Meu SciELO
Serviços Personalizados
Journal
Artigo
Indicadores
-
 Citado por SciELO
Citado por SciELO
Links relacionados
-
 Similares em
SciELO
Similares em
SciELO
Compartilhar
Podium. Revista de Ciencia y Tecnología en la Cultura Física
versão On-line ISSN 1996-2452
Rev Podium vol.19 no.1 Pinar del Río jan.-abr. 2024 Epub 19-Abr-2024
Original article
Activities to implement the pre-sports game through the combination of handball - football in university students
1Universidad Técnica Luis Vargas Torres, Esmeraldas. Ecuador.
Games as recreational activities constitute an important element in the development of the pedagogical process of Physical Education; tt contributes to collective work, formation of values such as: courage, perseverance, discipline, honesty, camaraderie, organization, respect for the rules, among others, which makes it contain great biological psychological and pedagogical value evidenced in its activities and in the benefits it brings to human beings. However, despite this approach being a strength in the Cuban educational system, the pre-sports game is not promoted from a scientific and academic point of view to achieve these aforementioned components. That is why the objective was projected to characterize the pre-sports games implemented by the teachers of the Physical Education department in the first two years of professional training at the Universidad de Oriente, Cuba. As empirical methods, an interview with teachers and an observation guide dedicated to the teaching-learning process in Physical Education are applied. An attempt is made to know the potential and weaknesses that pre-sports games have to improve the physical and sports skills of these students, in addition to the values in which comprehensive training can be contributed from these practices. The insertion of this type of games has had a very positive level of opinion from students and teachers.
Keywords: pre-sports games; Physical Education.
INTRODUCTION
Physical Education, as an integral part of the multilateral and harmonious formation of the personality, constitutes a pedagogical process aimed at the development of the individual's physical performance capacities based on the morphological and functional improvement of their organism, the formation and improvement of their motor skills, and the acquisition of knowledge and the development of their moral and volitional qualities, so that they are able to fulfill all the tasks that society assigns them (Loscher, 2006).
Currently, the learning process places the active subject (the learner), conscious and transformative, oriented towards an objective in interaction with another subject (teacher-student, student-student) and their actions with the object at the center of attention, with the use of various media in specific socio-historical conditions (Nozal, 2007).
One of the activities that attracts the most attention, especially at the beginning of Physical Education classes, is the practice of pre-sports games. These are responsible for introducing children to the basic concepts of sport and are not only elements that motivate students, but also commit the teacher to improve themselves further and find in their study innovative ways to captivate the insertion and passion of their students. for sports.
Games as recreational activities constitute an important element in the development of the pedagogical process of Physical Education; it contributes to collective work, formation of values such as: courage, perseverance, discipline, honesty, camaraderie, organization, respect for the rules, among others, which makes it contain great biological psychological and pedagogical value evidenced in its activities and in the benefits, it brings to human beings. This dedication includes the quality of life, so it is essential for the Physical Education teacher to select and investigate which games are conducive to each activity that allow the enjoyment of the learners and in what way these games facilitate the fulfillment of the formative and educational function as a necessary component for the multilateral and harmonious formation of the personality of man. (Otegi et al., 2014)
The activities developed in the game take on a character specific to the content, giving rise to very important changes in the child, since he or she is concerned about the internal aspects of said activity and its interrelationships that range from playful expressions to real ones. Through these, favorable conditions are created for the development of the moral and volitional physiognomy of the character; self-control is required of students; the capacity to self-regulate their actions is encouraged; it favors initiatives, independence in motor actions during the dynamics of the game, the increase to help teammates in the fight and common unity for victory as well as the capacity to overcome difficulties. When these qualities are repeated repeatedly in games, they become favorable moral and volitional traits, they become habitual and manifest in the social life of each of them (Builes-Ortiz, Aguirre-Navales, 2019).
Games constitute an important element in the education and formation of behavioral habits and quality of life; They become a means for Physical Education from an early age. It is a priority in this process to achieve a good state of physical and mental health, develop capacities, basic motor and sports skills, form values, attitudes and norms essential for daily tasks (Aules, 2020).
