Introduction
The trend of economic development in developed countries indicates the reality that economic is affected by entrepreneurship, where entrepreneurs have pivotal roles in economic development of developed countries and undeveloped countries did not consider its importance in economic development. What has more caused the emergence of entrepreneurship in economic field of developed countries is expansion of unemployment, especially the unemployment of graduated individuals in our country which is increasing. Actually, the expansion of unemployment of youths is the problem of the growing world. In recent years, protests from unemployment youths have assigned news outlines in England, Spain and other regions of Europe and South Africa to themselves.
In response to unemployment dilemma, planning organizations encourage educational centers to come into the fields of self-employment and entrepreneurship risks . By observation of decline in world occupational opportunities, entrepreneurship is an acceptable and suitable way . The world center of entrepreneurship control shows a disinteresting and unwelcome manner among youths to get involved in new and risky works in its reports. The vital role of entrepreneur youths in expansion and achievement to aims of each country and emergence of unemployment threats and signs indicating young university graduate students are not willing to get involved at entrepreneurship activities, have rapidly turned to a socio-economy challenge in countries.
Strategic thought is an expression which has widely used and is written in many scientific and university records, but has rarely used as a mental concept. Today, the expression of strategic thought is widely and publicly used which is endangered by threat of becoming meaningless. Numerous attempts have been made to make the strategic concept meaningful (Wilson, 1994; Torset, 2001; Bonn, 2005) and some individuals tried to conceptualize the strategic thought and provide models to help comprehend this issue. However, it seems that there is a long way to achieve an integrated, specific and practical concept and meaning of strategic thought, especially all of these statements and views are theoretical. Only one of these models, performed by Torest (2001), is the results of field survey research. According to Torest (2001), to develop strategic thought, individuals have to have a tendency, knowledge, and capacity to strategic approach. These factors depend on psychological, organizational and strategic background of each individual. According to Bonn (2005), organizational levels have to provide fields for individuals to form strategic thought. It is necessary that organizations provide structures, procedures, and systems to promote continues strategic dialogue among management team members and utilize of genius, initiative, and creativity advantage of each employee in organization. Thus, considering globalism and passage from industrial to data society, previous solutions are not beneficial for current and future problems and one has to think of new methods. This phenomenon also implies about organizations. Therefore, we have to look for new organizational solutions with modern structures.
To know new opportunities and increase efficiency, there is sense of urgent necessity to know system relation between human resources management and organizational entrepreneurship development within organizations (Kiakojori and Jafarian, 2011). (Sa'adat, 2011) defined the human resources management as identification, selection, recruitment, education of human forces in order to achieve organizational aims. Organizational entrepreneurship consists of innovation, establishment of new marketing in organization and performing dangerous projects and activities related to strategic renovation of organization . Organizational entrepreneurship is a concept which focuses on organization, not on individuals, cultures and organizational procedures (Jenings, 1994).
Organizational entrepreneurship is a series of activities which are from organizational resources and supports to achieve innovative results (Farhangi & Safarzadeh, 2007). In addition, organizational entrepreneurship is a procedure that organization passes to help all staffs perform their tasks as an entrepreneur and all the individual and group activities continuously, rapidly and conveniently eventuate. It consists of education of entrepreneurship behavior in an organization which has previously established and is a procedure that products (services) produce through innovative procedures and creation of entrepreneurs' culture, as well. In this type of entrepreneurship, a company or an organization, provide a situation that all the members participate at entrepreneurship affairs (Farhangi & Safarzadeh, 2007).
Other studies about the research are presented (Amini, et al., 2014). in a research titled prioritize of entrepreneurship barriers from physical education students viewpoint by TOPSIS, concluded that the greatest weight assigned to educational and individual barriers, respectively. performed strategic diagnostic of public exercise. Accordingly, promotion of national pride is possible through public exercise. Ghofrani et al. in a research titled design and provision of public exercise development strategy for Sistan and Balochestan province showed that in Sistan and Balochestan province with 2.5 million population, less than 0.007% of people get involve at public exercise which considering special geographic location of the province, unemployment rate, fuel and drug smuggle and also spread of all kind of diseases due to inactivity, one can provide public exercise development strategy and executive solutions through analysis of information and offering to officials of the department of physical education of the province to be organized and planned. Academic trainings fortify graduates for successful plans, beginning of and execution of commerce in three stages: 1.development of idea or plan, 2. Organization and establishing of cooperative or a company, 3. running a newly founded company. Due to little researches about relationship of strategic plan though model and entrepreneurship human resources development and considering the importance, the researcher tried to explore the strategic plan though model with organizational entrepreneurship at Ministry of Sport and Youth in Iran.
