Introduction
Nominated managers have substantial effects on the performance of the company through their decision makings, strategic plans and implementation of the strategies. The insider successions play the roles with more loyalty and acquaintance to the board and organization. Their contributions are motivation because of their career development and attractiveness to the company for the careers flexibility. On the other side decision making as the main task of managers straightly effects on the personal and organizational outcomes through different styles of making. Nowadays complicated and difficult environment increases essential need to make the right decisions by management.
Companies wisely accept this situation as the modern management challenge and obviously effective organization performance is to align the vital factors. Successful managers focus on strategic visions, the organization goals and its directions via adjusting and developing the organization resources and capabilities. To concur this approach; beside effective decision making styles , the organizational structure as the design by which the company administrated to regulate the power, decisions and activities will be considered a critical subject. Making a direct relationship between the human factor of decision making and organizational structure seems to be essential.
The effective structure and strategic objectives achieve through a decision making framework supporting the overall mission of the organization. No doubt that succession planning is a strategy for identifying and developing future leaders of the organization and crystal clear that a supportive structure along with cooperative and committed managers will be facilitating items to conduct effective succession planning management program which requires to be customized according to and aligned with the needs, vision and mission of the organization to be succeeded .Whereas substantial theorizing and empirical researches concentrated on each and every aspects of the study variables, less pay attention to the decision making styles relation and organizational structure as one of the contextual factors which means always related to something; a concern, cause or reason. Even if there is any strategy to tighter the likely relation. This study is focused on finding if succession planning as a systematic program can play a practical effective role to make more concrete relation between decision making styles and organizational structure.
Each and every organization can be survived and sustained only if they have qualified workforce on board. The organizations must be sure of flexibility, sustainability and accountability overtimes. While increasing turbulence in employment process effects by organizational restructuring, budget cuts and complexities; succession planning gained more attention, not only because of the importance role of human resource management but also as a distinguished strategic for ensuring organization development and prosperity (Waruiru & Kagiri, 2015). Changes in workforce's attitude, their need to independency and flexible training opportunities (Coscio, 2006), also environmental revolutionary changes and requirements for having dynamic capabilities (Busine & Watt, 2005) highlight succession planning as an important program which attracts competent and qualified talent pools to make effective and competitive edges and finally satisfied customers at the same time. Even the public organizations confront with challenging issues such as globalization, downsizing, outsourcing, succession planning has contribution toward boosting the performance. Succession planning is a strategic deliberate systematic plan for ever-increasing problems related to growth, globalization and competitions.
Succession planning strengthened the talent pool and directly impacts on organizational growth and development of talented staff; so is a vital factor in competitive industries and obviously needs a systematic approach. Studies confirms that increasing the workforce commitment is one of the advantages that succession planning brings to the organization. Robbins & Judge (2018), found that by increasing the commitment and engagement of the workforce, the withdrawals will decrease and causes promoting the customers satisfactory outside the organization (Mcshane & Von Glinow, 2015). At the same time stronger believe in the organization values and positive culture will be formed.
Succession planning helps to manage talent pipeline, improve chance of retaining key personnel, make greater job satisfaction with higher performance and definitely needs the system involvement and top levels support. The Hanover report (Hanover Research, 2014). 2014) revealed that a succession programming is a valuable stage to recognize the goals and expectations of now and future, organizational changes, top management priorities, curricular approaches, decentralization and etc. which requires supporting decisions and even decentralized structure. In general, the process of succession planning demands four main steps including 1) Policy and the management commitments, 2) assessment and selection of the qualified candidates, 3) development of the candidates and finally 4) evaluation of the process efficiency. This process is a kind of business strategic plan that should be well organized and connect with the main organizations objectives (Zarei Matin, et al. 2014).
Strategic succession planning improves the retention rates and even enhance the financial performance and operational effectiveness (Trepanier & Crenshaw, 2013). Rational and strategic approach in succession planning maintain the organization alive via promoting transition of successful leadership. Therefore, planning and development, selection and training, sustainability and evaluation steps would be recommended to build a formal systematic mechanism which is the concept of succession planning and to be implemented successfully and boosted requires factors such as engaged managers, reassuring culture, formalization and documentation, statistical system.
Succession planning is a strategic cycle based process which begins by analyzing the best candidate to be appointed according to the current and future visions and requirements of the organization. Therefore, due to have a successful implementation of the process, top manager support and strategic planning would be two essential subjects. These factors are challenging issues in organizations during succession plan proces. Management’s support through his decisions is also prominent whether structures are formal or informal. Managers should be aware that succession planning is an integral element and the success depends on having the right ready competence workforce at the right time (Mkama, 2013).
