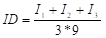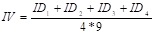Mi SciELO
Servicios Personalizados
Revista
Articulo
Indicadores
-
 Citado por SciELO
Citado por SciELO
Links relacionados
-
 Similares en
SciELO
Similares en
SciELO
Compartir
Mendive. Revista de Educación
versión On-line ISSN 1815-7696
Rev. Mendive vol.22 no.1 Pinar del Río ene.-mar. 2024 Epub 30-Mar-2024
Original article
Training in local development projects: Need for economics and planning cadres and specialists
1Dirección Provincial de Economía y Planificación. Pinar del Río. Cuba
2Universidad de Pinar del Río "Hermanos Saíz Montes de Oca". Cuba.
Local development in Cuba has become a priority of strategic importance as part of the National Economic and Social Development Plan until 2030, as well as a central axis and articulator of the agendas of governments at the municipal and provincial level as an alternative to Promote the development of the territories based on the country's strategy, so that municipalities are strengthened as a fundamental entity. The objective of the article was aimed at socializing the results of the initial diagnosis based on the training for the management of local development projects of the staff and specialists of the municipal directorates of economy and planning of the Pinar del Río Province. The use of theoretical level methods such as: historical-logical, analytical-synthetic, inductive-deductive and empirical level methods such as: observation, interview, survey and document review allowed us to verify that the diagnosis of training needs. about the contents for the management of local development projects and their planning are insufficient, there are few spaces for scientific exchange that guarantee socialization, limited use of information technology and communications technologies in training, imbalance between theoretical and practical in training activities and poor motivation of staff and specialists.
Keywords: training; project management; local development; cadres and specialists; economy and planning
Introduction
Local development in Cuba has become a priority of strategic importance as part of the National Economic and Social Development Plan until 2030, as well as a central axis and articulator of the agendas of governments at the municipal and provincial level as an alternative to promote the development of the territories based on the country's strategy, so that the municipalities are strengthened as a fundamental instance, with the necessary, sustainable autonomy, with a solid economic-productive, sociocultural, institutional and environmental base where in this process it results It is essential to strengthen the capacities of local actors to manage, in a context of decentralization, the set of strategies, programs and projects that give content to local development.
Likewise, an important place in the management of local development projects is occupied by the provincial directorates of Economy and Planning in their role for the approval, implementation, and planning of the financial and material resources that they demand from their representative and optional function to approve them of together with the specialists in charge of advising the cadres on this matter, executing the direct planning of said projects and submitting them to their provincial management.
Training in the management of local development projects for the staff and specialists of the municipal directorates of Economy and Planning should be considered as a permanent, systemic and directed training process, with the purpose of updating and deepening the theoretical and practical contents for the management of local development projects, from the conception of the stages of their life cycle, which streamlines their implementation, promotes the fulfillment of their objectives, the achievement of better performance so that they reach their effectiveness in a way that satisfies, the individual and collective needs and interests, current and perspectives of the entities, in accordance with the current demands of the professional pedagogical process.
There are numerous authors who have addressed the topic of local development, including: (Rodrigo et al., 2019), (Labrador, et al., 2019), (Díaz-Canel & Fernández 2020), (Polanco & Caballero 2020), (Alfonso, et al., 2022), who have delved into the obstacles that hinder the use of knowledge in local development, the management of training for better management in the Cuban socioeconomic context, project management as an interface of science and innovation for local economic development, have proposed methodologies to evaluate the impact of training in Cuban companies, government management, higher education, science, innovation and local development, strengthening the capacities of local actors to management of local development from culture, training of managers, to achieve sustainable business management and the preparation and improvement of personnel.
On the other hand, inspection visits to the municipal directorates of Economy and Planning, observation of training activities, review of documents, evaluation and practical analysis of projects, attendance at meetings of municipal Territorial Development groups and videoconferences with the actors that are inserted in this economic modality, both state and non-state, revealed the following deficiencies in the management of local development projects:
Insufficient motivation and interest of staff and specialists in the management of local development projects.
Training actions are not recognized based on achieving effectiveness in the management of local development projects.
Training actions are non-systemic and decontextualized.
Insufficient theoretical and practical knowledge in the management of local development projects.
The objective of the article was aimed at socializing the results of the initial diagnosis based on training for the management of local development projects in the staff and specialists of the municipal directorates of economy and planning of the Pinar del Río Province.