Methodology
The present research is descriptive and practical study that data gathered by field survey and questionnaire. The statistical population of the research is all the human resources of Ministry of Sport and Youth who were 850 and 265 of them were selected based on Morgan table.
Data of this research were from questionnaire of Nazemi, Mortezavi & Jafariani (2010), strategic program thought. This questionnaire comprises two parts that demographic questions (part one of the questionnaire) relates to overall characteristics of respondents such as gender, age, education, and occupation record and the second part consists of attitude questions considering factors effective on strategic program thought. Five-value Likert scale was used. To measure validity of questionnaire and alternatives, an index named validity coefficient has been used. Thus, Cronbach's alpha coefficient was used to determine the validity. Questionnaire of entrepreneurship human resources was used to calculate the entrepreneurship of human resources development of employees.
In this research, findings were analyzed in two descriptive and inferential parts. In descriptive part, frequency distribution tables and in inferential statistics, considering naturalness of data distribution, Kolmogorov Smirnov test, group t-test, t-student and factor analysis by spss23 at the significance level of P<0.05 and amos software were used.
Table 1 shows results related to descriptive statistics of studied sample. As is observed, among 260 employees of Ministry of Sport and Youth, the most participants were 176 men and the least ones were 84 women. In addition, of the 260 staff at the Ministry of Sport and Youth, the least participants were 110 single and the most ones were 150 married. Of the 260 staff at the Ministry of Sport and Youth, the most participants were 101 master level and the least ones were 24 doctorate level. Of the 260 staff at the Ministry of Sport and Youth, the greatest ages of participants were 59 among 41-45 years old and the least ones were 12 for below 25 years old. The greatest service record of participants was 68 for 16-20 years and the least ones were 9 for below 5 years of the 260 staff at the Ministry of Sport and Youth.
Table 1 Descriptive statistics of participants.
| Gender | Frequency | Frequency percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Man | 176 | 67.7 |
| Woman | 84 | 32.3 |
| Marital | Frequency | Frequency percentage |
| Single | 110 | 42.3 |
| Married | 150 | 100 |
| Education level | Frequency | Frequency percentage |
| Technician | 41 | 15.8 |
| Bachelor | 94 | 36.2 |
| Master | 101 | 38.8 |
| Doctorate | 24 | 9.2 |
| Age | Frequency | Frequency percentage |
| Below 25 | 12 | 4.6 |
| 26-30 | 41 | 15.8 |
| 31-35 | 43 | 16.5 |
| 36-40 | 43 | 22.7 |
| 41-45 | 59 | 16.9 |
| 46-50 | 44 | 16.9 |
| Above 50 | 18 | 6.9 |
| Service record | Frequency | Frequency percentage |
| Below 5 years | 9 | 4.5 |
| 5-10 | 24 | 12 |
| 11-15 | 55 | 27.5 |
| 16-20 | 68 | 34 |
| Above 20 | 44 | 22 |
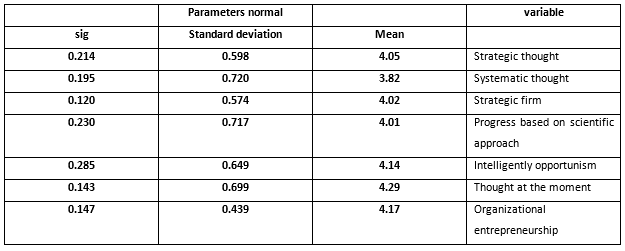
The values of normality of data distribution are depicted in table 2 which shows that significance level of variables of strategic thought and alternatives and organizational entrepreneurship is more than 0.05. Considering this conclusion, by 0.99% certainty, data distribution of the named variables are natural.
