Meu SciELO
Serviços Personalizados
Artigo
Indicadores
-
 Citado por SciELO
Citado por SciELO
Links relacionados
-
 Similares em
SciELO
Similares em
SciELO
Compartilhar
Revista Ciencias Técnicas Agropecuarias
versão On-line ISSN 2071-0054
Rev Cie Téc Agr vol.24 no.1 San José de las Lajas jan.-mar. 2015
ARTÍCULO ORIGINAL
Development of a citation style language CSL to describe the formatting of citations, notes and bibliographies of agricultural scientific articles
Desarrollo de un lenguaje de estilo de citas CSL para asentar citas, notas y bibliografía de artículos científicos agropecuarios
M.Sc. Rafael Cervantes Beyra,I Dr.C. Daniel Ponce de León,I Ing. Daybelis Fernández Valdés,I Dr.C. Carlos Balmaseda Espinosa,II M.Sc. Arturo Ocampo RamírezIII
I Universidad Agraria de La Habana, San José de las Lajas, Mayabeque, Cuba.
II Universidad Estatal Península de Santa Elena, Ecuador.
III Instituto Politécnico Nacional, Escuela Superior de Ingeniería Mecánica y Eléctrica, Unidad Zacatenco, Cuidad de México, México.
ABSTRACT
The development of files of citation styles that could be connected to reference management softwares is a viable option to reduce the errors in form of the articles sent to the agricultural journals. Sometimes, the publishing house committees do tedious works of bibliographical correction that often end with the return of numerous documents for this reason. The styles CSL (processors of citation, notes and bibliographies) describe the formatting of citations and bibliographies according to the styles of every journal and can be loaded by a wide range of citation programs; therefore constitute a powerful and indispensable tool in the making of scientific article. For that reason, the objective of this work was to development a citation style language CSL based on the guidelines ISO 690:2010 to describe the formatting of citations, notes and bibliographies of the agricultural scientific articles of the Revista Ciencias Tecnicas Agropecuarias (RCTA). For it, was used the CSL scheme v1.0, with complex XML based language, character encoding utf-8 and formatting of citations in text author-date. The operations of edition and validate were realized with the text editor Notepad ++ v4.7.5, the Visual (on-line) Publishing CSL and the (on-line) Validator.nu. As result, was obtain a file CSL that is supported by 25 reference managers that allows formatting the citations, notes and bibliographies of the agricultural scientific articles through of the style of the journal RCTA, according to the guidelines ISO 690:2010.
Key words: reference manager, citation style language, agricultural scientific articles.
RESUMEN
El desarrollo de ficheros de estilos bibliográficos que puedan ser acoplados a gestores de información científica, es una opción viable para reducir los errores en forma de los artículos que se presentan en las revistas de corte agropecuario. En ocasiones, los comités editoriales se ven envueltos en tediosos trabajos de corrección bibliográfica que muchas veces terminan con la devolución de numerosos documentos por este motivo. Los estilos CSL (procesadores de citas, notas y bibliografías) permiten realizar el asentamiento automático de las referencias utilizadas según las exigencias de cada revista y pueden ser cargados por una amplia gama gestores de reconocida preferencia; por lo que constituyen una potente e indispensable herramienta en la elaboración de documentos científicos. Es por ello que el objetivo de este trabajo fue confeccionar un lenguaje de estilo de citas CSL basado en la norma ISO 690:2010 para asentar la bibliografía de los artículos presentados en la Revista Ciencias Técnicas Agropecuarias (RCTA). Para la confección del mismo se utilizó el esquema CSL v1.0, con lenguaje XML, formato de codificación de caracteres utf-8 y tipo de citas en texto autor-año. Las operaciones de edición y validación se realizaron a través del editor de texto plano Notepad++ v4.7.5, el Visual CSL Editor (online) y el Validator.nu (online). Como resultado se obtuvo un fichero CSL compatible con 25 gestores bibliográficos que permite asentar de manera automática la bibliografía de los artículos científicos agropecuarios de RCTA, según las directrices de la norma ISO 690:2010.
Palabras clave: procesador bibliográfico, lenguaje de estilo de citas, artículos científicos agropecuarios.
