INTRODUCTION
In the hyperbaric pressure environment, the partial pressure of each gas component increases, which increases oxygen partial pressure. The increased partial pressure of oxygen leads to the generation of free radicals and oxidative stress. The detrimental effects of exposure to high concentrations of oxygen are due to the increased production of oxygen radicals or other reactive metabolites derived from oxygen.1 Oxygen is potentially toxic due to the production of free radicals.2,3 Oxygen-induced tissue damage is reported for most organs and should be considered when patients are exposed to an elevated oxygen concentration and pressure.4,5
The literature has numerous studies involving hyperbaric pressure in diving. However, these studies were mainly performed on divers,6,7 who had many years of dive experience and whose bodies had certain adaptations to the high-pressure environment. Moreover, the previous studies involved mostly wet diving activities; because of this, many other variables can affect the results in addition to the hyperbaric pressure. This includes the diver’s underwater activity and the temperature of the aquatic environment.
In order to appropriately assess the effects of the hyperbaric pressure environment on oxidative stress status, it is necessary to eliminate the variables introduced by the aquatic environment. It is also necessary to eliminate the variable of adaptation to the hyperbaric environment already existing among divers, through the selection of healthy subjects without prior exposure to the hyperbaric pressure environment.
The study’s objective was to determine the effects of hyperbaric pressure environment on the oxidative stress status using the biological markers Malondialdehyde, Catalase and Superoxide Dismutase in healthy non-diving subjects.
METHODS
Research design
This study was conducted in the hyperbaric chamber unit (Hyperbarichealth.com, Australia) of the Vietnam Navy Force from April 2020 to May 2020. Data collection and analysis occurred at 3 points in time: before entering the pressure chamber (before compression), after leaving the pressure chamber (immediately after decompression) and 1 hour after leaving the pressure chamber (1 hour after decompression).
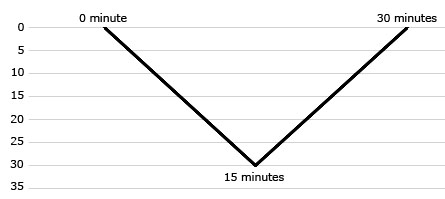
The diving procedure consisted of a dive using compressed air with compression speed of 2 to 2.5 meters/minute, up to a maximum pressure equal to depth of 30 meters of water (msw). When the maximum pressure was reached, decompression was performed immediately and ascent to normal pressure was conducted at 2 to 2.5 meters/minute). Total time in the pressure chamber was 30 minutes (Fig. 1).
Sample collection protocol
Three testing blood samples were collected from the subjects to measure the levels of Malondialdehyde (MDA) and antioxidant enzymes activity of Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) and Catalase (CAT). To exclude the impact of different diets, all subjects were on the same dietary protocol before and during the study.
Biochemical assays
Venous blood samples were collected from the antecubial vein of subjects in proper vacutainers. Blood samples were centrifuged to separate plasma and erythrocytes. Plasma and erythrocytes were immediately stored at -80oC until use.
Quantification of MDA level: MDA was quantified according to the ELISA method, based on the procedure of ELISA kit (BioVision, Milpitas, CA, USA). Unit of MDA is ng/mL.
Quantification of CAT and SOD: CAT was measured by colorimetry based on the principle that Catalase catalyzes the decomposition of H2O2 into H2O and O2; meanwhile, SOD was quantified by colorimetric method based on the principle that SOD catalyzes the reaction of converting superoxide (O2 •-) into O2 and H2O2,8,9,10 using a kit from BioVision (Milpitas, CA, USA). The CAT and SOD activity unit are mU/mL and ng/mL, respectively.
Subjects
Twenty-nine non-diving healthy men with no acute and chronic medical conditions were recruited to participate in the study. The study was performed in accordance with the procedure of the Vietnamese People’s Navy (Vietnam Ministry of National Defense. Circular: Regulations on health standards, pre-qualification, examination and recruitment, and health assessment of submarine forces of the Navy. Hanoi, Vietnam; 2011).
This protocol had been approved by the ethical committee for biomedical research of Vietnam Military Medical University. All subjects were fully informed about the study process and gave their informed consent.
This study included 29 subjects, with average age of 19.52 ± 1.09 years; average body mass index (BMI) was 19.82 ± 1.32 (kg/m2); average chest round was 83.45 ± 3.11 (cm); the average right-hand force was 39.24 ± 8.74 (kg); the average left-hand force was 36.93 ± 7.74 (kg); average back force was 118.45 ± 20.67 (kg).