Training, support and commitment of senior managers, clarified career path, positive visions, strong cultures, facilitator technology, flat structure and proper financial conditions are the succession planning outcomes which their lack considered as threats (Ebrahimi Mehrabani & Azmi Mohamad, 2011). Studies showed that the organizations with ability to implement strong business strategies and creating effective succession planning process will be profitable and competitive organizations as well (Eichenberger, 2017) and in contrary lack of succession planning system in place or missing a formal programs make difficulties for the organizations such as not filling the key positions in timely manner so they will be occupied by external candidates while there are constant horrors of turnover at key positions; potential replacements are never ready because of the lack in essential skills and finally the most qualified talents leave the organization. These are some problem areas which organizations face and never realize that it's just due to lack of formal planning and wrong decisions and accordingly the results would be disorder and chaos, poor image, bad publicity to stakeholders and cut down revenues and decrease in number of customers.
Having said the process, challenges and achievements of the succession plans, it is the decision maker’s turn to accept chaos in modern global economy (Hertz, 2013). External environments, features of organizational process and limited autonomy influence or even limit decision makings in public organization but beside all these challenges and hurdles, decision making is still one of the most predominant factors which effects organization practices, because every success or failure is the result of making decisions. Decision means finding an answer to a question and a selection between alternatives. Theories concentrate on its cognitive process by decision makers while it is cleared as internal process to gather information, evaluate and make a choice.
Finally, the best pay off alternative will be selected in decision process; although some studies found the best way to improve performance is strategic decision making, others reported rational decision makings as the effective method. Managers have different styles differ in terms of nature, effectiveness and outcomes. Having effect on life and attitudes of subordinates, directly in relation with self-esteem, satisfaction, self-efficiency and stress (Abood & Thabet, 2017). The decision styles do not act individually or independently, but in relation with other relevant critical factors such as values, believes, knowledge and skills, situations, culture, nature of task, time pressure and etc. The decision making styles are expression of decision maker's personal characteristics, environmental factors as well as specifications of duties and responsibilities. It means that decision made when the maker perceive, interpret data from surrounded environment. Scott & Bruce (1995), defined two main approaches; first decision making styles as a habitual pattern and second as individual characteristic mode of respond to decision making task.
They assessed decision making styles by general decision making styles consisting of five styles as rational, intuitive, dependent, avoidant and spontaneous. Rational style is a comprehensive search of gathering more information for logical assessments and are bounded by standards , laws and regulations to make the decision making predictable definition of intuitive styles explained as attention to details of information rather than logical and systematic way of research and rely on feelings ; dependent style is searching for others advices and guidance to make decisions and avoidant style attempts to escape the choice situation or delay the decision.
Spontaneous is a sense of prompt decisions to complete decision making process, the people because of time limitation stress (Ugurlu, 2013). Still may a question clicking the minds for the relation between decision and structure and a quick shortcut would be that decision making needs a solid defined and clear construct for empowering the managers in dealing with issues, creating efficiencies and dividing departments; illustrating the strategies, objectives and directions; assisting decision makers by flowing the information through different levels and making the managers to concentrate on the expected results ; distributing the made decisions and creating shortcuts to convey the feedbacks up and down for further steps and plans. Structure creates coordination and workforce division which are quite important during decision making process and facilitate decision making with appropriate reactions and provides efficient conflict solutions between departments.
It is a concept that organizes and coordinates all organizational activities via structural and contextual dimensions. Structural dimensions consisting of formalization, centralization and complexity exploring as decisions limits, work relationships and operational standard rules, regulations, authority in decision making strategy and resource allocation (Dekoulou & Trivellas, 2017).
The contextual dimensions listed as strategies, culture, technology, environment and size are the main points of unseen characteristics of the organization. These aspects expose fruitful information about the organization and their differences. For sustainable performances, decisions have to be aligned to reach the goals, as studies confirmed that different decision making styles effect the organization in different ways (Rehman, Khalid & Khan, 2012). Studies confirmed a strong and predictable effect of structure on the organization performance through decisions and their outcomes.
On the other side structures should be supportive and in line with the strategies. Also decision styles boost organizational performance by conducting the competitive strategies. The smart organization participate in making decisions to be aligned and make effective empowerment which is one of the succession planning characteristic as well. Decision alignment advantages support quality decision making and is a key component of success. The structure supports decision quality and fosters alignment. Mentioning the effects of succession planning and explaining different aspects of decision making styles and structure, this study aimed to pursue if succession planning can bond the likely relation between decision making styles and organizational structure in Agricultural Jihad organization of Kerman province. As far as researcher's information the identity of this research is unique.
Methodology
According to the purpose of the research and in order to collect the necessary information, we used appropriate methodology. The localized, adjusted and finalized version of the questionnaires for each variable distributed and collected to retrieve the required data from Kerman Agricultural Jihad Organization 461 employees including both managers and staff with diversity of 53.57% male and 46.42% female. 17.13% under age 30, 59.43% between age 30-45 and 23.42% above 45 years old age. 56.39% having the bachelor, 33.18% master degree and 10.41% having PhD degree.
