Introduction
As the business world becomes competitive, companies face tough competition with their competitors, so they are looking for finding new ways to deal with competitors and prove their superiority in the market.
On the other hand, customer expectations from companies have also undergone a wide range of changes so that they ask companies to have more social responsibility toward society rather than to take responsibility for the customer (Barone, Norman & Miyazaki, 2007). Since the beginning of the 1990s, widespread pressure has forced companies to take responsibility for their activities in the society. These pressure caused companies to turn to social responsibility and expand their cooperation with non-profit organizations to contribute with the cause-related purpose, as well as the development of the company image.
One of the strategies of corporate social responsibility is cause-related marketing. Cause-related marketing is a specific marketing activity in which the company undertakes to allocate an amount of product or service sales to certain cause-related activities (Van den Brink, Odekerken-Schröder & Pauwels, 2006).
Cause-related marketing is a way of showing the company's concern about society to retain customers. Cause-related marketing strategy involves the offering of brand promotion to customers to help determine a certain value for a given cause. In recent years, cause-related marketing is assumed to be an important marketing strategy. The growth of cause-related marketing from $ 120 billion in 1990 to $ 1.73 billion in 2012 indicates the importance of this issue (Vyravene & Rabbanee, 2016). Marketers have noticed this kind of marketing because cause-related marketing influences consumer behavior (Sen & Bhattacharya, 2001.(
cause-related marketing can bring many benefits to the company, including improving the image of its brand, increasing the awareness of the brand and Rising consumer attention to the brand (Barone, Miyazaki & Taylor, 2005) as well as increasing the intention of buying a particular brand (Cornwell & Coote, 2005). In addition, cause-related marketing can help build brand relationships that subsequently will result in Going up sales and brand loyalty (Van den Brink, et al, 2006).
Previous studies focus more on the effects of cause-related marketing campaign attributes on positive assessment of consumers, Relationship between brand and cause (Pracejus & Olsen, 2004), the effects of cause-related marketing campaigns on consumers attitudes toward the sponsor company, increase of brand equity, brand awareness by creating awareness of the brand, brand image and brand loyalty (Mazodier & Merunka, 2012), but studying the effects of cause-related campaigns on consumers response have not been examined adequately (He, Li & Harris, 2012; Marandi, et al, 2018).
The consumer’s response to cause-related marketing campaigns may be due to ethical judgment for helping people in the community (Kim, Magnini & Singal, 2012) and participants' identity filling with the company to introduce themselves to others with the same cause-related characteristics of the organization (Papista & Dimitriadis, 2012). In that case, routine shopping decisions provide an opportunity to show the ethical views and identifiability of individuals with the company (Kim & Johnson, 2013). The studies focus on how cause-related marketing strategies affect the ethical and identity aspects of scattered consumers (Moosmayer & Fuljahn, 2010).
In Iran, despite the fact that only 28 years of the implementation of cause-related marketing have passed in the world, and in spite of the novelty of scientific marketing activities in Iranian economic companies, the strategy has been frequently used by internal economic companies. For the first time in 2005, cause-related marketing was introduced by UNICEF to our country's economic companies (Rashidi, Esfidani & Salamam, 2015).
By raising the debates related to cause-related marketing, one of the fundamental questions is how customers respond to this type of marketing (Nerkar, 2013). In the case of the customer response mechanism to cause-related marketing, not enough research has been done. Furthermore, consumer’s response to cause-related marketing may originate from their ethical feelings to support others in community (Vyravene & Rabbanee, 2016). Therefore, by raising the trend of using this method of marketing in Iran, it is important to conduct research to determine the types of cause-related marketing strategies as well as response model to cause-related marketing. This research can help internal companies to use this type of marketing and choose the type of cause-related marketing strategy. Digikala is no exception to this rule as the largest internet store in the Iranian market and with a large number of brands that operate in different product groups such as digital products, home appliances, personal accessories and products related to culture, art, sport, and entertainment. The output of this study can help the company and other companies to improve and develop their markets (Vanhamme, et al., 2012).
Methodology
According to the questions, the present study is descriptive in terms of purpose and qualitative in terms of research method. The research strategy is a case study in the qualitative section and themes analysis in data analysis section.
In this study, the interviews were used to collect data and the theoretical sampling method for sampling, which is specific to qualitative research method. In this method, the sample volume must be that the researcher reaches theoretical adequacy. The population of this study can be divided into two groups. The first group is the managers of Digikala Company, and the second group is the customers of the company.
In this section, the findings of data collection and data obtained by separating each of the research questions are investigated. The research method in this study is qualitative. In this section, in the first step; qualitative data are analyzed. For this purpose, in order to analyze the data after implementation of interviews, qualitative data are first presented based on theme analysis method with documented evidences and extracted components from research literature and finally presented the pattern arising from interviews analysis.
Data Analysis
First question:
What kind of cause-related marketing strategies are in the Iranian market?