INTRODUCTION
There are known the frequent errors that are committed in the use of the bibliography of the different scientific works, as for example: incomplete reference; omission of elements of obligatory filling as the year of the publication, authors, ISSN, ISBN, pages, publishing houses; there are not put the references that are cited in the article, there are reference of cited that not appear in the text and especially that the filling of the chapter Bibliography is not carried out in a uniform way and under the parameters of form established by the bibliographical styles (way of presenting the used documents) of the journal (Osca-Lluch et al., 2009; Revista Fitotecnia Mexicana, 2012; Jabulani, 2014; Nixon, 2014).
In this sense, the reference management softwares (programs that carry out the establishment of the bibliography) realize in an automatic way the harvest and organization of the scientific information, from the metadata of the documents index-linked in the different international databases (Sánchez, 2014). These programs are free and they work under mutual compatibility standards with open source that allows the integration between them and the design of bibliographical styles adjusted at the requirements and desires of the thousands of users that develop them.
The styles (processors of citation, notes and bibliographies) that use these programs to generate the information, are contained in files of type CSL (Citation Style Language) based on language XML, under format of codification of characters utf-8. They are completely edited and of use shared for a wide range of reference managers of recognized international importance like Zotero (Ansorge y Kratochvíl, 2013; Watkins, 2013; Courraud, 2014), Mendeley, Papers, and others1. These characteristics have done that the autonomous creation of bibliographical styles for publishing houses and centers of publications of all kinds have been in increase and today more than 7000 of them are exhibited in places as https://www.zotero.org/styles/ and https://github.com/citation-style-language/styles/ of access free for the whole international scientific community.
The styles development is an advantage that the journal present to increase its visibility because the automatic standardization of the bibliographical requirements (principally of the documents index-linked in databases), allow the location and not omission of authors, terms, dates, titles; that constitute trailing elements for the systems of position of the databases and as result increases the recognition and visibility of the works (Giles et al., 1998; Freysteinson, 2013; Castolo et al., 2014).
Is in the establishment and organization of citation, notes and bibliographies where its main advantage has. The styles CSL allow better handling of the information sources scientist for the international community and it is considered very beneficial for the journals because its form requirements are fulfilled by major facility and relevancy. This is something that has attracted attention of authors, publishers, journals, universities, research centers, associations; who have found in the styles of type CSL a viable opportunity to humanize the management of the bibliography, reduce the errors and avoid the constant documents return for this motive (Mengxion, 2014).
The way of presenting the references, as well as the information in them, change according to the needs and the nature of the bibliography. For it, the publishing houses in its style norms, usually give guidelines on the dispositions that they consider to be more suitable2, (Quir, 2014; Rivera, 2014). From each of them dissimilar styles CSL have developed for orientate the authors and assure the of the bibliographical requirements established by every center of publication.
Every time there are more the styles that adopt the norm ISO 690:2010, or partly of it, because allow a good grade of unit (exempt of the localisms), at the time that it allows the necessary flexibility to adapt itself to diverse situations; nevertheless, the manual creation of the bibliographical references is a bothersome work that provokes repeated errors that end with the rejection of the articles presented in the journal. For that reason, the objective of this work was to development a citation style language CSL based on the guidelines ISO 690:2010 to describe the formatting of citations, notes and bibliographies of the agricultural scientific articles of the Revista Ciencias Tecnicas Agropecuarias (RCTA).
METHODS
General descriptions
The style belongs to the Revista Ciencias Tecnicas Agropecuarias. The same one presents ISSN 1010-2760 and it is index-linked in different international directories as SciELO Citation Index of the Web of Science. The norm ISO 690:2010 was used of guide for the presentation of the bibliography because its guidelines make possible major grade of unit and adjustment of the requisites established by the publishing committee of RCTA. One worked under the License Creative Commons3 because allow copying, redistributing in diverse ways or formats, adapting, updating and transforming the material for any purpose. Recognize the personal responsibility of the original version, as well as of the updates because are ruled by the same license.
Basic anatomy of the style. Elements definition
The scheme CSL 1.0 was used for the shape of the style of RCTA4; where, cs:style was the biggest class of the root, inside were defined and characterized the different elements, terms, variables and items (Figure 1) that described the wished bibliographical behavior.
• In the design of the style five elements was established subordinated to the class cs:style, that were used to gather the general information, define terms and variables, characterize the type of citation in the text, and represent the format and composition of the bibliography. These elements are constituted for:
• cs:info, is the first element of the root of the style and provides information reference the CSL (I metadata of the CSL) like title, date of the last update, URL of the CSL and of the document of instruction of the journal, authors, category of the format of citation and of the field of the journal, ISSN and eISSN, bibliographic standard used in the style, version and rights of license.