According to Betancourt et al., (2020), the results of pedagogical observations of Physical Education classes, in the review of the preparation (planning) of the subjects, at the teaching levels, especially in Higher Education, the results of reports related to the implementation and validation of the subject programs of the Study Plan `D' (study plan preceding the current E), have expressed the need to incorporate pre-sports games in the pedagogical process of this subject. The reasons that make these games an important part of a class are the following:
They are ways and means that motivate and enhance the improvement of sports performance and physical efficiency.
They promote harmonious balance in the exercise of the different muscular planes during general physical conditioning. (p. 35)
The intention of this work consists of the proposal of the pre-sports game "MIXED BF", interpreted as a combination between Handball and Soccer. This fair fusion has managed to become a means that favors the improvement of aerobic endurance and harmonious balance in the exercise of the muscular planes and extremities of the upper and lower body of children and adolescents during general physical conditioning (warming up) in the pedagogical process of Physical Education.
On this topic, Popovych et al. (2020) state that pre-sports games can be a complement to the teaching-learning process of sports technique and its effectiveness, despite the short implementation time; stimulate the athlete with different variants of pre-sports games; avoid negative bioadaptation to physical stimulus. On the other hand, girls enjoy training as the game method is prioritized, resulting in greater motivation towards achieving the specific objectives of basketball sports training. It is recommended to extend the study to a larger sample of players of different ages and educational centers.
According to Peláez (2021), the logical structure of the games, the motives and interests of the participants, the circumstances in which each one is forced to participate, requires that the teacher use the methodological steps for teaching the games and with this will guarantee the children's mastery of the game content and their active participation in them.
Veloz and Palchisaca (2021) emphasize that the work in pre-sports games is aimed especially at acquiring initial skills and movements that will serve to later develop sports skills. In fact, sports games are the maximum expression of games, they carry a high degree of demands related to the level of competition and both individual players and the team must know the rules that are used officially.
Popovych et al. (2021) defend the idea that the mental states of pre sports games constitute significant characteristics in the regulatory function of an athlete. In the course of this extensive training, over time the regulatory function of mental states becomes a key function for competitive activities. A predominant mental state in pre-sports games affects the content of sports activities.
Muñoz and Martínez (2021) for their part, emphasize that the purpose of sports games is for children to learn the first rules of sport, in addition to certain skills. The intention is not for them to be excellent in sporting activity, but rather for them to acquire the most significant skills in their contact. Among other aspects, they recommend to improve concentration: leave negative thoughts aside when the competition approaches, motivate themselves while setting goals, and establish routines to structure thoughts that allow them to maintain attention on the present activity.
Majin et al. (2021) focus more on the practice of pre-sports games for children with disabilities, these authors affirm that the presence of these games not only addresses the affective-volitional area of the students, but that these activities organically release endorphins that are natural happy chemicals in the body that reduce stress hormone levels that often generate behavioral alterations in these children. So, these games can reduce cortisol levels, which is responsible for triggering anxiety, depression and self-aggressive and extremely suicidal behavior.
Specifically, in sports, Gómez (2022) points out that for the athlete to be successful in certain sports such as soccer, it is necessary to promote actions to guarantee that this individual is capable of mastering these components: endurance, speed, agility and coordination
Vargas-Cuenca and Ávila-Mediavilla (2022) continued the idea of those previous authors, but with a more experimental perspective since they pointed out a path of how to investigate the topic of pre-sports games from empirical methods such as: survey and observation sheet. The survey was prepared in the form of a questionnaire, directed at the coaches, in order to have an approach and from their experiences collect valuable information regarding their work methodology. The observation guide, was applied to adolescent students who practice the discipline of soccer in the Academies of the city of Macas with the purpose of verifying the progress obtained during their training process to date.
