Introduction
Codification of the policies is of great importance for the ineffectiveness of the administrative system. The general policies are a set of orientations and major strategies for the realization of the goals of the system and the constitution in a specified period. These policies are in fact the major administrative demarches passed on by the Supreme Leader leading the actions and measures of the tripartite powers (the Executive, the Legislature, the Judiciary), non-governmental organizations, and armed forces, as a standard and guide. For implementation of the administrative system general policies, it is required to, besides codifying the administrative policies related to the elements of the administrative system, the plans for transition in the administrative system be prepared and implemented, so that by promotion of the administrative system, a good means for implementation of the contents of 1404’s Vision can be provided. The administrative system would be efficient and effective when its components form the consistent and interactional activities in the system. The components of this system are formed by the technological, structural, human, policies, and objectives factors, and one of the most important components is the human resources, which plays an important role in the success or failure of the governmental organizations plans.
Especially, with the beginning of the transition and reformation in the administrative system, the efficient and competent human resources for the realization of the plans is of a great importance. One of the factors related to the human resources are the behavioral factors, which are referred to as a set of employees behavioral and personality traits and the dominant social atmosphere in the administrative organizations, which are manifested in the framework of the organizational culture and the interactions between the employees themselves and between the employees and the clients. The behavioral factors include the human factors and relations within the organization which form the behavioral norms of the informal relationship and interconnected special patterns, as well as the main content of the organization. These content factors are in fact considered revitalizing and productive, and any factors and variables directly related to the human resources are categorized under this class. The behavioral factors are intra-organizational and confined to the organization’s system boundaries.
The studies have shown that various factors are effective on the emergence of a behavior. Therefore, recognition of the behavioral factors and the factors affecting them is of a great importance. This recognition must occur in the individual, group, organizational, and environmental levels. Thus, regarding the studies conducted on the administrative system, today, paying attention to the behavioral factors in the implementation of the plans in the organizations, is necessary. Therefore, the current study aimed at designing a behavioral pattern related to the implementation of administrative system general policies in the body of the Islamic Republic of Iran.
The administrative system in each organization is an inseparable part of that organization. This system is in fact a bed for the realization of the organizational goals and plans, and the efficiency and effectiveness of all the components of the organization depend on it (Behroozi & Ahmadi, 2017). The administrative system consists of four sub-systems as “Organizational structure", "manpower", "working methods" and "the dominant rules and regulations". The quality of this set is affected by the general policy at the national and international levels. Generally, the administrative system of each government is indicative of its approach to the administering and management method for that country and the role of the administrative system in the economic, political, social, and cultural structures, and its effect on the realization of the society’s major systems goals, is so important that without having an efficient and effective administrative system, the achievement of the goals is not possible. In the recent years, the transition and reformation of the administrative system and promotion of the management have been followed as a main prerequisite for the growth and development of the country and a main objective. The administrative system general policies as the major administrative policies and the model and guide for the activities and measures of the governmental systems themselves lead to the promotion of the administrative system capabilities. The administrative system is a set of interconnected elements including the structure, the dominant values, and function, which are interacting for the achievement of the political, economic, and social objectives of the country (Ahmadi & Movahed, 2019).
The administrative system of each country is similar to a regulatory organization for all the activities to achieve the determined objectives, which besides the creation of the harmony between the different parts of the society, prepares the platform needed for the realization of economic, social, cultural, and political affairs (in accordance with the constitution and the country’s regulations). For the implementation of the administrative system general policies, it is required to, besides codifying the administrative policies related to the administrative system elements, the plans for the transition and reformation of the administrative system be prepared and implemented, so that by promoting its capabilities, a proper means for the implementation of the contents of 1404’s Vision can be provided. Thus, firstly, the sun-policies of each general policy related to each subsystem should be codified through the classification of general policies based on their subsystem, so that it can be a manual for planners to codify the administrative system promotion plans. The studies have shown that among the important elements in the administrative system and its transition is the human resources including the positions, norms, national service regulations; recruitment, promotion, reward; appointment; and decision-making power of the managers and employees (Featherstone, 2014). The human resources is an important factor for the organizations’ success and performance, and management of the human resources and the individual and group behaviors are considered as the most important factor affects the efficiency increase (Zarei Matin, 2015).