Statistical analysis
The research data was processed by computer using SPSS 22.0 software based on biomedical statistics method. The results were shown in the following form: Mean ( X ), standard deviation (SD), standard error of mean (SEM). Data distribution was checked with the Shapiro - Wilk test and depending on results, the appropriate parametric or non-parametric test was used. Comparison of the means by testing quantitative variables on paired samples (Pair-Sample T Test or Wilcoxon Test). The difference was statistically significant, with p< 0.05.
RESULTS
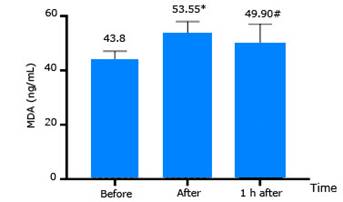
The change of MDA levels is presented in figure 2. MDA activity increased immediately after decompression compared to that before compression. At 1 hour after decompression MDA activity tended to return to the same level as that before compression.
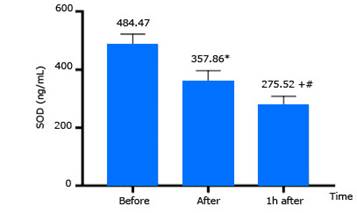
SOD enzyme activities determined before compression, and immediately after, and 1 hour after decompression are presented in figure 3. SOD enzyme activity decreased significantly after decompression compared to that before compression (p< 0.05).
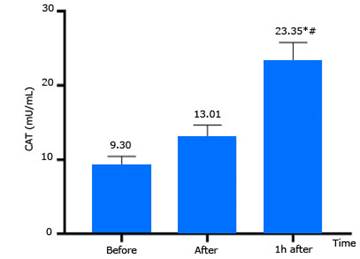
CAT enzyme activities determined before compression, and immediately after, and 1 h after decompression are presented in figure 4. CAT enzyme activity at 1 h after decompression increased more than that before compression, and immediately after decompression significantly (p< 0.05).
DISCUSSION
MDA activity: In this study MDA increased immediately after decompression and decreased gradually at one hour after decompression (Fig. 2). Ferrer et al.5 studied the effects of high pressure on a group of divers performing a dive at a depth of 40 meters breathing compressed air with a total time of 25 minutes, versus another group of healthy males breathing oxygen at a pressure of 2.2 ATA for 60 minutes in a pressure chamber. The results showed that MDA activity increased after hyperbaric exposure, but it was not statistically significant. The study by Sureda et al.11 was performed on 7 professional divers conducting a dive at a maximum depth of 40 meters for total time of 25 minutes and breathing compressed air. The ascent process took a 5-minute safety stop at the 3-meter decompression station. After the dive, it was reported that MDA activity had some statistically significant changes.
Kozakiewicz et al.12 compared diver’s MDA activity before and after exposure to hyperbaric pressure in a pressure chamber equivalent to 30 msw (4 ATA). The result was that erythrocyte MDA activity increased immediately after being exposed to hyperbaric pressure; the change was statistically significant. In 2012, Sureda et al.6 studied 9 professional divers breathing compressed air diving at a depth of 50 meters for a total time of 35 minutes. The study demonstrated that MDA did not increase immediately after diving, but 3 hours after diving MDA activity increased significantly compared to before diving.
The results of this study showed an earlier increase in MDA compared to Sureda’s et al.6 study, and the MDA activity in the current study was lower. We believe this is due to the fact that the in current study subjects were healthy young men who had never participated in diving. The MDA activity in the current study ranged from 40 to 60 ng/mL (0.56-0.83) µmol/L. MDA molecular weight (72.07) is equivalent to healthy human MDA activity.13 However, subjects in the Sureda’s et al.6 study were professional divers, so these subjects had adapted to oxidative stress, with high MDA activity.
SOD activity: Results in this study demonstrated that SOD activity decreased after decompression (Fig. 3), which was not consistent with some other studies. The study by Sureda et al.11 was conducted with dives to a maximum depth of 40 meters, for a total time of 25 minutes breathing compressed air. The results of this study showed that, although plasma SOD activity increased immediately but not significantly after the dive, up to 3 hours after the dive, plasma SOD activity increased more significantly than before the dive. The activity of antioxidant enzyme in red blood cells did not have a statistically significant change. In 2012, Sureda et al.6 reported an increase in activity of SOD enzymes after the dive to a depth of 50 meters, for a total time of 35 minutes while breathing compressed air. Radojevic-Popovic et al.14 studied 32 professional divers with an average age of 32 ± 5.1 years and diving experience from 3 to 18 years. They made dives to 30 meters’ depth breathing compressed air for 30 minutes. Their descent speed was 10 meters/minute, the ascent speed was 9 meters/minute, with a 3-minute safety stop at 3 meters. The results demonstrated that SOD activity decreased after diving (before diving 1 416.26 ± 334.15 U/g Hb x 103; immediately after diving: 1 275.91 ± 378.51 U/g Hb x 103), however, this change was not statistically significant.