• cs:locale, locates automatically terms, miscellaneous and punctuation in the CSL, and codifies the exit of these elements fallowing the parameters of form of the style RCTA.
• cs:macro, contains basically 42 macros in relation to the quantity of terms and variables used. It contains instructions of structure of some elements that facilitate the understanding; establishes the existence of rolls, variables that are edited and used in cs:citation and cs:bibliography.
• cs:citation, describes the characteristics, format and creation of the citation in the text and in the notes. Also, it was used to specify like the citation will be organized inside the citation process.
• cs:bibliography, establishes the general parameters of creation and the types of items that will be edited by the style RCTA; as well as the instructions of structure and organization of terms and variables declared in cs:macro, inside every bibliographical reference.
Terms, variables and types of items used
For the creation of the CSL was used a set of elements that allowed establish persons categories and miscellaneous, compose the bibliographies and define the characteristics of the types of documents allowed by RCTA. One of these elements constitutes it cs:term, that was used like linkage particle between authors names in the citation, to differ between singular and plural, to place names of variables in the short form, to define distinctive symbols and to place numerical variables in ordinal form, they were:
• cs:term: issue, note, page, section, line, part, accessed, anonymous, edition, et-al, from, in, interview, online, retrieved, volume, ordinal, no date, day, month, year, author, editor, interviewer y translator.
• Other elements named variables were used to register the information of each sources of different nature (standard, numerical, date and name) located in the bibliographies and in the notes. These were put previously inside cs:macro, where some of them (date and name) were described to generalize its characteristics in all the items. The variables defined according to the style of RCTA, were:
• Variables: abstract, archive, archive_location, collection-title, container-title, DOI, event, event-place, genre, ISBN, ISSN, jurisdiction, locator, medium, original-publisher, publisher, publisher-place, scale, section, title, title-short, URL, version, collection-number, edition, number and number-of-pages.
• The items are subordinate to cs:bibliography and define the different types of documents that are accepted by RCTA for the creation of the scientific articles. In these were represented all the necessary elements (metadata); in each one of the cases, for that the indexed material could be identified and found. The objective is provided with a wide information status to increase the visibility and the recognition for the systems of position that establish, across different indicators, the index of citation of RCTA and the impact of its publications (De Bellis, 2009).
• Items: book, program-computer, map, article-journal, article, article-magazine, article-newspaper, chapter, entry, entry-encyclopedia, entry-dictionary, paper-conference, thesis, post, webpage, post-weblog, report, patent and interview
Software used for the edition and validation
For the creation of the style CSL were used like software Visual CSL Editor (on-line)5 and the editor of plain text for Windows Notepad ++ v4.7.5 because it presents edition support for XML, automatic identity, closing of tags and checkup of the scheme CSL. After constructed the anatomy, was checked the setting of the style of RCTA using Zotero Preview pane6, that generates a sight previous to the form of exit of the citation and the bibliography of the different documents. To detect possible errors in the writing XML and in the scheme CSL v1,0, was used Validator.nu (On-line)7 and then a personal review (webmasters CSL). After that, was up the style in the repository of zotero8 according to the indications established for these cases. Of this way, was validated its compatibility whit 25 reference managers so that the author can select their favorite tools (Zhang, 2012; Fenner et al., 2014), how:
• ACS ChemWorx Desktop, BibSonomy, Bielefeld University Librarys Katalog.plus!, Cite This For Me, colwiz, CrossRef, digi-libris Reader, Docear, Drupal, Fidus Writer, Islandora, Jekyll, Logos, Mendeley, Multilingual Zotero, pandoc, Paperpile, Papers, Qiqqa, ReadCube, Refeus, Talis Aspire, WordPress (KCite and Zotpress plugins), and Zotero.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Defined the parameters of the profile based on the guideline ISO 690:2010, was made the style CSL called Revista Ciencias Técnicas Agropecuarias (Spanish), using the version 1.0 and location language in Spanish (es-Es). The same one, constitutes an independent style because contains its own instructions of form of citation, notes and bibliographies declared in the instruction to the authors. Author-date was class of style of cites in-text selected, so that the responsibility and the year could be identified inside the reading without having to go to the references. There was established the field of the knowledge to belongs RCTA (engineering), as well as its international standard serial number (ISSN-eISSN) (Figure 2).
