Meu SciELO
Serviços Personalizados
Artigo
Indicadores
-
 Citado por SciELO
Citado por SciELO
Links relacionados
-
 Similares em
SciELO
Similares em
SciELO
Compartilhar
EduSol
versão On-line ISSN 1729-8091
EduSol vol.24 no.87 Guantánamo apr.-jun. 2024 Epub 15-Abr-2024
Original article
Integration of Universal History and Moral and Citizenship Education contents in elementary school
1Universidad Hermanos Saíz Monte de Oca, Pinar del Río. Cuba
2Universidad de Guantánamo. Cuba
The international context makes possible the citizenship education from the integration of the contents, therefore the scientific problem is how to contribute to the integration of the contents of Universal History for the development of Moral and Citizenship Education in Basic Secondary Education. The objective is to explain the integration of the contents of Universal History for the development of Moral and Citizenship Education in Basic Secondary Education. Research methods were used, starting from the general dialectical-materialistic method. The results are oriented to the foundation of the necessary integration of the contents of Universal History and Moral and Citizenship Education.
Key words: Content integration; Universal History; Moral and Citizenship Education; Basic Secondary Education
Introduction
The world's third Scientific Revolution, the interdependence of the sciences and the intensification of global problems, including climate change and the war between Russia and Ukraine, are characteristics of the contemporary world. Therefore, it is necessary to achieve, from an interdisciplinary thinking that allows the understanding of the processes of reality, the integration of contents to contribute to the solution of problems in learning.
Hence, in the Third Improvement of Cuban Education, in the new model of basic secondary education, there is a need to carry out research aimed at finding solutions to problems and for this, it is unavoidable to carry out actions to eliminate the existing deficiencies in terms of the integration of contents.
The deficiencies that have been referred to are related to:
Insufficiencies in the understanding of the dialectical path of knowledge, which prevents assimilating the history of the objects, phenomena and processes being studied and, consequently, they do not appropriate their internal logic.
In lower secondary school, the presence in the same grade of contents from different historical periods was evident, which hinders their assimilation and comprehension by students.
The linking of the contents of Universal History with those of Moral and Citizenship Education in secondary education is scarce.
The contents of basic secondary education are not always studied from an interdisciplinary perspective, and this affects their understanding from the point of view of the demands of integration as an essential process of the current level of development reached by the sciences.
There is insufficient treatment of the contents of the discipline of Universal History, which offer ample possibilities of integration with those of the new discipline Education for Civic Life.
Regarding the integration process, Piñón (2011), refers to the process of differentiation and integration of the sciences; Sierra (2004), states the need to train students with an integrative vision; Banasco et al. (2008), explain the need for the integration of sciences; Limia (2013), insists on social cooperation; while Suárez (2019), argues the need for the formation of logical historical thinking for the integration of the contents of Universal History and History of Philosophy in the Marxism Leninism and History course that tributary to the subjects of the discipline Education for Citizen Life belonging to the Third Improvement of Education in Cuba.
On the need to develop Education for Citizen Life in the formation of students, Chacón et al. (2019), reveal the transcendence of History, Civic Education and Political Culture in the significant contribution to the process of forming a consciousness of national and cultural identity from the study of Cuban thought; following these authors, Suárez (2019), emphasizes the need for the formation of logical historical thinking in students to develop citizenship education; meanwhile, Lama and González (2020), state the significance of Universal History for the formation of national and local culture in students.
That is why it is formulated as a scientific problem: How to contribute to the integration of the contents of Universal History for the development of Moral and Citizenship Education in elementary school students?
The objective of the article is to explain the integration of the contents of Universal History for the development of Moral and Citizenship Education in elementary school students.
Development
The integration of the contents of World History, a necessity for the development of Moral and Citizenship Education in the formation of Basic Secondary School students.