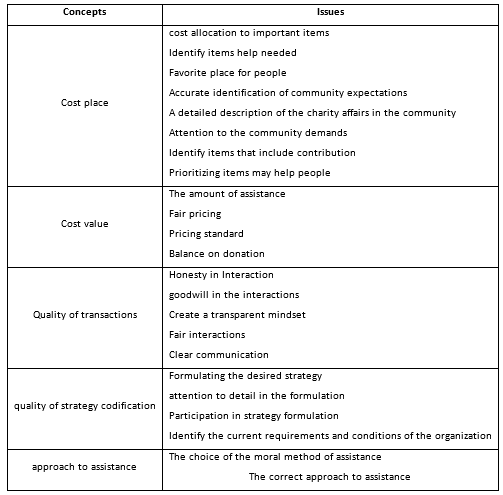
During the interview process, if there is any ambiguity in the statement with other questions, the interviewees were asked to provide more and more clarification. In this section, after analyzing the most important verbal statements contained in the interviews, open coding was conducted and initial codes were identified and extracted. Then they were classified into the research questions using the results of semi-structured interviews inspired by the theoretical and empirical literature (Table 1).
Table 1 - Questions and concepts related to the first question.
| Concepts | Issues |
|---|---|
| The exchange programs | Allocation a percentage of profit Allocation of Sales Profit Parallel Sales |
| Collaboration | Collaborative participation Joining to the Campaign Participating in cause-related marketing campaigns organizational Cooperation Cooperation with the community SMS campaigns |
| Founded | Establishing an independent subsidiary Support the charity affairs Establishment of subsidiary organization |
| licensing programs | Referring to government and government agencies Obtaining approval |
Second question:
What are the incentive and disincentive factors of cause-related marketing strategies?
The incentive and disincentive factors of cause-related marketing strategies can be used in the same concept. In this way, a concept is considered to be a incentive in nature when it is in a positive state and disincentive when it is in a negative state in nature. Therefore, identifying effective concepts on cause-related marketing strategy can lead to the identification of incentive and disincentive factors of cause-related marketing.
During the interview process, if there is any ambiguity in the statement with other questions, the interviews were asked to provide more clarification.
Thus, after answering the second question, and using the results of interviews inspiration by theoretical and empirical literature, after the open coding phase, the identified issues will be categorized (Table 2).
Third question:
What answers do customers make in favor of cause-related marketing strategies?
Following the analysis of the third question, and using the results of interviews inspired by theoretical and experimental literature, the identified categories are Table 3:
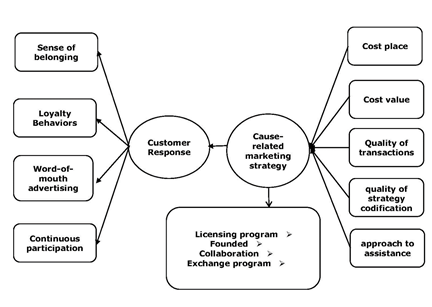
Studying and analyzing the data from interviews with experts have led to the formation of a conceptual model of Research to describe (Figura 1).
Discussion
Today, a large part of the activities of companies is related to social responsibility and serving the community and people. Companies are seriously trying to solve a social problem by uniting one or more social organizations. Cause-related marketing is an effective way to establish brand name, knowledge about the company's products and restructure the company's values. Cause-related marketing is the most popular way of doing business and aims to achieve the company's objectives, including the introduction of new products, increasing sales, or increasing popularity on local and national markets.
The cause-related marketing method introduced in this paper is one of the most modern ways of marketing. It seeks to attract and retain customers committed by increasing the credibility of the organization among customers by demonstrating the honesty and integrity of the organization's business. Three questions were raised in this study. The answer to this question is the research model. Based on the results of this study, Digikala Company customers had four responses: Sense of belonging, Loyalty Behaviors, Word-of-mouth advertising and Continuous participation in cause-related marketing and there were also four cause-related marketing strategies: licensing, established and collaborative programs and the factors such as cost place, cost value, quality of transactions, quality of formulation and approach to assistance were identified as incentive and disincentive factors of cause-related marketing strategies.
Conclusions
This study outlines key points for brand managers. It can be helpful especially when making decisions on different advertising strategies for the brand as well as advancing selected outcome strategy. These results suggest how customers respond to marketing responses and what strategy companies can implement their cause-related marketing thoughts and advance cause-related marketing strategies relaying incentive factors and removing the disincentive factors, In this study, four strategies (licensing, established, collaboration and exchange programs) were identified to implement cause-related marketing.
Companies can choose the appropriate strategy according to the internal conditions of company and conditions prevailing on the market, of course, their goals and according to factors that were identified as incentive and disincentive factors of these strategies (cost place, cost value, quality of transactions, quality of formulation, and approach to assistance) plan and target in order to implement it. On the other hand, since the beginning of the 1990s, widespread pressure has forced companies to take responsibility for their activities in the society. Such pressure caused companies to turn to social responsibility and increase their cooperation with non-profit organizations to contribute to charity affairs and enhancement of company image.
One of the strategies of corporate social responsibility is cause-related marketing. The results of this study in section of customer response to cause-related marketing show the positive effect of this strategy on customers and their positive responses on this kind of strategy can be a compelling reason for companies to choose cause-related marketing as a way to implement corporate social responsibility.