When analyzing this historical and conceptual framework, it is declared that although this initial exploration has been very valuable, it is clear that there is still a lot of ground to investigate and taking as reference the investigative forms used by such relevant authors as Vargas-Cuenca and Ávila-Mediavilla ( 2022) it has been decided to establish the objective of this work: to carry out a study on the characteristics of the pre-sports games implemented by the teachers of the Physical Education department in the first two years of professional training at the University of Oriente, Cuba
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The population of this research coincide with the sample, because the 25 students of the first year of the Degree in Physical Culture and the 29 teachers of the Department of Physical Education (PE) of the Universidad de Oriente in the school year 2022-2023 were involved.
In order to seek more information on this topic, the authors of this work decided to replace the survey with an interview with the teachers and maintain an observation guide, but focused on the teaching-educational process and not only the students, in this case, to five Physical Education classes.
Brief characterization of the teachers and students participating in the research:
The teachers have the necessary preparation and capacity for the development of the research, they have a degree in Physical Culture and 95% of them have continued their academic improvement, whether in Master's, Specialty or postgraduate courses that have helped them to maintain their knowledge and skills on the topic at hand. The teachers expressed their good will and disposition to be the object and subject of research, they collaborated with their responses in a coherent manner.
The students who make up the first group in the first year of the degree; 87% chose the career as their first choice. In them, the male gender prevails for 90%. Only 45% are boarders, who live together in the student residence and take advantage of the center's sports areas during extra-class hours, although in general, more than 60% practice sports systematically.
Regarding the dimensions and indicators used in the research, we start from the definition pre-sports games are a recreational, motor-type form intermediate between games and sports, which contain elements related to a sports modality and which are the result of the adaptation of sports games with a much lower structural complexity and function, due to their structural content and purpose allows the development of motor skills that serve as a basis for the development of sports skills since it contains elements related to a sports activity (p. 28)
Taking this criterion into account, the authors of this work establish the following dimensions: 1- motor 2- sports 3-structural 4- developer (focused on sports skills) (Table 1)
Table 1. - Dimension-indicators relationship
| Dimensions | Indicators* | ||
| D-Motor | Development of gross muscle control | Development of fine muscle control | - |
| D-Sports | physical well-being | Mental and spiritual well-being | Motivation towards practicing sports |
| D-Structural | planning | execution | control |
| D-Developer (skills) | h-cognitive | h-socioemotional | h-techniques |
Note: (*) These indicators were selected within their respective dimensions because they are the ones most closely related to the training of PE teachers.
To prepare the observation sheet, the following indicators were taken into account:
Pre-sports games that develop gross and fine muscle control (in what way) are inserted into the classes.
These pre-sports games in class contribute to physical, mental and spiritual well-being.
These games motivate the practice of sport. They are prepared with originality and creativity by the teachers.
It is perceived in the classes that these games increase students' knowledge, they feel positive emotions and learn algorithms and procedures to resolve situations or improve sports skills.
On the other hand, in the survey applied to teachers, these indicators were taken into account as follows:
How do you methodologically conceive these pre-sports games, refer to their three phases (planning, execution and control)?
Comment on some experience (if possible) about a pre-sports game that you have used in class and that has provoked new knowledge, feelings and/or skills.
How do the pre-sports games you use in class take individual differences into account?
Comment on the material conditions to sustainably insert pre-sports games.
RESULTS
Through the observation guide it was determined that:
This classification is not taken into account to implement pre-sports games: The few that are used, whether related to passing the ball or dribbling corresponding to basketball, are only used to motivate the class, not with the intention of developing muscular control
In a certain way, it can be argued that pre-sports games promote well-being, especially spiritual, since it is perceived, that students feel good when practicing it, but potentially not physically, since these games are not implemented in all classes, only two out of five and considering the low frequency and short duration, no notable development of physical abilities is estimated.
The games used, despite being well accepted by the students, do not guarantee creativity and originality in the teachers since all of them are only transferred from other traditional sports practices (basketball, volleyball, soccer, among others).
Although naturally practicing a sport actively and consciously always generates new skills and knowledge, these are not the purposes of the games used. There is an atmosphere of joy in the classes as soon as these games are played and if more emphasis were placed on the cognitive, procedural and axiological values of these sports, the results would be much more satisfactory.