Adaptation of the antioxidant system that occurred in professional divers was considered to be an important factor in the absence of significant changes in the activity of SOD. A study by Zwart et al.15 evaluated the effects of a long-term dive on SOD change and found the decrease in SOD activity after the dive. Based on results in current study and others, professional divers adapted to hyperbaric pressure environment, so the change in this enzyme activity seems to be of slower appearance. In addition to the long period of the dive, can be a reason which led to the presence of oxidative stress, and the antioxidant capacity of SOD enzyme can be decreased. Subjects in current study are healthy men, who do not adapt to high pressure environment, their response can occur earlier and stronger than the that of professional divers.
CAT activity: Catalase catalyzes the decomposition of H2O2 to water and oxygen.8,9,10 Change of CAT activity suggest that oxidative stress status appeared. In this study, CAT increased immediately after decompression, which was significant at 1 hour after decompression (Fig. 4) and consistent with other studies. Ferrer et al.5 studied the effects of high pressure on the antioxidant system of lymphocytes on a group of 7 divers with a mean age of 26.0 ± 4.7 years old. They performed a dive to 40 meters breathing compressed air for a total time of 25 minutes. This included 10 minutes at 40 meters depth and 5 minutes at a 3-meter decompression station. The results of this group showed that CAT activity increased significantly at 3 hours post-dive (27.9 ± 2.2 K/109 lymphocytes) compared to before dive (21.4 ± 1.1 K/109 lymphocytes). Another group of this study consisted of 12 healthy males with mean age of 25.3 ± 3.9 years, breathing oxygen at a pressure of 2.2 ATA for 60 minutes in a pressure chamber. The results showed an increase in the activity of CAT after the end of hyperbaric oxygen pressure breathing (26.2 ± 2.2 K/109 lymphocytes) compared to before exposure to hyperbaric oxygen 22.2 ± 2.4 K/109 lymphocytes), but the difference was not significant. (5)
Sureda et al.11 conducted research on diving to a maximum depth of 40 meters with a total time of 25 minutes while breathing compressed air. The results of this study showed that plasma CAT activity increased significantly immediately after the dive (276 ± 23 Kat/l) compared with before the dive (200 ± 18 Kat/l); 3 hours after completion of the dive, CAT activity recovered, which was similar to before diving. Meanwhile, the activity of this antioxidant enzyme in red blood cells did not have a statistically significant change. In 2012 Sureda et al.6) conducted a research on diving to a depth of 50 meters with in a total time 35 minutes while breathing compressed air; they reported an increase in the activity of CAT enzyme after the dive.
Gasier et al.7) performed a study on 100% oxygen breathing for 2 hours at 1 ATA, 1.5 ATA and 2 ATA in the pressure chamber. The study showed that erythrocyte CAT enzyme activity 1 hour after breathing oxygen was significantly reduced compared to before breathing oxygen (1.5 ATA); at 2 ATA pressure it was observed to decrease at all 3 time points, after 15 minutes, after 1 hour, and after 2 hours breathing oxygen compared to before breathing oxygen. Meanwhile, plasma CAT activity did not change significantly following all of the hyperbaric oxygen exposures. (7) Radojevic-Popovic et al.14 performed diving with compressed air to 30 meters for 30 minutes. The results showed that there was an increase in CAT activity immediately after diving (before diving 5.21 ± 2.38 U/g Hb x 103; immediately after diving 6.39 ± 3.25 U/g Hb x 103); but, this change was not significant. The authors reasoned that the study subjects were professional divers with frequent diving, so the antioxidant system had adjusted already in the direction of adaptation. Therefore, a new dive did not lead to any changes in CAT activity.
The results of this study have some similarities but also some differences compared with the results of other authors. In author’s opinion this is due to the following factors: First, during dry diving in the pressure chamber the subjects did not actually carry out any physical activities. This is different from these previous studies, where subjects conducted dives with different activities to perform descent and ascent. Second, our study subjects were healthy men exposed to a hyperbaric barometric pressure environment for the first time, so they had not yet adapted to these environmental conditions. Thus, changes of oxidative stress (MDA activity) occurred more rapidly and antioxidants (SOD enzyme and CAT enzyme activities) changes early, which is different from previous studies.
As a limitation, the current study followed the impact of a hyperbaric pressure environment in a short duration of only 1 hour after leaving the pressure chamber, lacking a longer follow-up time of 3 to 6 hours after hyperbaric pressure. Longer follow up will yield more information on the evolution, resilience as well as the changeable level of biologic markers.
In conclusion, some changes in the biologic markers MDA, CAT and SOD suggest the appearance of oxidative stress under the influence of a hyperbaric pressure environment.