Introduction
Economic growth in various historical periods was provided using a wide range of both fiscal and monetary instruments. The uniqueness of the existing external and internal factors of economic development justifies the lack of universal solutions in the complex of socio-economic programs. At the same time, the need for measures to ensure economic growth inherent in state programs is a frequent reason for their wide discussion in the expert community.
In some cases, the banking system itself acts as an intermediate link through which money enters the market and leads to accelerated economic growth. The final beneficiaries in this case are not only organizations, but also the population, whose expenses are stimulated simultaneously from several parties. The creation of new jobs, the growth of production and accessibility of goods take place, while consumer opportunities increase.
Until recently, there were no unequivocal decisions on the most effective methods of stimulating economic growth. Despite the predominant use of integrated approaches in solving the indicated problem, it is important to determine the effectiveness of individual incentive instruments, among which it is currently logical to single out indicators of incomes and expenses of the population, as well as indicators of consumer confidence.
The aim of the study is to identify the relationships between the welfare of individuals and economic growth in an environment where investment in fixed assets cannot lead to the achievement of projected macroeconomic parameters.
Development
The problem of ensuring economic growth as a paramount task can now be considered not only from the perspective of stimulating domestic supply, but also domestic demand. Aggregate domestic demand is inextricably linked with the level of human wellbeing. The simultaneous provision of both economic growth and wealth growth is a complex multi-level task.
The influence of monetary policy on the economy was examined in detail in the works developed by Barida (2014); Eyubov (2014); Mogilat (2017); Yudintseva (2017); Pustovarov (2018), Koren (2018). Central banks are involved in regulating the investment climate through the transmission mechanism. Central banks are guided by decisions in accordance with their obligations. An important provision in regulating emerging economies is the Washington Consensus, which limits countries in their abilities.
Problems of state policy in the field of improving the life quality of the population, approaches to assessment and also analytical conclusions were made in the works of such modern authors as Grineva & Gorobtsova (2015); Aronova (2016); Nekrasova (2018); Suchkov, et al. (2020); Zelenev & Prokhod (2020). Improving the standard of living is a consequence of planning and is implemented in connection with the available opportunities in the macroeconomic and geopolitical conditions, as well as within the framework of the existing fiscal system.
Issues of the impact of crisis conditions on the financial performance of organizations are reflected in the works by Volkov & Nikulin (2012); Leevik & Vorobieva (2013); Kolyshkin, et al. (2014). Management under such conditions applies anti-crisis measures, some of which are universal for companies in various sectors of the national economy.
Studies of consumer behavior were conducted by Dementieva (2014); Ibragimova (2014); Perovoi & Perov (2015); Kolodeznikova & Kuznetsova (2017); Lapteva, Trusova & Grishina (2018); Shakleina (2019). Predicting consumer behavior is important at all levels of decision making. Moreover, the number of factors that models take into account is wide, but objectively insufficient. Statistical surveys are widespread in the study of consumer expectations.
The need for studies of the interrelations between indicators of population incomes and economic growth determined the choice of the topic of the paper, the logic of the disclosure of conclusions, and also the format of the statistical data analysis.
The methodological basis of the study was the analysis of a large amount of statistical data covering the basic parameters of a market economy such as investment, GDP, loans, household income, and debt burden. The data used in the analysis process made it possible to obtain many conclusions, estimates and forecasts of the further growth of the Russian economy.
Being a synthetic indicator reflecting economic growth apart from other macroeconomic indicators, gross domestic product does not fully reflect the state of affairs in various countries. In the history of Russia, economic growth has not always been accompanied by an increase in wealth. Table 1 presents the dynamics of population incomes between two crisis phenomena. Raising the standard of living in social states in the face of the expected recession and external risks requires a comprehensive review of this problem.