The evaluations have shown that in fact, through proper governmental management and consequently, full realization of the government’s role in administrative transition in Iran, fulfilment of the administrative system general policies, and moving towards the objectives of the Vision Plan, the steps towards the full-scale development in all aspects can be taken. Rahnavard (2012), have categorized the administrative system general policies and its strategic goals in three categories as the administrative values, administrative structure, and the function. Among the factors effective on the successful implementation of the administrative system general policies that is also related to the human resources, are the cultural and behavioral factors, which are according to Tehrani & Maleki (2016), in a study titled ‘the administrative system of development plans’, are among the harmful factors within the administrative system, and accordingly, identification of such factors and the factors affecting them, can be useful for the successful implementation of the country’s policies, objectives, and plans, since the content or material poured into the organization container is the very human behavior (Mohammadi Aras & Asli Zadeh, 2016) in a study titled ‘the measurement of realization of the administrative system general policies passed on by the Supreme Leader’, dealt with the evaluation of the realization of four aspects as the justice-orientation, religion-orientation, knowledge and skill, and reverence of the clients, out of the 12 cases of administrative system general policies passed on by the Supreme Leader.
Hizaamu (2014), in a study, has expressed the main components of the reformation of general administration in Uganda to be the processes and means for the reformation, the need to obtain general efficiency and effectivity, development of the public sector’s human resource ability, time management and organizational discipline, and development of the public sector. He also believes that the challenges are resistance to the reformation with special Bureaucrats, the limits on the financial resources for the full implementation of the reformations, lack of the expertise and awareness of all the beneficiaries, the weak attitude of the employees in the reformed administrations, lack of the required consistency, lack of the comprehensive consultation, and political support (Parizi, et al, 2019). Songtao (2006), in a study titled ‘reformation of the public administration in China’, has considered the public administration as a component of the reformation in economic and political systems, and believed that restructuring of the government, improving the people, the system of duties, and the delegation can be effective in refining the public administration (Sepehri & Sheikhalizadeh, 2019).
The Behavioral Factors related to the Implementation of General Policies of the Administrative System
The well-being of the administrative system is caused by several factors some of which rooted in the organizational members’ values and beliefs, which if refined and reinforced, would obviate many problems and ethical anomalies in the organizations. Some issues also are related to the intra-organizational affairs which are either stemmed from the improper structures or the improper behavior in the relationships between the managers and employees (Sheikhi, 2011). Since the human resources are the most valuable production factors and the most important assets of the organization, and the main resource of competitive advantage, creating fundamental capabilities for the organization, one of the ways to achieve the competitive advantage in today’s conditions is to make the employees more efficient. Regarding the important role of human resources in the realization of organization’s plans and goals, recognition of it for making the organizations more efficient is of a great importance. Especially, the behavior and culture of the human resources play a vital role in the successful implementation of the administrative system plans and policies. Therefore, the main content of the organization consists of the human behavior and human activities and behaviors are also exhibited to achieve the predetermined organizational goals. The result of human’s work and energy and the organizational structures and structures are manifested in the main functions or tasks of the organization. In recognition of the behavioral inconvenience, the center of attention is the functions, and those factors should be evaluated that distort the organizational or human performance, and deviate them from the normal state, damaging their effectivity to the extent that it creates crises in the organization and totally prevent it from a healthy growth. By the behavioral aspect, the human factors are meant that through behavioral and communicative forms and specific patterns, shape the main content of the organization and by its entrance, the organization is revitalized and personal interactions are created. The human resources, which is the main factor in each organization, is also defined as the main factor for work execution, ignoring which would lead to the irreparable damages.