In order to consider the importance of the integration of contents that contributes to the development of Moral and Citizenship Education in the education of Basic Secondary School students, it is necessary to analyze the concept of integration considered as a "complementary process, which has implied the formation of multidisciplinary teams with very precise tasks and this requires that science be considered as a work process and specialized activity" (Sierra, 2004, p. 62).
In this way, integration is carried out among multidisciplinary teams with actions of coordination and peaceful coexistence, two fundamental aspects to relate the contents of the discipline of Universal History that contribute to the development of Moral and Citizenship Education in the formation of students of Basic Secondary Education, they require motivations, aspirations, interests, capacities and, above all, desires to do.
In this sense, students demand, for the development of Moral and Citizenship Education, the learning of varied contents, they need the characterization of the international context, which makes possible the way for the necessary integration of the contents as the processes and facts of the society in which they live are transformed and become more complex. In order to support the processes of educational integration, it is our responsibility to work in terms of citizenship education. Integration makes possible the integral development of the citizen.
That is why the integration of the contents of the discipline of Universal History in Basic Secondary Education contributes to the formation of the national, social, regional, local, cultural and patriotic identity of students as Cuban citizens, to the recognition of their duties and rights that typify them as individual human beings, but who in turn must comply with certain rules of coexistence according to the society in which they live.
This integration acquires importance for the development of Moral and Citizenship Education in the students, allowing them, from the previous knowledge of 6th grade, to learn about the conformation of the nation, from the concepts of democracy, citizen, Republic that they study for the first time in the subject History of the Ancient to Medieval World in 7th grade, the same are developed in 8th grade in the subject History of the Modern to Contemporary World and fed back in Moral and Citizenship Education in the three grades.
Through the assimilation of the contents of the facts and processes of the different historical periods through which humanity has passed, as well as the advances in science and technology through the study of the Industrial Revolution in certain stages of mankind, the adolescent acquires the knowledge that is developed in Basic Secondary School, therefore the integration of knowledge, skills and values, allow the development of collectivism, science, more responsible and respectful attitudes in students, enabling their inclusion in all activities of the homeland.
That is why the study of World History awakens an extraordinary interest among students, as it has the great privilege of enriching their imagination and creativity. It also plays a fundamental role in the development of patriotic feelings and convictions based on a deep identification with the traditions of revolutionary struggles and the cultural heritage of the people to defend the homeland and establish their own government with the participation of all citizens.
On the teaching of history, Martí (1963), stated:
This is a humanity that unfolds and concentrates in seasons and phases. Today it is necessary to study in something the residues of the societies that have lived. With serene judgment, with distrustful spirit, with logical rectitude, with skill and comparison and fine scruple (p. 76).
Marti's work becomes a mobilizing tool for the knowledge and behavior of human beings, so it becomes a necessity in the development of activities in Universal History classes to awaken the interest, motivation and feelings of students.
The current challenge of teaching history at the lower secondary level - taking into account the modifications proposed by the Third Improvement Program - is to integrate the contents of other subjects into the historical discourse, without diminishing the specificity of its treatment. It is necessary to demonstrate from the classroom that the solidity of historical knowledge is the result of an act of cultural integration, that is, an interdisciplinary exercise in itself. Hence, the linkage with contents of several areas of knowledge is declared, where the nodes of school disciplines approached independently until now are evident, as is the case of Moral and Citizenship Education.
The determination of the treatment of the contents cannot be schematic and will depend on the analysis carried out in each group based on the general results of the diagnosis and the required adaptations, but the study, the modes of action and the general objectives of the Basic Secondary Education programs must be taken into account, thus guaranteeing the knowledge of the characteristics of the subject in the corresponding grade. However, in the Universal History programs there is insufficient treatment of the general aspects of Moral and Citizenship Education, which contributes to the development of citizenship education in students of Basic Secondary Education.
In addition, there are two problems that constitute real challenges for the discipline of World History in basic secondary education, in this sense; we assume the deficiencies expressed by:
Insufficient treatment to the participation of citizens in the different stages of the development of humanity, which allows understanding its continuity.