In this sense, the importance of implementing training actions must be recognized as a fundamental way to achieve efficiency and effectiveness in the performance of the staff and specialists of the municipal directorates of Economy and Planning, in the management of local development projects in a manner that they achieve the preparation for their implementation, as well as the planning of the financial and material resources that they demand.
Materials and methods
To carry out this research, the total population of the staff and specialists of the municipal directorates of economy and planning of the province of Pinar del Río was taken as a sample, consisting of 11 directors and 11 specialists designated to take care of the local development projects.
To search for both theoretical and practical information, methods of the theoretical level were used such as: historical-logical, analytical-synthetic, inductive-deductive and theoretical systematization, for the analysis of the sources that provide the theoretical references about the object, in the interpretation of the results derived from the initial diagnosis, the historical evolution, trends and generalizations of the object investigated, the determination of needs for a new strategy for the training of cadres and specialists in the context of municipal entities and for the interpretation, enrichment, confrontation, modification and construction of theoretical-practical knowledge on training in local development project management.
Empirical level methods were also used such as; the analysis of documents, bibliographic review, observation, interview and survey of directors of the municipal entities with the objective of analyzing the reports of the control and advisory visits to the entities, the individual work plan of the specialists, the study of the current training program, as well as the regulations for local development projects, which provide valuable information both for the diagnosis, the direct perception of the training process and to know the opinions of the cadres and specialists regarding their preparation. , the planning and results of the training of this staff, and its impact on professional performance, as well as the most used avenues for training and their opinions in this regard, taking into account the following dimensions and indicators:
Dimension I: Process planning, with indicators:
I.1. Level of knowledge of training needs in local development project management
I.2. Level at which you master the regulatory documents for the training process in local development project management
I.3. Level of participation in the planning of the training process in local development project management
Dimension II: Organization of the process, with indicators:
II.1. Level of compliance with the local development project management training schedule
II.2. Level of access to materials that will be used in training in local development project management
II.3. Level of attendance and punctuality in the training process in local development project management
Dimension III: Execution of the process with indicators:
III.1. Level of motivation regarding the training process in local development project management
III.2. Level at which teamwork exercises are carried out in the training process in local development project management
III.3. Level of effectiveness of the result of the independent study on the management of local development projects
Dimension 4: Evaluation of the process, with indicators:
IV.1. Qualification level obtained in the training process in local development project management.
IV.2. Level of correspondence between the results achieved and those planned in the training process in local development project management
To process the data obtained, index calculation was mainly used as a descriptive statistics technique and five categories were assumed to evaluate the indicators, dimensions and the variable in general.
The indicators are evaluated as Very low when the index (I) is between (0<Id"0.2); Low when the index is between (0.2 <Id"0.4); Medium when the index is between (0.4<Id" 0.6); High when the index is between (0.6<Id"0.8) and Very high when the index is greater than (0, 8<I) based on the results of the parameterization of the variable, the dimensions and the variable are evaluated based on the index calculation as a result of the evaluation of the indicators where numerical values are assigned to each of the categories to calculate the index.
Based on the indicators of the dimensions and the variable, the decision rules (Table 1) and the formulas for calculating the index of the dimensions and the variable were established as shown below:
Table 1 - Decision rules for the evaluation of the variable
| Rating scale | Abbreviation | Quantitative scale |
|---|---|---|
| Very high | M.A. | 9 |
| High | TO | 7 |
| Half | I | 5 |
| Low | b | 3 |
| Very Low | M.B. | 1 |
Where:
To calculate the dimension index, the following formula is used:
The value of I is the evaluation of the indicator where it is taken to the quantitative scale and in the denominator, 3 is the number of indicators and 9 is the maximum value it takes on the quantitative scale.
To calculate the index of the variable, the formula is used:
In this case, the value of the index of the four dimensions is added and divided by the result of multiplying the number of dimensions (4) and the maximum value taken by the quantitative scale (9).
To carry out the qualitative analysis of the variable, the calculation of the index of each indicator is taken into account based on the comparison with the rating scale and the triangulation of the information provided by the applied instruments is carried out.
Results
Based on the triangulation of each of the instruments applied to the selected sample, the training process for the management of local development projects of the staff and specialists of the municipal entities of Pinar del Río is evaluated, in each of the dimensions and indicators in order to find possible coincidences and discrepancies that make it possible to reach more complete conclusions from the diagnostic process.
In dimension I (process planning), the indicators, level of knowledge of training needs in management of local development projects and level of participation in the planning of the training process in management of local development projects are evaluated as low. with indices of 0.28 and 0.25 respectively and the indicator, level of mastery of the normative documents for the training process in local development project management, is evaluated on average with an index of 0.41, therefore the dimension is evaluating medium level with an index of 0.41.