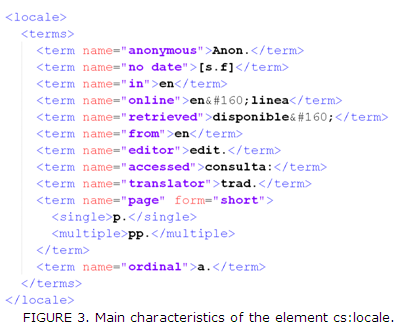
The terms definitions are necessary to identify some variables inside the bibliography once generated by the reference managers. This way it is possible to distinguish between personages like author, publisher, translator; establish the differentiation between singular and plural; contract variables and declare symbols. For it, these terminologies are registered inside cs:locale (Figure 3), in addition to others like Anon. and [s.f] that appear if the person or the year of publication not appear inside the citation in-text. It is valid to clarify that any item of RCTA can be used without these elements.
In this sense, was changed the representation of the terms in, online, retrieved, accessed and from (established by default), for en, en línea, disponible, consulta and en; because those elements are represented inside of the bibliography and must be in relation with the language of location defined in the style (Spanish). To differ between the different rolls of the persons that take part in the dressmaking of an item were assigned the prefixes edit. and trad. to the variables publisher and translator; while to generate the number of edition of an ordinal way and to define the number of pages was used a., p., pp. respectively.
Another important element in the definition of the wished characteristics of the style was cs:macro. It was used principally to declare the variables that were used and characterized in an individual way in cs:bibliography. It allowed having more control of the particular characteristics of the items and it made possible to improve the edition process because grouped in every type of document the set of variables to be used and the peculiarities of form of each one, these were:
• Event, title, container-title, médium, genre, publisher-place, issue, volume, publisher, archive, archive_location, page, number-of-pages, abstract, note, jurisdiction, original-publisher, number, version and section.
• Nevertheless, there is another group of variables that present a similar behavior in each one of the items of the style RCTA, therefore does not have sense declare it inside cs:macro and characterize it again in each types of documents that appear. Because that, was declare its forms structures inside every corresponding macro, so that the element always present the same behavior independently of the item inside which it was declared, these were:
• Author, editor, translator, interviewer, responsability, author-citation, container-author, collection-editor, container-responsibility, year-date, year-date-responsibility, date, date-responsibility, edition, accessed, collection, isbn, issn, doi, url, online and scale.
This allows that in all the types of documents the authors to be generated in capital letters and of the short form, where is set the first surname of the main author and then the initial of the name and of the second surname. Between the surname and the initial is put a comma and the same procedure follows for the rest of the authors. The separation between authors is by a semicolon, and two points are placed after initial of the last author (Figure 4).
For other rolls like publisher, translator and interviewer, the names are established after the title and the long form. These names are set at first continued of the first and second surname. The first letter of the name and the surnames are placed in capital letter without separation element between them. In the cases that some of these rolls contains more than one person is set , to separate them and y before the last author (Figure 5).
Of same way, other variables used to establish dates (year-date, year-date-responsibility, date, date-responsibility) has the same behavior in each item. These represent dates of creation and consultation of the documents, and contain in turn the parts day, month and year; because some documents make use of a part of it. Thus the macro date or year-date are declared in the different types of documents in cs:bibliography according to the part of the date that it wants to place. To separate each parts of date is set the preposition de (Figure 6).
Inside the text, the citation is rendering of the form author-date (e.g. Cervantes, 2014). If they are two authors there is placed the first surname of each one separated for y, and next , year (e.g. Cervantes y Fernández, 2014). In the cases that the authors are more than two it is put et al. after the surname of the main author fallowing of , year (e.g. Cervantes et al., 2014). If the citation belongs to multiple sources, each one will be separate by ; (e.g. Cervantes, 2014; Cervantes y Fernández, 2014; Cervantes et al., 2014). If the year of publication is the same for several citations that present the same responsibility, it is will differ with the letters a, b, c, etc., (Figure 7).
Finally, in cs:bibliography was established that the reference, with discharging between lines and between item of one (<bibliography entry-spacing = 1 line-spacing = 1>), is organized alphabetically from the first letters of the surname of the main author and is continued with the date and the title (<sort>), (Figure 8). Every part of the items will be separated by comma and point will be placed only after the year that will always appear in the end. The title of chapters of books, encyclopedias, articles in conference, newspapers and article of journal will be placed between quotation marks (<text macro = title prefix = ¨ suffix = ¨,/>) and for the rest of the documents will settle without quotation marks and in italics (<text variable = title font-style = italic/>). The names of the article of journal, newspapers, encyclopedias, web pages, congresses, symposiums, seminars, workshops and events are placed of the original form (without abbreviate) respecting the original grammar and in italics.