Decision making styles questionnaire consisting of thirty-one indicators categorized under five styles created by Scott & Bruce (1995), namely as rational, intuitive, spontaneous, dependent and avoidant style. Organizational structure questionnaire having forty-five indicators under two main structural sorted by three components of formalization, centralization and complexity and contextual dimensions listed by five components of organization’s size, technology, environment, strategy and culture (Robbins & Judge, 2013). Succession planning running as a mediator measured by conceptual model presented by Kim (2006), consisting of four main components of (1) organizational policy dividend into the management commitment to succession planning and defining key positions ; (2) evaluation of the candidate divided into defining the competencies and selection of the qualified candidates ; (3) candidate development dividend into development by outside and inside company training and developing methods and (4) evaluation of the succession planning efficiency in the organization dividend into the process and the results assessment which all make thirty indicators. Before distribution; the validity and stability of the questionnaires assessed in terms of content and construct validity by Delfi method and t test using Likret scale.
The outcomes showed all t indicators above 3.00 so they considered as approved and remained with no changes or omissions. Respectively the construct validity tested by using explanatory factor analysis. Applying validity test and sampling accuracy method (KMO) implied KMO value for decision making styles is 0.939, for organizational structure is 0.917, and for succession planning is 0.925 (p <0.05). Values above 0.7 considered as meaningful scales and statistics above 0.05 considered meaningful in Bartlett’s test so all reached acceptance. Stability of the questionnaires evaluated via two parts of internal consistency reliability by Cronbach’s Alpha and its result showed values above 0.7 were approved with high consistency reliability.
The construct stability evaluated by composite reliability (CR) and average variance extracted (AVE). Composite reliability calculated and the outcomes approved CR of the variables and the result showed research values are highly acceptable in terms of consistency reliability of the variables reaching the values of decision making styles (0.935), organization structure (0.850) and succession planning (0.954). AVE calculated results for decision making style (0.803), organization structure (0.740) and succession planning (0.839) approved a high construct reliability of variables. The results showed in Table 1. By approving data collection instrument, went through by stratified random sampling method and the sample size considered 461 people and it took eight months to collect the data and gather the filled questionnaires.
Table 1 Validity and reliability results.
| Construct | No. of questions | Cronbach Alpha | CR | AVE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organizational Structure | 45 | 0.864 | 0.850 | 0.740 |
| Structural dimensions | 19 | 0.763 | ||
| Contextual dimensions | 26 | 0.849 | ||
| Succession planning | 30 | 0.914 | 0.954 | 0.839 |
| Policy | 7 | 0.781 | ||
| Candidate assessment | 9 | 0.753 | ||
| Candidate development | 6 | 0.873 | ||
| Evaluation of the efficiency | 8 | 0.903 | ||
| Rational style | 6 | 0.798 | 0.953 | 0.803 |
| Intuitional style | 4 | 0.750 | ||
| Spontaneous style | 4 | 0.852 | ||
| Avoidant style | 3 | 0.759 | ||
| Dependent style | 2 | 0.736 |
Results and discussion
Analysis carried out through their reference to the content of the instrument used. Path coefficient implied the relation between variables. The relations approved positive which are shown at Table 2.
Table 2 - Path coefficient analysis.
| Relation | Result | P value | T value | Coefficient | Hypothesis / Path |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Supported | 0.001 | 8162 | 0.455 | Rational Style → Succession Planning |
| Positive | Supported | 0.001 | 8.002 | 0.421 | Intuitive Style →Succession Planning |
| Positive | Supported | 0.011 | 2.538 | 0.106 | Spontaneous style →Succession Planning |
| Positive | Supported | 0.001 | 4.052 | 0.184 | Avoidant Style →Succession Planning |
| Positive | Supported | 0.001 | 6.054 | 0.395 | Dependent Style →Succession Planning |
| Positive | Supported | 0.015 | 2.432 | 0.135 | Rational style → Organizational structure |
| Positive | Supported | 0.005 | 2.806 | 0.150 | Intuitive style → Organizational structure |
| Positive | Supported | 0.001 | 7.363 | 0.323 | Spontaneous style→ Organizational structure |
| Positive | Supported | 0.017 | 2.649 | 0.129 | Avoidant style → Organizational structure |
| Positive | Supported | 0.035 | 2.107 | 0.132 | Dependent style→ Organizational structure |
| Positive | Supported | 0.001 | 7.022 | 0.667 | Succession planning → Organizational structure |
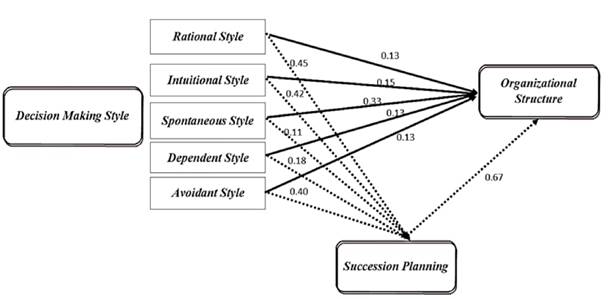
At the next step the aim is to receive the scales of each direct relation by running path coefficient analysis. Going through the process the results showed direct relations between decision making styles including rational (0.455), intuitional (0.421), spontaneous (0.106), avoidant (0.184) and dependent (0.395) with succession planning. Also emerged from the results that relation between rational style (0.135), institutive style (0.150), spontaneous style (0.323), avoidant style (0.129), and dependent style (0.132) with organizational structure took the mentioned positive values. The outcomes cleared a positive value relation between succession planning and organizational structure measured as (0.667).