The integrating activities related to citizen participation, equity, tolerance and inclusion are not at the desired levels.
Insufficient work to establish the relationship between personal identity, social citizen identity and national identity of citizens.
Insufficient treatment of Marti's and Fidel´s thought, as essential content of the discipline Education for Civic Life.
The one referred to the deficiencies that students have regarding the formation and development of dialectical thinking, which makes it difficult to understand the phenomena, objects and processes of reality in order to understand the spatio-temporal context in which they act as citizens.
The insufficient treatment to the integration of the contents of Universal History for the development of Moral and Citizenship Education.
In spite of these inadequacies, the program of Universal History in Basic Secondary Education, of the Third Improvement, has different strengths:
It allows compliance with the rules of coexistence, norms and goals established in its family context, in the school group, in its institution and in society, by studying the historical, legal, cultural and citizen potential of universal history, of Cuba and its localities, rejecting all types of discrimination, violence and corruption.
It is identified in the historical becoming, the juridical, cultural and citizen potential that emanates from the study of universal historical events and processes (aspects or categories studied in Moral and Citizenship Education).
The features of Athenian democracy are explained, and the concept of citizenship in Athens is explored in depth, in order to corroborate the limitations that existed in the moral-legal sphere within the framework of a slave-owning society.
The individual is interrelated with the collective; the social movement.
Therefore, in the Universal History program there are weaknesses in the treatment of the categories of Moral and Citizenship Education.
The proposal presented here responds to the search for actions that favor the demands of the new Improvement of Education, which makes possible the integration of the contents of Universal History for the development of Moral and Citizenship Education in basic secondary education.
For its part, Moral and Citizenship Education, according to Chacón et al. (2019),
(...) must contribute to the formation of the foundations of the student's civic culture, at the core of which are the contents of the historical bases of civics: ethical-moral, political and legal, in interaction with the remaining ideological forms of social consciousness, for his self-regulated participation in the public space of the construction of socialism in Cuba, of his life project as a Cuban revolutionary citizen, honest, decent worker, knowledgeable and respectful of the law and its principles, protagonist of personal and collective rights and duties, on the basis of the consolidation of his national identity and patriotic pride in the revolutionary historical memory of the Cuban people. (p. 9)
This subject provides knowledge of the Constitution of the Republic of Cuba and other laws such as the Law of National Symbols and the Family Code, which every Cuban citizen should be aware of. In Moral and Citizenship Education, the integration of the contents with the components for the integral education of the student is achieved, with greater emphasis on citizen behaviors. The contents are updated in accordance with the new approaches, both in the knowledge of Social Sciences and Didactics. The study of Marti's and Fidel's ethics is highlighted.
For the students' performance in the subject Moral and Citizenship Education in 7th, 8th and 9th grades, an integrated learning is required which, with its challenges, makes it possible to raise the significance of the integration of the contents, allowing the students' participation as the axis around which all the potentialities of the assimilated knowledge are deployed.
Universal History, according to Lama and González (2020):
It is the accountability of a society. That is why it is so important for schoolchildren to appropriate a historical culture that fosters the development of national, Latin American and third world identity, a sense of belonging, and the assimilation of national and universal traditions. It is about a culture located in time and space that allows us to know the past, the self-understanding of the present and the transforming projection towards the future, that is to say, it is necessary to reveal the progressive sense and continuity of the historical process. (p. 9).
We agree with this researcher, although it is necessary to state that Universal History also contributes to the formation of a civic culture, to the social civic identity. This is evidenced in the study of civilizations from classical slavery, from the History of the Ancient World to the Medieval World, in 7th grade, in which concepts such as democracy, citizenship, senate and others are worked on, which the student must know and apply in his development to exercise responsible citizenship in Cuba.