In the case of dimension II (organization of the process), the indicators, level of compliance with the training schedule in management of local development projects and level of attendance and punctuality to the training process in management of local development projects are evaluated. high with indices of 0.69 and 0.71 in order and the indicator, level of access to materials that will be used in training in management of local development projects is evaluated as low with an index of 0.34, as As a result of the analysis, the dimension is evaluated at a high level with an index of 0.63.
On the other hand, dimension III (execution of the process), the indicators, level of motivation regarding the training process in local development project management and level at which teamwork exercises are carried out in the training process in local development project management. local development is evaluated as low with indices of 0.31 and 0.39 respectively and the indicator, level of effectiveness of the result of the independent study on the management of local development projects is evaluated as medium with an index of 0.66, then the dimension in general is evaluated as low level with an index of 0.40.
Likewise, in dimension IV (process evaluation), the indicator, level of qualification obtained in the training process in management of local development projects is evaluated at a medium level with an index of 0.50 and the indicator, level of c Correspondence between the results achieved and those planned in the training process in local development project management is evaluated as low with an index of 0.31 and in general the dimension is evaluated as medium level with an index of 0.44. The variable is evaluated at a medium level with an index of 0.56, confirming the following insufficiencies:
- Insufficient diagnosis of the training needs of the staff and specialists of the municipal entities of Pinar del Río in content regarding the management of local development projects.
Insufficiencies in the planning of content related to the management of local development projects.
Limited number of scientific exchange spaces for the socialization of professional experiences for the management of local development projects from the integration of acquired knowledge.
Limited use of computer and communications technologies in the training of personnel.
Insufficient motivation of the cadres for the contents about the management of local development projects.
Imbalance between theoretical and practical content in training activities.
Discussion
The results of the methods, techniques and instruments that were applied in the diagnosis allowed us to characterize the current state of the training process for the cadres and specialists of the municipal directorates of Economy and Planning in Pinar del Río and its consequence on the success of the management of local development projects, so the need to delve into this article is evident in a way that allows us to substantiate the need to plan training actions in this sense.
It has been confirmed that there are difficulties in diagnosing training needs for the management of local development projects, which has the consequence that the contents in the programs that the cadres truly need are not planned. It is then necessary to carry out a survey to determine which contents are most needed based on project management so that the actions that are outlined can be more effective, and even in training matters it is necessary to know the level of knowledge that has before the training action, regarding the contents that are declared to compare them with those that it reports having obtained once the action is completed, aspects that are highlighted by (Guerra 2021).
According to the above, there are also insufficiencies in the planning of training for the management of local development projects, which has the consequences that there is no integrated and commonly accepted conception at the institutional level about local development and its mechanisms and tools. of management, strengthen local capacities and design and manage municipal development strategies to ensure the strategic management of local development, improve project management, efficiently use the different sources and financing mechanisms, among others the absence of systemic policies of innovation at a local scale and the need to prioritize the training of a qualified workforce in the territories in close connection with municipal development strategies, which is why they raise the need to train public servants and provide them with the necessary knowledge and tools (Díaz-Canel & Fernández 2020).
In relation to the above (Labrador et al., 2019), as a result of the diagnosis in a research on the management of training for better management in the Cuban socioeconomic context, they determined that the main weaknesses were not conceiving it with a strategic approach, not design appropriate instruments to carry out the diagnosis of training needs, which means that the planning process is not adapted to real needs and in correspondence with the peculiarities of each organization, individual differences and strategic development plans are not taken into account. of human resources.
Furthermore, to conceive training with a strategic approach, prospective planning must be taken into account, starting from a careful evaluation of the environmental conditions and an analysis of the strengths and weaknesses of the territory, which leads to the identification of key challenges for the design of these strategies, (Garrigó et al., 2022).
Also related to the training of managers (Rodrigo et al., 2019), they determine as insufficiencies that there is no knowledge and mastery of the meaning of sustainable business management and its implications, low perception of the benefits for the entity of sustainable business management, weak organizational culture and standards of action of its members and insufficient incorporation into training programs and actions of aspects related to sustainable development.
These shortcomings are also part of the contents of the management of local development projects and must be assumed in the contents of the training programs for the staff and specialists of the economics and planning directorates in order to improve the management of local development projects. to guarantee affordable and nutritionally and culturally adequate food, economic sustainability, the democratization of agri-food systems and external independence, (Rivas & Cussó 2023).