The first question asked in this research is: in what level is the strategic thought at Ministry of Sport and Youth?
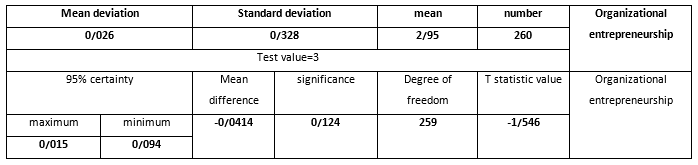
Results show that average of provided responses by statistical sample about strategic though at Ministry of Sport and Youth is 2.35 out of 5 based on Likert spectrum and since the test value equals 3 but the average is less than that, difference is significant but is not in line of research assumption. On the other hand, the assumed average is more than real average. One can deduce that strategic thought is not at suitable level at Ministry of Sport and Youth. According to table 3, t value obtained from test is 1.38 and since this is less than critical value ±1.96, assumption one is rejected and zero assumption is accepted at 95% certainty.
The second question of this research is: at what level is the organizational entrepreneurship at Ministry of Sport and Youth?
The average of provided responses by statistical sample about organizational entrepreneurship at Ministry of Sport and Youth based on Likert spectrum is 2.95 out of 5 and since the test value equals 3 but the average is less than that, difference is significant but is not in line of research assumption. On the other hand, the assumed average is more than real average. One can deduce that strategic thought is not at suitable level at Ministry of Sport and Youth. According to table 4, t value obtained from test is 1.546 and since this is less than critical value ±1.96, assumption one is confirmed and zero assumption is rejected at 95% certainty.
The third question of this research is: how is the strategic thought relationship model with organizational entrepreneurship at Ministry of Sport and Youth?
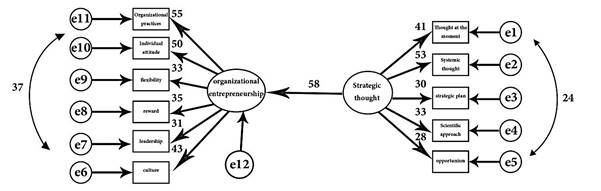
Evaluation indices of whole the structural equation considering suitable level of these indices reveal that the presumed provided model confirms by research data. In other words, data extrapolation is fitted to model and all the indices confirm the suitability of structural equation model (Table 5 and 6).
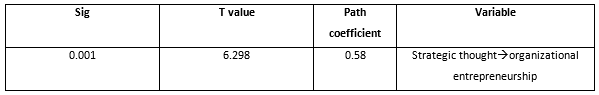
Considering depicted diagram in fig. 1, it is determined that strategic thought has positive and significant effect on organizational entrepreneurship at Ministry of Sport and Youth. On the other hand, it clarified that strategic thought is effective with 0.001% error with organizational entrepreneurship at Ministry of Sport and Youth.
Discussion and result
The present study is a descriptive and practical research that the data were collected by field survey and questionnaire. The statistical population of the study is all 850 human resources of the Ministry of Sport and Youth, about of who 265 were randomly selected according to Morgan table. The results showed that of the 260 employees in the Ministry of Sport and Youth, the highest participants were men with 176 and the lowest were women with 84.
The lowest participants were 110 single and the highest numbers were 150 married, of the 260 staff at the Ministry of Sport and Youth.
Of the 260 staff at the Ministry of Sport and Youth, the most participants were 101 master level and the least ones were 24 doctorate level. Of the 260 staff at the Ministry of Sport and Youth, the greatest ages of participants were 59 among 41-45 years old and the least ones were 12 for below 25 years old.
Analysis results of the first research question indicated that strategic thought is not at appropriate level at Ministry of Sport and Youth. In explanation of results, one can deduce that at governmental and private organizations, individuals continuously enhance their ability to make results which are really suitable to them.
Organizational creativity and innovation causes that a new and widespread mental pattern breeds and individuals continuously learn how to learn as a team. Organizations with these characteristics receive signs from environment and then interpret and apply them at opportunities because of innovation encouragement, gaining knowledge and development of abilities. Hence, knowledge management should be considered at each organization. In future, societies and organizations expect to progress if allocate more contribution of knowledge to themselves. These changes lead to progressive growth of knowledge management and gaining important position at universities and occupations.