Regarding the interview applied to the teachers, the results listed below were obtained:
Of the 20 teachers interviewed, only 10 % (2) of them declare having conceived these games from planning, execution and control as an organized structure, the purpose is more focused on motivating the PE class, dismissing the value they have. these games to discover talents and strengths regarding the practice of sports.
Only 20 % of them comments on examples where pre-sports games have generated desires for sports practice and this was the case of two students who made baskets from a distance and three others who scored a goal in a penalty shootout organized by two teams in the class.
There was a case where a diagnosed teacher approached a student who had been absent due to health problems to teach him how to act from the soccer goal to defend the team. This professor was interviewed and with great responsibility he argued about this case.
After analyzing these insufficiencies, the work team decided to find a solution to take advantage of many of the advantages offered by these pre-sports games.
Below is an example of the activities that are proposed to work with these students from the characteristics that correspond to a pre-sports game. In this sense, the dimensions and indicators of the initial diagnosis that were previously presented are taken into consideration.
Name of the game. Mixed BF. (handball-football).
Aim: exercise technical fundamentals of handball (dribbling, passing and receiving the ball, movement with or without the ball and shooting on goal) and football (passing and receiving the ball, movement with the ball (driving and dribbling) or without the ball and hitting or shooting on goal). During the game, cooperation is developed to promote the harmonious balance of physical conditioning (warming up) of the muscular planes and extremities of the upper and lower body of children and/or adolescents practicing in the context of the pedagogical process of Physical Education or Sports Training.
Material: two (2) balls that will be used are: a female or male handball and another 1 indoor or official soccer ball, two official handball goals or two mini goals 2m wide by 1m high.
Number of participants: it is made up of two teams with the same number of members. They are applicable for both sexes.
Organization: the members of each team will be dispersed on each of the fields to be defended and facing the opposing team's field. Prior to the start of the game, the teacher together with the captains of each team will determine: (1) the first team which will begin the offensive and (2) with which of the two balls the game will begin.
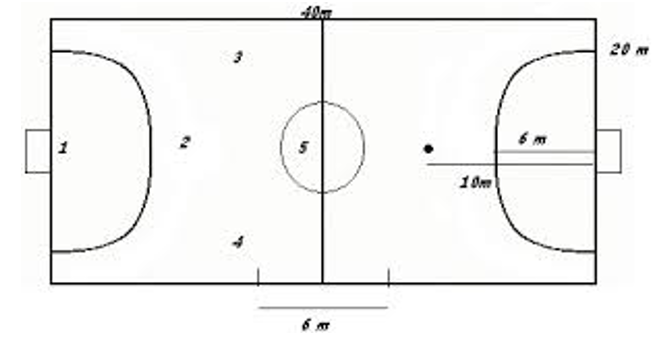
Diagram: the proposed game must be played on a rectangular field that has the following dimensions: 10 meters wide x 20 meters long or 20 meters wide x 40 meters long, with a semicircular crescent (goalkeeper's area) of 4 or 6 meters respectively field where a handball goal must be located; all terrain lines must be five centimeters wide (Figure 1).
Development: from the midline and center of the field to the teacher's whistle, the game begins by performing a serve. The main skills that the players must practice in the development of the offensive game are: handball (dribbling, passing and receiving the ball, moving with or without the ball and shooting on goal) and football (moving without the ball, passing and receiving the ball, driving and dribbling with the ball, hitting or shooting on goal).
During game development if one of the members of a team commits a foul on offense, carries the ball out of bounds or scores a goal, the opposing team that was on defense goes on offense. At that moment, the teacher-referee will always decide with which of the two balls to continue playing, and consequently the technical skills they must use must be in accordance with the ability of each sport. Included are shots on goal that will be validated after passing the midline of the field of play to the area that delimits the goalkeeper's area. The use of one ball or another during the game will be determined by the teacher.
Rules: Passive or inactive players are not allowed throughout the game; they may be penalized with the loss of the ball or a penalty in favor of the opposing team.