Finally, the study looked for evaluation of the indirect relations between decision making styles and organizational structure by effected by the mediation of succession planning which illustrated in Table 3. The indirect relation between decision styles with organizational structure found as following values: rational style (0.438), institutional style (0.431), spontaneous style (0.394), avoidant style (0.252) and dependent style (0.395). As the results, it can be reach to the idea that indirect relations between decision making styles and organizational structure through succession planning is clearly stronger than direct effect.
Table 3 - Direct and indirect effects, path coefficient analysis.
| Total | Indirect effect | Direct effect | Hypothesis |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.455 | -- | 0.455 | Rational Style → Succession Planning |
| 0.421 | -- | 0.421 | Intuitive Style →Succession Planning |
| 0.106 | -- | 0.106 | Spontaneous Style →Succession Planning |
| 0.184 | -- | 0.184 | Avoidant Style →Succession Planning |
| 0.395 | -- | 0.395 | Dependent Style →Succession Planning |
| 0.438 | 0.303 | 0.135 | Rational Style → Organizational Structure |
| 0.431 | 0.281 | 0.150 | Intuitional Style → Organizational Structure |
| 0.394 | 0.071 | 0.323 | Spontaneous Style → Organizational Structure |
| 0.252 | 0.123 | 0.129 | Avoidant Style → Organizational Structure |
| 0.395 | 0.263 | 0.132 | Dependent Style → Organizational Structure |
| 0.667 | -- | 0.667 | Succession Planning→ Organizational Structure |
Based on the mentioned relations both direct and indirect, by applying structural equation modelling reached to the following presented model in Figure 1.
It would be obvious that just exactly as other elements of the organization, the decision making styles need supportive, appropriate and alignment structure as contextual vital element. On the other side any new changes in organizations will create more challenging situation to decision makers. At certain points all organizations have one thing in common, they must deal with changes to improve.
Nowadays one of the manager’s challenges is succession planning management as a systematic strategic plan and as one of the available remedies to assure of having talented developed and ready employees always available in talent war world. Knowing how to get the best balance decisions will make an organization great and on the other side succession planning strategies will bring enforcement to the employees, satisfaction to the customers and workforce, increasing the revenue and respectively success to the stakeholders.
The results supported the study hypothesises and showed logical answers for the implied questions of the research. The statics cleared an explanatory meaningful and direct relation between decision making styles and organizational structure. Findings also confirmed that undoubtedly must be a balance terms and situation between what and how the managers make decisions and what is called as organizational structure as the way to conduct, rule, behave and effect. In the meantime, findings revealed that the relation between decision making styles and succession planning is a meaningful positive relation. Succession planning program requires strong and solid cooperation of a committed management and senior members of the company.
Conclusions
The managers experience, personal characteristics, specific situations will shape their decisions and the decisions should be made toward and in line with strategies and goals indeed. The succession planning program in action and various instructions and instruments to conduct it successfully and thoroughly demands any mode of decision making styles from senior managers to cope with upcoming hurdles to proceed.
Based on the study literature and the analysis findings, the succession planning execution requires formalization, centralization, systematic and regular steps in line with cooperative factors of management commitment and organizations structure. Clearly organizational structure is considered vastly as one of the factors for implementation of a successful strategy because the organization performance and reaching the goals is effected directly by how the activities are structured.
Elements of organizational structure define the positions and boundaries of decision makers, relations, coordination, integration and culture of the organization. The strategic plans such as succession management create a must for having more and more solid relation between decision making styles and structure of organization.
Respectively an operating succession planning management in Kerman province Agricultural Jihad organization as a strategic plan stabilize and toughen the relation between decision making styles and the organizational structure. Respectively and based on the close links, organizations which step toward building succession planning systems not only gain its vast positive privilege and cultivate expertise for current and future needs but also make a bridge to unify the binds between the critical factors of organization such as decision making and organizational structure to have an ideal performance.