The discipline of Universal History, in the Third Improvement, in 7th grade, presents a multiform character of the transition from communitarian societies to tributary, slave and feudal societies. It is possible to work on the contents that contribute to inclusion, by analyzing the characteristics of slave societies in which slaves and women were excluded from society, without duties and rights, while at the same time integrating activities related to the participation of men in the socioeconomic development of society can be developed, as in the case of the civilizations of the Ancient East.
In 8th grade they are integrated into a single program, which follows the logic of the historical content being treated and favors its systematization in a single grade and allows the use of a single textbook covering Modern and Contemporary History. "From the Modern to the Contemporary World". In this grade, the emergence and development of capitalism up to its imperialist phase is studied, so the attitude and participation of citizens in the defense of their people, the social citizen identity and the necessary equity must be treated, it is also necessary to analyze Marti's thought on capitalism.
The integration of the contents in the formation of students in basic secondary school.
In past times regarding the integration of sciences, we find the contributions of different philosophers since Ancient Greece, who recognize the importance of the specialization of activity as a result of the social division of labor. Platón (1871) (IV, b. n. e), was one of the first to think science with an integrating vision, he proposed the relationship between grammar, rhetoric and music: this tendency was continued by the school of Alexandria of neoplatonic orientation.
Subsequently, with the scientific and technological development of society, the integration of contents in educational processes has become significant. Therefore, the need for the integration of contents and changes in programs, disciplines, subjects. Thus, Banasco et al. (2008), state the trends of the historical development of science for the understanding of the integrative approach to education in educational institutions: "they are: integration of knowledge, differentiation of knowledge, and differentiation-integration, whose reflection is manifested in the teaching-learning content" (p. 31).
This integration has its origins in the development of the sciences that shows, since the end of the 19th century, their interactions and reaches its maximum exponent in the third scientific-technical revolution with its integrative tendency, to reveal the complex problems of reality. "The development of scientific-technological knowledge demonstrates its contradictory character; the more the differentiation of sciences develops, the more the possibilities for their integration are created" (Piñón, 2011, p. 17).
The development of science describes two interrelated processes: one aimed at the search for the most essential determinations (object of research of particular sciences, which promotes specialization in the domain of the object of research), and the other is oriented towards the search for meeting points and integrative frameworks. This is one of the trends in the development of science and technology today.
As a consequence, in the teaching-learning process there is a contradiction between the continuous specialization in the disciplines and the indispensable integration of the contents of these disciplines in an orderly system. The greater the specialization, the greater the unavoidable integration of those contents that have points of contact with each other; for this reason, integration is a process that requires the search for the relationships that exist between the elements that make up that ordered system, formed by the disciplines referred to.
In order to analyze the importance of content integration in the education of elementary school students, the first step is to understand the concept of integration. For Pérez and Merino (2008), "...integration always involves coordinated effort, joint planning and peaceful coexistence among the sectors that make up the group. This is the only way in which the parts can constitute a whole, even without losing their individuality" (p. 2).
In this way, the integration between groups is emphasized with actions of coordination and peaceful coexistence, two fundamental aspects for the contents of Universal History that contribute to the development of Moral and Citizenship Education in the formation of students of Basic Secondary Education, they require motivations, aspirations, interests, capacities and, above all, desires to do. Therefore, students demand learning of very dissimilar contents, they need the characterization of the historical-social context, which paves the way for the necessary integration of knowledge, skills and values to the extent that the processes and facts of the society in which they live are transformed and become more complex.
The contents of the Universal History disciplines are interconnected with those of Moral and Citizenship Education, through interdisciplinary work in the integral preparation of teachers. In this sense, the discipline of Moral and Citizenship Education presents certain contents of the disciplines of Universal History, which express its significance for the formation of social, national and cultural citizenship identity, based on the ideology of the Cuban Revolution, which allows the study of Cuban thought related to Marxism and Leninism, third world and Latin Americanism.