Each team designates or selects a goalkeeper who during the game may leave their area according to the collective strategy or when the teacher determines it, taking as a premise the dynamics or intensity of the game.
Variant: After the game has been developed, the teacher can make variants and along with these the introduction of new rules. The variant is that, using the same organization, the movements can be changed, complexity increased, among others, always meeting the set objective.
Classification: the aspects of classification must be taken into account, such as: form of participation, duration of the game, complexity, characteristics, location and activity to be carried out.
The implementation of the proposal constitutes a means that favors; the motivation to know and practice the essential technical elements of one or another sport (handball and soccer), students exercise all the muscular planes in a balanced way during the game; this is one of the ways for the systematization and integration of knowledge and skills.
The game based on the selected terrain and the time available for its development will favor the general physical conditioning of the students in the introductory part of the classes, as well as a means for physical preparation (aerobic endurance or continuous work).
DISCUSSION
In this work, it was possible to demonstrate through the scientific method that despite the usefulness of pre-sports games to enhance the PE class, theoretical and practical approaches are still insufficient to achieve better results in the preparation and behaviors of the students of Physical Culture in training. However, there are works that by making certain transfers can be taken into account to reinforce certain dimensions. This is the example of Páez et al. (2022) which offers a booklet of compensatory corrective pre-sports games for schoolchildren with intellectual disabilities, these consist of 15 games and include: objective, name of the game, motor skills to be formed, communication skills to be formed, physical capacities that favor their development, method to use, procedures and organizational forms, materials, organization, development, rules and variants.
Liens and Rodríguez (2023) for their part, also contribute to the implementation of sports games, but from the familiarization of students with the sports motor skills of volleyball; a didactic-methodological alternative is proposed to be used in Physical Education classes. In this reference work, not only technical aspects of sport are addressed, it also contributes to forming moral, social and volitional qualities of the personality. Also contributing to the well-being that is aspired through pre-sports games, it contributes to the improvement of the health status of the students, as well as their spiritual, biological, psychological and social growth.
Since during the diagnosis, basketball as a sports game was one of the most used, the work of Tipán and Dávila (2023) is recognized and consulted, who offers a proposal to motivate high school students to practice this sport, dosing short periods of time in their PE classes where students practice this sport in a competitive and developmental way. Complying with the inclusive sphere in the role of pre-sports games, it is important to add that, in the research of Cruz and Artunduaga (2023), methodological steps are provided to encourage motor skills in children with certain disabilities, especially visual disabilities cognitive and competitive that pre-sports games offer.
CONCLUSIONS
In this work, some theoretical references are proposed that demonstrate the benefits produced by the insertion of pre-sports games in the PE class and the limitations that exist regarding the knowledge and implementation of these games in the diagnosed teaching-learning process.
In this diagnosis, results were obtained that reveal the need to systematically establish a group of pre-sports games that not only develop the technical part of the sport, but also the cognitive, motor, axiological and strategic part.
From the research carried out, dimensions such as motor, sports, structural and developmental were raised.
The proposed activities have received a very positive level of acceptance from the diagnosed students and teachers.