Table 1 - Dynamics of real disposable household cash income in Russia, in % to the previous year.
| 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 |
| 102,4 | 103,0 | 105,9 | 100,5 | 104,6 | 104,0 | 99,3 | 96,8 | 94,0 | 98,9 | 99,9 |
The emphasis in national projects of 2018 is made on improving the human well-being: the development of human capital, improving the life quality and incomes of the population. The combination of measures should help ensure the goals set by the President to ensure GDP growth in comparison with the global average (Barida, 2014).
This is not the first time that the country has faced the exhaustion of an economic growth model. For example, in 1987-1988 a sharp short-term economic recovery was achieved due to the growth of the budget deficit and public debt, and in the next ten years the economy fell (Eyubov, 2014).
The rapid economic growth of 1999-2008 greatly accelerated the approach to exhaustion of the reserve for economic growth: the pre-crisis level of production of 1989-1990 was achieved. At that time, growth was largely due to the availability of free capacity and labour, macroeconomic and political stability. The limited growth opportunities of the domestic economy and the global economic crisis had a profound effect on Russia.
Low rates of economic growth and a recessionary trend force Russian authorities to look for mechanisms to ensure increased investment in the economy and increased consumer demand (Mogilat, 2017). From 2017 to 2018, investments in fixed assets grew by 1.4 trillion roubles. This volume is insufficient given the rate of inflation.
Here we should consider foreign experience in combating the slowdown in economic growth and the possibility of its use in the Russian macroeconomic model. Thus, in Japan, in the USA and in a number of European countries, a quantitative easing policy has been successfully pursued, which involves stimulating economic growth by injecting additional volumes of liquidity into the market. To do this, central banks redeem significant volumes of government bonds, which contributes to the growth of the money supply with the possibility of withdrawal in the future (Yudintseva, 2017).
Nevertheless, the possibilities of stimulating economic growth by quantitative easing in Russia are sharply limited. The high level of inflation and lending rates does not allow increasing the money supply in significant volumes for the economy. The risk of a decline in purchasing power as a result of accelerated inflation is considered to be too high to speak about the possibility of the effective use of quantitative easing methods.
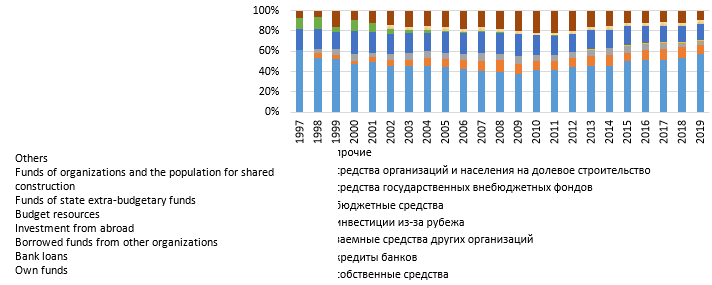
Fig.1 shows the structure of sources of borrowed funds in the Russian economy since 1997. The dynamics show that the role of bank lending is increasing, but does not exceed 10%. Until now, the main source of lending is own funds, and the second largest is public funds (Grineva & Gorobtsova, 2015; Suchkov, et al., 2020).
For example, in 2018, the free funds of the banking and non-financial sectors approached 6 trillion roubles; the country's gold and foreign exchange reserves amounted to 470 billion dollars and the federal budget surplus was 2.2 trillion roubles. It should also be noted the loss of foreign exchange reserves during currency conversion by the Central Bank of Russia: the sale of euros for dollars in 2017, as well as de-dollarization in favour of the yuan and other currencies in 2018. For two years, the diversification of currency risks cost the country $ 14 billion (Volkov & Nikulin, 2012; Leyevik & Vorobyova, 2013).
Given the reduction in the key rate and the availability of Central Bank deposits in commercial banks, conditions have been created for using banking instruments to stimulate economic growth. However, given the imbalance in the development of sectors of the domestic economy, monetary stimulus will have a limited impact on economic growth. An increase in the money supply in such conditions may be accompanied by a decrease in money turnover and an increase in inflation (Kolyshkin et al., 2014).