Country sport is a transnational and national phenomenon that has wide executive, popular and international dimensions. Sport is not just a medal; it should burden the millions of obese, diabetic, stroke and sick people and should help educate children and youths and generate wealth and create jobs and expand our international relationships, offer women and girls happiness and health and to give hope to elderly and to alleviate their suffering and to enhance our national unity and … so, like each other part of the country, sport should be governed according to planned and announced program, which unfortunately is not the case. Strategic document of comprehensive country sport development system (sport comprehensive plan) was prepared to depart from this shortcoming once forever and tell the world that our sport has a strategic plan but unfortunately, those who were governing the field who had no believe in the literature and considered it as a luxurious tool or found themselves needless of any program. By the way, a plan developed and people with the message became the pivot, thus finding the weakness or strength points of sport got hard and one cannot predict at each part of sport in what point we will be. If the strategic document of comprehensive country sport development system (sport comprehensive plan) is updated and implemented, it will highly compensate the shortcoming and if necessary, during implementation, required adjustments will be made.
Implementation of this includes all elements of sport, its structure, organization, budget, human resources, and specific principles for the development of educational, public, championship and professional sports, and includes all infrastructure and software elements of sport. Optimum use of the development plan and other plans and bills will also be complementary. Unfortunately, even healthy, expert, and mighty executives in Iranian sport unable to think about development and excellence in this field because of structural and organizational weaknesses and absence of an integrated, and most managers have been and will be in the idea of passing days. Therefore, the future management of the country's sport can spin the wheel, but he will face difficulty if he takes a look at the development and excellence, and will require a multidisciplinary team, purposeful and scientific plans and a double effort to bring the country's sport conditions to favorable indices at world- and region- class. In a scientific sentence, it must be said that our sport needs a strategic though more than anything or anybody else. The results of the analysis of the second question of the study indicated that organizational entrepreneurship in the Ministry of Sport and Youth is not favorable. The results of this question are not in agreement with Amini, et al. (2014); Yaghoubi & Bahmani (2010); Yadollahi Farsi, et al. (2010). In explanation of obtained results, one deduces that entrepreneurs have pivotal roles in economy development of developed countries, but undeveloped countries ignored their roles. Our country is a semi-developed country, ignores entrepreneurs and through applying difficult and rigid rules against entrepreneurs, makes them disappointed. This lack of attention to entrepreneurs is in sport, as well. In Ministry of Sport and Youth, legal political, economy, socio-cultural, technological, and international barriers have had some meaningful effect on organizational entrepreneurship of Ministry of Sport and Youth.
Legal ignore for the development of sports cooperatives and their support for the advancement of sports, the weakness of the legislative process in the employment affairs and supportive services of staff, the lack of rules for supply and the balanced distribution of sports equipment and facilities, the arrival of managers unfamiliar with sports, political, and sports field management of the country, lack of economic security infrastructure to attract domestic and foreign investment, employing people with irrelevant education and skills, lack of culture and training for voluntary social contributions in sports, lack of identification or introduction of successful sports entrepreneurs, lack of attention at transfer and exploitation of sports modern science and technology around the world, lack of required substrates to host large international events, and ... are among the strong and effective factors in preventing organizational entrepreneurship in the Ministry of Sport and Youth. Ministry of Sport.
Conclusions
Youth is also a newly established ministry relative to other ministries and its establishment backs to middle of the tenth government. Since the establishment of this ministry, a stable management has not been governed, and it was either governed by a supervisor or continuously relocated its minister. These factors go hand in hand to avoid paying attention to entrepreneurship at this ministry. In addition, sport in Iran is still in the hands of the government, and this issue has closed the hands of private-sector entrepreneurs. The results of the analysis of the third question of the study indicated that all of the strategic thought indices indicate the desirability of the structural equation model. The results obtained in this question are in agreement with the results of Eyal & Kark (2004), Rahman Seresht & Kafche (2008). In explanation of results, it can be argued that strategic thought promotion leads to small and medium- and large organizations fostering strategic entrepreneurship and one of the ways to increase entrepreneurship in small and medium businesses is to promote strategic thought of individuals.