The disciplines Universal History and Moral and Citizenship Education present thematic axes that are found in all the contents, as is the case of the cultural and identity conception that promotes the understanding of the true meaning of culture and its expression in values; the understanding of the practical-spiritual nature of thought; the economic, political, socio-classist and ideo-cultural conditioning that favor the development of man, taking into account the different times and historical contexts in which he has had to live.
For this reason, integration makes it possible to reflect in the content the object of study, has its germs in the links between subjects, which determine the dialectical interrelations, which act objectively in nature and are known by current sciences.
The contents of the program of the subject History of the Ancient World to the Medieval comprise the universal history from the process of hominization to the decadence of the feudal economic-social formation and the gestation in it of the capitalist society, but it is necessary to give treatment, from the study of the different civilizations of the classic slavery, to citizen participation, the norms of social coexistence, inclusion and respect for the homeland, topics that are weakly treated in the program and that allow, from the integrating activities elaborated and oriented by the teachers, the development of Moral and Citizenship Education in the students.
On the other hand, the contents of the program of the subject History of the Modern and Contemporary World in 8th grade are interconnected and refer to the most significant historical facts and processes of the mercantile, industrial and monopolistic stages of capitalism, from the 17th to the 21st century. In addition, the gestation and development of a new society is studied: the socialist one. It is necessary to deepen the awareness of citizens in the transformation of society to their benefit, as well as in the participation for the care and conservation of the environment due to the aggravation of environmental problems, aspects that are treated in the subject of Moral and Citizenship Education.
The 7th grade Moral and Citizenship Education program contributes to the development of social, national and cultural citizenship identity; its previous knowledge is found in the subject of Citizenship Education in the Third Developmental Stage of Primary Education. Its contents are aimed at the formation of civic, moral and legal values in students, as well as the foundations of legal culture from the knowledge of the Constitution of the Republic of Cuba. This subject enables the work to develop the active participation of adolescents in the different activities of the environment in which it is developed.
The program of Moral and Citizenship Education in eighth grade refers to the knowledge of the system of socialist legality in Cuba, of the legal norms that determine the State, contributes to the development of responsibility and citizen participation of the family, the school and the community in all activities of society.
The main objective of the subject is to value the role and responsibility of the family in the preparation of Cuban adolescents in the construction of Cuban society in the current historical context, the need to develop in them feelings of love and respect towards the family and to develop aptitudes before the duties and rights in the framework of the family. The contents can be treated in the subject History of the Modern and Contemporary World in the unit of the French Bourgeois Revolution, precisely when analyzing the French Constitution and its legal norms, but the methodological preparation of the teachers' collective is needed to select the common contents of both subjects.
One of the categories present in the disciplines of Universal History and Moral and Citizenship Education in Basic Secondary Education is the citizen, which has as its antecedent the emergence and development of cities (this element is studied in the medieval period), which is the product of the development of socioeconomic conditions, in this way this process leads, inevitably, to the division of society into social classes emerging the political structure of society and the establishment of certain political rights and duties in correspondence with the economic position occupied in the city. Likewise, the citizen demands an education that prepares him to carry out his social activities from an early age in Cuba.
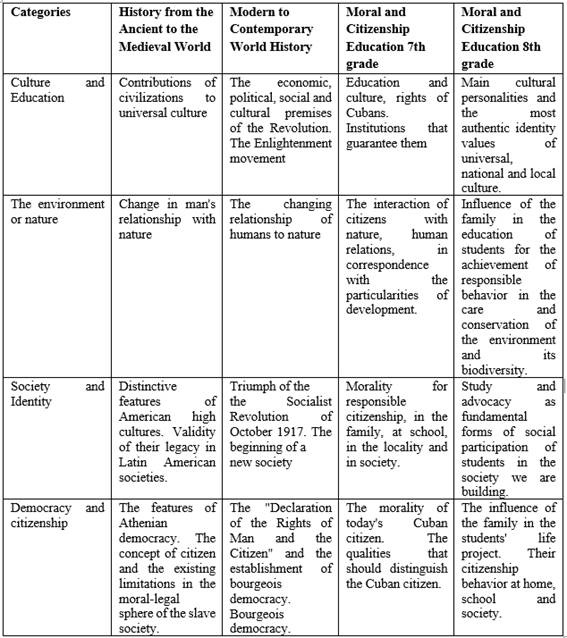
In order to determine the contents that can be integrated into Universal History, which contribute to Moral and Citizenship Education in Basic Secondary Education, the most common contents are selected, which can be part of a syllabus Yániz and Villardón (2006). The organization in lessons or in blocks according to broad areas of a discipline. For this reason, the following list of Universal History contents that can be integrated with Moral and Citizenship Education is presented, as shown in table 1.