Taking into account the above, it can be assured that a need for training in the management of local development projects is knowledge management, which cannot do without the integration of actors to the territory and must function on the basis of creation. and the promotion of information and knowledge networks, however, in accordance with the above, the limited dissemination of knowledge and experiences derived from science, which contribute in a sustainable manner to the solution of the needs of the population and society, have been detected as insufficiencies. existence of insufficient popularization of science and technology in topics relevant to society (Martín & Gorina 2019).
Therefore, it is necessary that the training of the staff and specialists of the municipal economic and planning entities, regarding the management of local development projects, be planned taking into account the diagnosis to treat those contents that are most needed in a way that raises the abilities and competencies, based on the acquisition, updating and deepening of theoretical and practical content, the motivation to incorporate new knowledge into their professional performance and concentrate modes of action for the solution of professional problems, which leads to the integration of pedagogical content , didactic and technical, to influence the objects of the profession and demonstrate satisfaction for the management of local development projects that allow the staff and specialists of the municipal directorates of Economy and Planning in Pinar del Río, to function efficiently in the professional process to achieve the goals conferred by society.
Regarding the low motivation of the cadres for the contents related to the management of local development projects, it is logically due to the way in which this is conceived and results in the poor assimilation and development of knowledge. In this sense, it should be noted that managers, as subjects and objects, are responsible for continually making decisions based on their knowledge, skills and attitudes so that their organizations can generate products and services that satisfy the needs or exceed the expectations of customers and society, promoting higher levels of development, ( Bú et al., 2019) it is necessary to guarantee professional improvement and the continuity of their studies in the different postgraduate figures through the plans developed for the different entities, as well as the evaluation of the impact of the knowledge acquired (Alfonso et al., 2022).
In this sense, a novel aspect must be taken into account, which can be motivating when training staff and specialists from the Economics and Planning departments, and that is the management of local development from culture, where (Polanco & Caballero 2020) are based on limitations, such as the lack of representativeness of the government in the figure of decision-makers in training, management, work meetings and dialogue and the lack of protagonism and raise the need to contextualize the development projection defined for each territory, based on options that incorporate social themes that express the demands limited to the lifestyles of its resident population that are available to local actors, which is why it is necessary to incorporate these contents in training programs.
It has also been noted that in training activities there is a lack of balance between theoretical and practical content, which affects the treatment of content and even decreases motivation on the part of the cadres during the process. In this sense, cooperative learning must be put into practice in training, which implies that students help each other, share ideas and develop their skills from a joint point of view (Navarro et al., 2019), so that work within the framework of the group and work teams, using attitudes and mechanisms of cooperation and coordination, which is favored by the types of activities that are developed that allow them to discover, observe, exchange opinions, ideas, criteria, dialogue and discuss (Matos et al., 2021). That is, use different forms to organize the process, such as the workshop, exchanges of experiences and others, so that debate about the contents is generated from different perspectives.
Other limitations that have been noted are the few spaces for scientific exchange that are generated for the socialization of professional experiences, for the management of local development projects from the integration of acquired knowledge, which is why it is necessary that training of cadres and specialists, the workshop is used as non-academic forms of improvement since it allows the collective construction of knowledge to face reality and act on it and serves as a stimulus in the development of the professional's competencies, (Ávila et al., 2019).
Regarding the limited use of computer and communications technologies in the training of personnel, it can be argued that this insufficiency results in it not being exploited as a very opportune way in these times and that it constitutes a motivating element that has taken boom and is an increasingly stronger trend among companies and workers in the world, who take advantage of this modality as a comfortable way for their continuous preparation, which adapts to their times and needs (Rodríguez et al., 2020). Therefore, it constitutes another form of training that helps generate exchange and debate.
Training for the management of local development projects in the business field needs to be contextualized in an organized and directed manner in a sequence of actions and operations with a systemic approach and must express both individual and collective professional development and the creation of a harmonious climate. that achieves the motivation to be deployed in a process of joint solution of pedagogical tasks, both of an instructive and educational nature, in changing conditions and full communication between the trainers and the cadres and specialists of the entities, requiring a creative attitude and careful, organization, execution and control of its pedagogical actions for the training of professionals.
The deepening of the training process for the staff and specialists of the municipal economic and planning directorates supports the need to prepare them in the theoretical and practical content that allows them to achieve greater effectiveness in the management of local development projects, based on the conception of the stages of their life cycle, to carry out actions in each of them, which of course will be very useful to promote their implementation, promote the fulfillment of their objectives and the achievement of better performance, which is achieve relevant performance and effectiveness.