Miscellaneous of variables and personages were defined in cs:bibliography to differentiate them inside the bibliography. It was indicated that in front of the interviewer, publisher of the series, author of the book when is cited a section of this, publishing house, series and date of exit of norms and patents, should be placed the prefixes entr., edit. ser., en, Ed., ser. and Vig. respectively (e.g. <text macro=publisher prefix=Ed. suffix=,/>). In the cases that it corresponds, next of the number of edition will put ed. and in front of the number of volume vol. except for the articles of journal that they are not placed (Figure 9). The notes on the foot of page continue the same guidelines established by the style, only that are not placed in the references, but rather is set at the end of the page where was indicated.
Of this way, in layout was completed all type of documents that are frequently used by the author that writer for the journal. It is the container for all rendering elements in citations or bibliographies (it, and its content, contains all the layout rules), and is itself a rendering element (Figure 10). So the structure of the layout has not only the items allowed in the journal; but other types that can be used for written other documents in different academics works. These types are established in else until complete 35 kind of different items, these were:
Article, article-magazine, article-newspaper, article-journal, bill, book, broadcast, chapter, dataset, entry, entry-dictionary, entry-encyclopedia, figure, graphic, interview, legislation, legal_case, manuscript, map, motion_picture, musical_score, pamphlet, paper-conference, patent, post, post-weblog, personal_communication, report, review, review-book, song, speech, thesis, treaty and webpage.
CONCLUSIONS
• Was developed a multiplatform file CSL supported by 25 reference managers that set, in an automatic way, the bibliography of the agricultural scientific articles of RCTA. The style is based on the guideline ISO 690: 2010, cite in-text as the form author-date and organizes the bibliography alphabetically. It takes as distinctive features that in the bibliography the authors are put of the short form, after the authors there is placed two points (:), the elements are separated by comma and the year always appears in the end. It is capable of recognizing, organizing and filling correctly 35 types of different items and can be used for the management of the scientific information of any type of work.
Notas al pie
1 CitationStyles.org | The Citation Style Language - open and free citation styles, [en línea] Disponible en: http://citationstyles.org/ [Consulta: 3 de junio de 2014].
2 Cómo citar la bibliografía en los trabajos académicos, [en línea] Universidad Politécnica de Valéncia, España, 2014. Disponible en: https://www.upv.es/entidades/ADE/infoweb/fade/info/U0655397.pdf [Consulta: 15 de agosto de 2014].
3 CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported, [en línea] Disponible en: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/ [Consulta: 16 de junio de 2014].
4 ZELLE, R.M.: Citation Style Language 1.0.1 Language Specification, [en línea] 3 de septiembre de 2012, Disponible en: http://citationstyles.org/downloads/specification-csl101-20120903.html
5 CSL style editor, [en línea] Disponible en: http://editor.citationstyles.org/ [Consulta: 19 de junio de 2014].
6 Zotero Preview pane, [en línea] Disponible en: chrome://zotero/content/tools/cslpreview.xul [Consulta: 19 de junio de 2014].
7 Validator.nu, [en línea] Disponible en: http://validator.nu [Consulta: 19 de junio de 2014].
8 Zotero Style Repository, [en línea] Disponible en: https://www.zotero.org/styles/ [Consulta: 6 de junio de 2014]. .
REFERENCES
1. ANSORGE, L.; KRATOCHVÍL, J.: A Description of the Template ISO 690:2011 in the CSL Language for the Reference Manager Zotero, ProInflow: asopis pro informaní vdy, [en línea] ISSN-1804 -2406, 5 (2), 2013. Disponible en: http://pro.inflow.cz/sites/default/files/pdfclanky/Kratochvil_Ansorge_Sablona_0.pdf
2. CASTOLO, M.C.; ROMERO, G.F.; DÍAZ, L.M.M.J.; GÓMEZ, A.A.P.; GONZÁLEZ, C.S.; EGAN, L.A.V.: Indicadores bibliométricos de la Revista CONAMED, 2008-2012., Revista CONAMED, ISSN-1405-6704, 19 (2): 59–66, 2014.
