contributing to improve the teaching - learning process and has among its main tasks, of scientific - methodological character, to analyze and propose the improvement of the programs.
It should be taken into account that these scientific - methodological investigations cannot be carried out effectively if the daily work of the group's teachers is not used; This means that the scientific - methodological work cannot be separated from the teaching - methodological work that is carried out according to the model of the professional that is trained and the redesign of the programs linked to the study plan in the blended modality.
The design and planning of the research carried out by the group as a function of this form of methodological work has to envision and maintain constant feedback that includes: the experiences of each teacher in the self-preparation process and the teaching of class- meetings; It must be systematically recorded in the critical analysis carried out at the end of each meeting, in the qualitative reports on the progress of the teaching process and in the semester assessment of the group.
Do not dismiss the work of the head of the Complex Teaching Discipline in front of the collective, which can hold a workshop where receptions and generalizing the best experiences of advanced collective in the organization, development and structuring of the contents of the programs and the adequate distribution of these by the forms of organization of blended teaching, as well as the search and evaluation of the most effective methods in the implementation of the programs redesigned by the group.
The main tasks of scientific- methodological work are:
Organize the development work of the DDC collective with a view to perfecting the educational action.
Refine study plans and programs so that scientifically supported proposals are made.
Investigate about problems that have to do with didactics and elaborate the tasks for the introduction of the results in the teaching- educational process.
Study and recommend scientifically based methods to increase the effectiveness of the students' training process.
Studying the experience of organizing and conducting the educative teaching process, both in the territory and in the country and make appropriate recommendations.
Forms of scientific - methodological work
The scientific - methodological work of the teacher allows innovating and perfecting educational practice, in order to integrate theory and practice, achieving student learning and improving the teaching - educational process.
The scientific - methodological work of a group of teachers is developed in a cooperative way with the purpose of introducing changes in educational practice. The problems detected during the teaching - educational process are taken as a starting point to establish the objectives to be achieved. The investigations to be carried out are registered in the corresponding register of the teaching department for their monitoring and control.
The scientific methodological meeting is the kind of work scientific-methodological work that makes possible the analysis and decision-making in the department linked to ongoing educational research.
The scientific - methodological seminar is a scientific work session that takes place in the faculty, municipal university center and branch, teaching unit or department, whose content will respond, fundamentally, to the lines and topics of pedagogical research that are developed in those instances.
The scientific - methodological conference is a scientific event that takes place at the level of higher education institution and whose content will respond, fundamentally, to the lines and topics of pedagogical research of greater importance in the process of professionals training.
Scientific methodological workshop is a form of methodological work that allows to collect, organize, illustrate, deepen, complement, control and support the knowledge acquired in the methodological meetings, normative documents or in the scientific pedagogical literature. In itself, it contributes to raising the level of preparation of teachers(MES, 2018b, p.24).
An essential element of the workshop is the self-preparation of teachers for the debate of the selected problem to contribute experiences and exchange professionally; In other words, the high level of participation of the attendees depends largely on their success.
Some forms can be combined with each other in this cycle, for example, it can be given in a training session such as a consultation or a methodological class, or it can be given in a meeting or training.
What elements distinguish the methodological work in Complex Teaching Disciplines from the methodological work in the other disciplines?
What distinguishes one from another is
The new forms of teaching - methodological work that are proposed.
Because teachers have a full - time and part - time teachers working in them.
Because they require an interdisciplinary relationship much more than the others.
Because it works in different modalities.
So the preparation of these teachers who work in these disciplines at the disciplinary level becomes much more complex.
Why these new forms of methodological work and not others?
There are these new forms and not others because they are more flexible and enable the methodological training to a discipline level, compared to a discipline that works in both modes of study, that have teachers at full time or at part - time, and It has a number of subjects that are closely related to each other and that it is been working at different moments of the career.
What results have been derived from the application of the proposal?
The heads of discipline have become aware of the importance of the methodological preparation of their teachers when recognizing CDD. The heads of disciplines already incorporate didactic terms associated with methodological work when they discuss the preparation of their teachers. They recognized when they are facing the DDC, they recognized the need for greater preparedness to manage methodological work in front of the DDC, They suggest a preparation for managing the methodology work in the coordinated disciplines.
It can be concluded that, to contribute positively to the efficient management of the teaching - learning process, it is necessary the execution of a process of an effective methodology preparation from integrating forms of methodological teaching work and forms of the methodological scientific work based on the self-preparation of teachers as an essential way in the self-learning of students.
On the other hand, the methodological work in the CDD is conceptualized as the management process that the head of the CDD carries out from Didactics based on the methodological preparation process, based on inter-subject relationships, from which relationship is achieved the integration of the type of teachers, the study modalities and the teaching subjects, in order to achieve a self-learning of the students that leads to the training of a competent professional, according to the professional model that is formed and fostered in turn ,the construction of specific didactics.
Referencias bibliográficas
Álvarez, C. (2020). La escuela en la vida. La Habana, Cuba: Editorial Félix Varela. [ Links ]
Álvarez, R. (2019). Pedagogía y Didáctica. Universidad de Pinar del Río. Disponible en: http://ftp.ceces.upr.edu.cu/centro/repositorio/textuales/Libros/Pedagogía. [ Links ]
Cruz, C. y Fuentes, H. (2020) El diseño curricular de carreras universitarias en la concepción de la educación superior cubana. Pedagogía Universitaria, 7(3), p. 1. [ Links ]
Fiallo, J. (2012). ¿Cómo formar un pensamiento interdisciplinario desde la escuela?. Cuba, La Habana: Editorial Pueblo y Educación. [ Links ]
Hernández, M. & Aguilar, T (2020). Teoría de la complejidad y aprendizaje: algunas consideraciones necesarias para la enseñanza y la evaluación. La Habana: Editorial de Ciencias Sociales. p. 145. Disponible en: http://www.efdeportes.com/efd121/teoria-de-la-complejidad-y-aprendizaje.htm [ Links ]
Horruitiner, P. (2011). El diseño curricular en la Educación Superior en Cuba. La Habana: Editorial Félix Varela. [ Links ]
Konstantinov, F. (1976). Fundamentos de filosofía marxista leninista. Materialismo dialéctico, La Habana, Cuba: Editorial de Ciencias Sociales. [ Links ]
Mena, T. A. y López, E. (2017). Una nueva mirada a la Disciplina Docente: La disciplina docente compleja. Cuba. Ciencias Pedagógicas 4(2), pp-10. Disponoble en: http://www.cienciaspedagogicas.rimed.cu/index.php/rcp/articl. www.iccp.rimed.cu. [ Links ]
Mena, T., Silva, L. & Hernández, M. (2019). Ciencias Pedagógicas: Sistema para el trabajo metodológico en disciplinas docentes complejas. Una reflexión para tener en cuenta. Las Tunas, Cuba: Editorial Académica Universitaria. (pp.48-61) Disponible en: http://edacunob.ult.edu.cu/ [ Links ]
Ministerio de Educación Superior. (2018a). Documento Base para la Elaboración de los Planes de Estudio E, La Habana, Cuba: MES. [ Links ]
Ministerio de Educación Superior. (2018b). Resolución No.2-2018. Reglamento de Trabajo Docente y Metodológico. La Habana, Cuba: MES p.24 [ Links ]
Sandín, M.P. (2020) Retos actuales de la formación en investigación cualitativa en educación. Revista EDUCARE - UPEL-IPB - Segunda Nueva Etapa 2010 (3). https://www.researchgate.net/publication/279694524_. P-35 [ Links ]
Received: November 15, 2019; Accepted: October 26, 2020











 text in
text in