REFERENCIAS BIBLIOGRÁFICAS
Betancourt, F. F. B., Quilca, A. D. M., & O'farrill, A. R. G. (2020). Juegos predeportivos y perfeccionamiento del ataque en voleibol escolar. Lecturas: Educación Física y Deportes, 25(266). https://efdeportes.com/efdeportes/index.php/EFDeportes/article/download/2321/1257?inline=1 [ Links ]
Cruz, M. M. J., Verano, C. D. M., & Artunduaga, E. P. (2023). Juegos predeportivos del atletismo paralímpico como medio para favorecer las actitudes hacia la discapacidad visual. Lúdica Pedagógica, 37(1), 1-14. https://revistas.pedagogica.edu.co/index.php/LP/article/view/18233 [ Links ]
Popovych, I., Pavliuk, M., Hrys, A., Sydorenko, O., Fedorenko, A., & Khanetska, T. (2021). Pre-game expected mental states in men's mini-football teams: A comparative analysis. Journal of Physical Education and Sport, 21, 772-782. https://doi.org/10.7752/jpes.2021.02096 [ Links ]
Liens, B. G., & Rodríguez, V. L. O. (2023). Juegos predeportivos y familiarización con las habilidades motrices deportivas del voleibol. Revista peruana de investigación e innovación educativa, 3(1), e24732-e24732. https://revistasinvestigacion.unmsm.edu.pe/index.php/repiie/article/download/24732/19425/91389 [ Links ]
Loscher, A. (2006). Juegos predeportivos en grupo. Editorial Paidotribo. https://books.google.es/books?hl=es&lr=&id=9x9sztwy72IC&oi=fnd&pg=PA69&dq=juegos+predeportivos&ots=z7g-tWPpIG&sig=6-A4a5MMdzcOsfY-6_9w12jaY28#v=onepage&q=juegos%20predeportivos&f=false [ Links ]
Otegi, J. E., Del Barrio, S., Urdangarin, C., Usabiaga, O., & Oiarbide, A. (2014). Ganar, perder o no competir: la construcción temporal de las emociones en los juegos deportivos. Educatio Siglo XXI, 32(1 marzo), 33-48. https://revistas.um.es/educatio/article/view/194051 [ Links ]
Majín, Y. R., González, M. D. L. M. Z., Caveda, D. L., & Morgado, E. Z. C. (2021). Juegos pre-deportivos de fútbol y sus beneficios para estudiantes con discapacidad intelectual (Revisión). Revista científica Olimpia, 18(3), 208-220. https://revistas.udg.co.cu/index.php/olimpia/article/view/2753/5441 [ Links ]
Muñoz Casallas, O. A., & Martínez Guana, C. C. (2021). Los juegos predeportivos como estrategia para el mejoramiento de la concentración. Universidad Libre. https://repository.unilibre.edu.co/handle/10901/19323 [ Links ]
Páez Basabe, M., Arcia Melgarejo, S., Escalona García, C., Vargas Géliga, E., & Darias Ávila, N. (2022). Folleto de juegos predeportivos correctivos compensatorios para educandos con discapacidad intelectual. Podium. Revista de Ciencia y Tecnología en la Cultura Física, 17(3), 1006-1017. http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?pid=S1996-24522022000301006&script=sci_arttext [ Links ]
Peláez, E. L. T. (2021). Incidencia de los juegos predeportivos en el desarrollo de la técnica del lanzamiento en mini baloncesto. Lecturas: Educación Física y Deportes, 26(278). https://efdeportes.com/efdeportes/index.php/EFDeportes/article/download/3030/1427?inline=1 [ Links ]
Popovych, I., Pavliuk, M., Hrys, A., Sydorenko, O., Fedorenko, A., & Vargas-Cuenca, G. M., & Ávila-Mediavilla, C. M. (2022). Juegos predeportivos como estrategia metodológica en la práctica del fútbol en adolescentes escolarizados. CIENCIAMATRIA, 8(3), 713-737. https://www.cienciamatriarevista.org.ve/index.php/cm/article/view/800 [ Links ]
Tipán, V. A. C., & Dávila, L. E. L. (2023). Juegos pre-deportivos para favorecer el desarrollo de los fundamentos técnicos del baloncesto en los estudiantes del bachillerato de la Unidad Educativa Pángua. Polo del Conocimiento, 8(7), 263-289. https://mail.polodelconocimiento.com/ojs/index.php/es/article/view/5785 [ Links ]
Quishpe Veloz, K. A., & Torres Palchisaca, Z. G. (2021). Juegos Predeportivos en el Proceso Formativo de la Natación. Revista Arbitrada Interdisciplinaria Koinonía, 6(Extra 2), 546-567. https://dialnet.unirioja.es/servlet/articulo?codigo=7968478 [ Links ]
Received: November 13, 2023; Accepted: December 19, 2023











 texto em
texto em