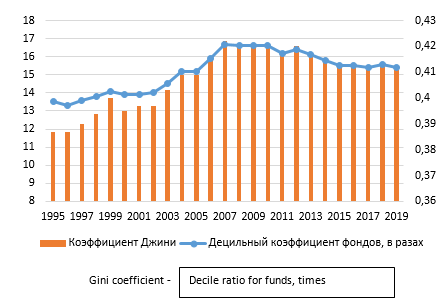
Economic growth is associated not only with investments in the economy, but also with overall growth in consumption. Measures of state support for young families, pensioners, socially unprotected people, as well as raising the minimum wage, and a policy to increase the salaries of budgetary workers help to solve the problem (since the state is still the largest employer), but it does not solve the problems of workers in the commercial sector (Ibragimova, 2014; Perova & Perov, 2015). Fig. 2 presents the indicators characterizing the inequality (Nekrasova, 2018). From the data it follows that the problem of inequality is not exacerbated, but at the same time it is at the same level. We should recall the negative experience of the USSR, when in the period from 1975 to 1985 the standard of living of the population did not fall and did not grow, but at the same time the incomes of the population continued to stagnate.
It is important not only the material situation of people in itself, but their expectations and forecasts (Kolodeznikova & Kuznetsova, 2017; Lapteva et al., 2018). Fig. 3 shows the quarterly dynamics of the assessment by the population of the favourable conditions for large purchases. The survey is representative; the sample includes more than 5 thousand people over 16 years old (Dementieva, 2014; Dementieva & Shakleina, 2019; Shumik et al., 2019; Vorozhbit & Levkina, 2017; Terentieva, et al., 2016; Levkina & Titova, 2019). The findings accumulate subjective opinions about the financial situation and the surrounding economic conditions.
From the data it follows that almost half of the respondents are more inclined to believe that the time for large purchases is not the most favourable. Highs of absolutely negative attitudes were observed in the crisis and post-crisis periods.
The above information shows that, the state is taking incentive measures to increase investment in fixed assets for general modernization and reconstruction, which however should be considered insufficient. On the other hand, not only financially limited, but also more negatively inclined economically active population, whose initiative and work depends on the effectiveness of incentive measures, limits the renewal and acceleration of economic cycles. Current government decisions are aimed at solving the problem of overcoming poverty and the general maintenance of demographic parameters, improving the life quality. But the problem of the level of wages in Russia is associated mainly with the existing structure of the economy, where low-value-added industries account for a significant proportion. In addition, the low diversification of the Russian economy contributes to a fall in real incomes of the entire population by one of its indirect limitations in the event of an unfavourable pricing environment in commodity markets.
The features of a particular economic model play an important role in assessing welfare factors and their impact on economic growth. Thus, emphasis in a number of foreign countries is placed on monetary stimulation, which subsequently leads to recovery and future acceleration of economic growth. Moreover, such methods can be quite effective and have a positive impact on consumer confidence indices; they lead to an increase in incomes and expenses of the population.
Conclusions
Currently, the stagnation of economic growth has become one of the most significant problems of modern society, and therefore attracts more and more attention. Russian practice used in the struggle to stimulate GDP growth an approach based primarily on investment growth. Nevertheless, given the predominantly raw nature of the economy and the low diversification of industries, the expected effect could not be realized to the necessary extent.
Monetary stimulation methods, excess liquidity and high quality instruments of the debt market are classic tools for creating incentives for the development of the economy. These tools have proven themselves in the past, and are also successfully used in foreign countries. Unfortunately, their positive impact in the conditions of unbalanced high value-added industries will be very limited.
Consumption growth is one of the most effective factors in economic development. In this regard, the stagnation of incomes of employees in the commercial sector is still a rather difficult problem. Its solution largely consists in ensuring macroeconomic stability, increasing consumer confidence and applying accurate tax incentive measures. In addition, subsidies and payments to families with a minimum income should play a positive role.