Referencias bibliográficas
Alfonso, G., García, M. & Figueroa, A. (2022). La preparación y superación de los cuadros: tarea de orden de la Filial Municipal Baraguá. Opuntia Brava, 14(1), 174-184. https://opuntiabrava.ult.edu.cu/index.php/opuntiabrava/article/view/1497 [ Links ]
Ávila, M. E.; Santos, I., Mederos, M. & Espert, B. (2019). La superación del maestro primario: vía para el mejoramiento de su desempeño profesional pedagógico ambiental. Universidad y Sociedad, 11(5), 89-98. http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?pid=S2218-36202019000500089&script=sci_arttext [ Links ]
Bú, B., Sosa, I. & Castilla, L. (2019). Análisis sobre la evaluación del impacto de la capacitación en el Desarrollo Local Sostenible. Santiago, (149), 418-433. https://santiago.uo.edu.cu/index.php/stgo/article/view/5051 [ Links ]
Díaz-Canel, M.M. & Fernández, A. (2020). Gestión de gobierno, educación superior, ciencia, innovación y desarrollo local. Retos de la Dirección, 14(2), 5-32. http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?pid=S2306-91552020000200005&script=sci_arttext [ Links ]
Garrigó, L. M., Borrás, F., & Puentes, L. (2022). Un enfoque prospectivo para el desarrollo sostenible territorial. Revista Cubana de Educación Superior, 41(Especial 2), 249-266. https://revistas.uh.cu/rces/article/view/183 [ Links ]
Guerra, S. (2021). Metodología para evaluar el impacto de la capacitación en las empresas cubanas. Revista Universidad y Sociedad, 13(6), 237-249. http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?pid=S2218-36202021000600237&script=sci_arttext&tlng=pt [ Links ]
Labrador, O.; Bustio, A.; Reyes, J. & Cionza, E. L. (2019). Gestión de la capacitación y capacitación para una mejor gestión en el contexto socioeconómico cubano. Cooperativismo y Desarrollo, 7(1), 64-73. http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?pid=S2310-340X2019000100064&script=sci_arttext&tlng=en [ Links ]
Martín, M. E. & Gorina, A. (2019). Gestión universitaria de la divulgación científica orientada al desarrollo local. Revista Santiago, 148, 91-107. https://santiago.uo.edu.cu/index.php/stgo/article/view/4826 [ Links ]
Matos, L.; Rodríguez, P. & Matos, M. (2021). La capacitación político-ideológica desde el puesto de trabajo de los cuadros políticos. Maestro y Sociedad, 18(3), 1051-1069. https://maestroysociedad.uo.edu.cu/index.php/MyS/article/view/5393 [ Links ]
Navarro, I., González, C., López, B., & Contreras, A. (2019). Aprendizaje cooperativo basado en proyectos y entornos virtuales para la formación de futuros maestros. Educar, 55(2), 519-541. https://www.raco.cat/index.php/Educar/article/view/v55-n2-navarro-gonzalez-lopez-contreras [ Links ]
Polanco, A. & Caballero, M. T. (2020). Fortalecimiento de capacidades de los actores locales para una gestión del desarrollo local desde la cultura. Retos de la Dirección, 14(1), 45-67. http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?pid=S2306-91552020000100045&script=sci_arttext [ Links ]
Rivas, M. & Cussó, X. (2023). La soberanía alimentaria como indicador de la transformación integral de los sistemas agroalimentarios. Historia agraria: Revista de agricultura e historia rural, (90), 7-38. https://dialnet.unirioja.es/servlet/articulo?codigo=9069431 [ Links ]
Rodríguez, V. R.; Ledesma, A. M.; Tamayo, N., Gayoso, R.; Solórzano, M. R. & De Armas, R. (2020). La superación de directivos de la Administración Pública en el Centro de Estudios de la Administración Pública de la Universidad de La Habana. Revista Cubana de Administración Pública y Empresarial, 4(2), 165-178. https://dialnet.unirioja.es/ejemplar/629600 [ Links ]
Rodrigo, J. E.; Ferreiro, A. &González, M. L. (2019). La capacitación de directivos, una perspectiva para el logro de una gestión empresarial sostenible. Didasc@lia: Didáctica y Educación, 10(1), 253-268. https://dialnet.unirioja.es/servlet/articulo?codigo=7242301 [ Links ]
Received: October 02, 2023; Accepted: December 21, 2023











 texto en
texto en