3. COURRAUD, J.: Zotero: A free and open-source reference manager, Medical Writing, [en línea] ISSN-2047-4806, DOI-http://dx.doi.org/10.1179/2047480614Z.000000000190, 23 (1): 46–48, 2014.
4. DE BELLIS, N.: Bibliometrics and Citation Analysis. From the Science Citation Index to Cybermetrics, Ed. Scarecrow Press, Inc, ISBN-13: 978-0-8108-6713-0, United States of America, 2009.
5. DON, H.: Notepad++, (Versión v4.7.5), [en línea] [Windows], Ed. Free Software Foundation, USA, 14 de enero de 2008. Disponible en: http://notepad-plus.sourceforge.net/
6. FENNER, M.; SCHELIGA, K.; BARTLING, S.: Reference Management, En: Opening Science. The Evolving Guide on How the Internet is Changing Research, [en línea] Collaboration and Scholarly Publishing, ISBN-978-3-319-00025-1, pp. 125–137, Ed. Springer, 2014. Disponible en: http://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-319-00026-8_8 [Consulta: 27 de agosto de 2014].
7. FREYSTEINSON, W.M.: The language of scholarship for novice writers., Journal of continuing education in nursing, [en línea] ISSN-0022-0124, DOI-10.3928/00220124-20131121-13, 44 (12): 533–534, 2013.
8. GILES, C.L.; BOLLACKER, K.D.; LAWRENCE, S.: CiteSeer: An Automatic Citation Indexing System, [en línea] ser. DL 98, ISBN-0-89791-965-3, DOI-10.1145/276675.276685, pp. 89–98, New York, NY, USA, 1998. Disponible en: http://doi.acm.org/10.1145/276675.276685
9. INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ORGANIZATION: Information and documentation Guidelines for bibliographic references and citations to information resources, [en línea] ser. ISO 690, Ed. Switzerland, 3a. ed., pp. 40, Geneva, 2010. Disponible en: http://www.iso.org
10. JABULANI, S.: An analysis of the language of attribution in university students academic essays, South African Journal of Education, ISSN-0256-0100, 34 (3): 1–10, 2014.
11. MENGXION, L.: Progress in documentation the complexities of citation practice: A review of citation studies, Journal of Documentation, [en línea] ISSN-0022-0418, DOI-10.1108/eb026920, 49 (4): 370 - 408, 2014.
12. NIXON, K.: Our Common Pedagogical Dilemma: Designing Literary Essay Assignments Not Easily Bought or «Found», Journal of Language and Cultural Education, ISSN-1339 - 4045, (2): 2, 2014.
13. OSCA-LLUCH, J.; MOLLÁ, C.C.; ORTEGA, M.P.: Consecuencias de los errores en las referencias bibliográficas. El caso de la revista Psicothema, Psicothema, ISSN-0214-9915, 21 (2): 300–303, 2009.
14. QUIR, R.E.M.: Recomendaciones para redactar, diseñar y estructurar una publicación de caso clínico, Revista de Especialidades Médico-Quirúrgicas, ISSN-1665-7330, 19 (2): 229–235, 2014.
15. REVISTA FITOTECNIA MEXICANA: Guía de Autores (Versión 2013-2015), Revista Fitotecnia Mexicana, ISSN-0187-7380, 35 (4): 355- 363, 2012.
16. RIVERA, R.: Normativa de presentación de artículos de la Revista Perspectivas Rurales. Nueva época., Perspectivas Rurales Nueva Época, ISSN-1409-3251, (24): 137–139, 2014.
17. SÁNCHEZ, G.M.: Global Library of ozone, a tool for research, Revista Española de Ozonoterapia, ISSN-2174-3215, 4 (1): 79–82, 2014.
18. WATKINS, A.: Zotero for Personal Image Management, Art Documentation: Journal of the Art Libraries Society of North America, ISSN-0730-7187, 32 (2): 301–313, 2013.
20. ZHANG, Y.: Comparison of select reference management tools", Medical reference services quarterly, [en línea] ISSN-0276-3869, DOI-10.1080/02763869.2012.641841, 31 (1): 45–60, 2012.
Recibido: 19 de febrero de 2014.
Aprobado: 22 de septiembre de 2014.
Rafael Cervantes Beyra. Universidad Agraria de La Habana. Facultad de Agronomía. San José de las Lajas, Mayabeque, Cuba. Correo electrónico: cervantes@unah.edu.cu