Conclusions
The systematization of the theoretical references showed the existing interconnection between the contents of Universal History for the development of Moral and Citizenship Education in students of Basic Secondary Education.
The systematization of the referents, determined the need for the preparation of Basic Secondary Education teachers in the work with the selection of the reiterative contents of Universal History and Moral and Citizenship Education that allows the development of participation, the norms of social coexistence and the defense of the homeland in the students.
The conception of the citizen allows analyzing him/her as an active and transforming human being, conscious that participates in all the activities of the environment, committed to the homeland and socialism.
Referencias bibliográficas
Banasco, J., Caballero, C. A. y Pérez, C. (2008). Una alternativa de integración de los contenidos de enseñanza de las Ciencias Naturales. Universidad Pedagógica Enrique José Varona. Revista VARONA, 47 [ Links ]
Chacón, N. L., Silva, R. D., Güemez, M., Cabrera, O. R., Palmero, A., Sierra, J. J., et al (2019). Aproximación a una concepción de la Educación para la Vida Ciudadana en la formación docente. Publicaciones Acuario. http://www.cfv.org.cu [ Links ]
Lama, E. y Gonzales, N. (2020). La Historia Universal en el Tercer Perfeccionamiento de la Educación Cubana. VARONA, Revista Científico-Metodológica, 70. http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo. [ Links ]
Limia, M. (2013). Retos del Marxismo en la Cuba de hoy. Pueblo y Educación. [ Links ]
Martí, J. (1963). Los Cuadernos de Apuntes. Obras Completas. O C. Tomo XXI. Imprenta Nacional de Cuba. [ Links ]
Piñón, J. C. (2011). Integración científica e interdisciplinariedad. VARONA, Revista Científico-Metodológica, 5. https://www.redalyc.org/ [ Links ]
Pérez, J. y Merino, J. M. (2008). Definición de integración. http://definicion.de/integracion/) [ Links ]
Platón L.. (1871). Dialogo X El Banquete. Obras completas de Platón, por Patricio de Azcárate, tomo quinto, Madrid. https://www.filosofia.org/cla/pla/azc05297.htm [ Links ]
Sierra, J. J. (2004) La Educación Jurídica. Propuesta de un sistema de trabajo teórico y metodológico para la formación inicial y permanente de maestros primarios. (Tesis de Doctorado, Instituto Central de Ciencias Pedagógicas, La Habana). https://www.eumed.net/libros-gratis/2011c/983/983.pdf. [ Links ]
Suárez, M. (2019). Formación del pensamiento histórico-lógico para la integración de los contenidos de Historia Universal e Historia de la Filosofía. (Tesis de Doctorado, Universidad de Ciencias Pedagógicas Enrique José Varona, La Habana). https://www.eumed.net/libros-gratis/2011c/983/983.pdf. [ Links ]
Yániz, C. y Villardón, L. (2006). Planificar desde competencias para promover el aprendizaje. El reto de la sociedad del conocimiento para el profesorado universitario. Bilbao: ICE de la UD. Cuadernos monográficos del ICE, 12. https://dialnet.unirioja.es/ [ Links ]
Received: September 06, 2023; Revised: November 20, 2023; Accepted: January 09, 2024











 texto em
texto em