The motivation, working spirit, job satisfaction, approaches, values, assumptions, and finally, the emergence of different behaviors are among the content or behavioral factors. The behavioral factors can include the justice in treating the employees, improving their livelihood, education and training, observance of the meritocracy, rewards, and punishments (Salehi Amiri & Shadaluei, 2013). Generally, if the good and bad aspects of the social life are distributed fairly, the people would become more committed, and more inclined to devotion for the group. On the contrary, when unfair occurrences are seen, the people become less inclined to the loyalty and endeavor, and they may opt for theft, aggression, and rebel. When the payments in the organization are unfair, the livelihood of the employees would be improved and this sense of justice in the organization, and lack of financial problems for the employees can be effective on the decrease of administrative corruption.
Also, basically, as a supplement of the motivational system, it should be said that the employees should occupy the positions based on the meritocracy system. Clearly, any position has some specific requirements which include special talents and attributes that must exist in the applicant. It can be said that many of the abilities (talents) can be acquired by the education and experience. If the employees, in spite of creation of required motivational atmosphere by the managers and leaders, do not exhibit the expected performance, behavior, and ethics, in case there are no environmental variables to obstacle it, it can be concluded that they do not deserve the current position with its special requirements (punishment). In case their performance is to the extent, or above the expectations, it is revealed that the person has the competence required for the occupation of that job, or promotion (reward). For the first state (punishment), it should be noted that not encouraging is itself a type of punishment.
Generally, the behavioral factors based on the theoretical models, can be evaluated in the individual, organizational, group, and environmental levels. For behavior guidance, the recognition of the past behaviors and prediction of the future behaviors play an important role in the organizational success, and therefore, investigation of the employees behaviors in the three individual, group, and organizational levels, is of a great importance. Among the behavioral components in the individual level, the personality, value and approach, ability, perception, motivation, individual learning, individual decision-making, job satisfaction, and the emotional intelligence can be named. The leadership, group structure, communications, conflict, power and politics, teamwork, opposition and negotiation, changing the organizational culture, and political behavior are among the behavioral components in the group level. Factors such as organizational culture, organizational environment, organizational design and structure, job design, and technology are among the important components in the organizational level (Gholi Pour, 2015; Zarei Matin, 2015).
The behavioral components in the behavioral level: the environment is one of the fundamental factors in upbringing, being effective on the mood and behavior. The rules and regulations, economic factors, etc. are among the environmental factors. In this regard, Tehrani & Maleki (2016), in a study titled “the administrative system of the development plans (a review on the harms in this area and their prioritization)” have noted that the cultural and behavioral indices are among the obstacles of the development plans. Khandozi (2016), in a study titled ‘on the general policies of the resistive economy (transition of the administrative system, the prerequisite of effectivity of the resistive economy policies)’ noted that in that study, the pathology of the administrative system from the behavioral and structural aspects have been dealt with, and the requirement for the realization of the resistive economy policies is the implementation of administrative system plans. According to him, paying attention to the behavioral aspects is greatly important for the success of the administrative system plans. Samadian (2010), in a study titled ‘the effects of organizational factors on the generation of innovative ideas’ state that the rewarding system, management support, risk taking, non-centrality of the decision-making, and allocation of free time in the organization are effective on the innovative behaviors of the employees. Ahangar Pour, Hosseini Fard & Bayat 2014), in a study titled ‘the behavioral and organizational factors that are effective on the maintenance of knowledge’ have identified several behavioral factors such as leadership, organizational support and encouragement, approach and knowledge sense, and knowledge behavior.
Methodology
Since the current study aimed at designing a behavioral pattern related to the implementation of administrative system general policies in the body of the Islamic Republic of Iran (case study: administrative systems of Kerman Province), it is of correlational descriptive type in terms of the method, and of developmental-applied type in terms of objective, which was done by the field studies method. The statistical population of the current study included 4596 managers in the administrative organizations of Kerman Province, among which a sample of 580 participants was chosen by the stratified sampling method. The behavioral factors and the administrative system general policies questionnaires with a validity of 92.7 and 88.7, and reliability of 89.6 and 96.2, were used for the purpose of data collection. The data analysis was done through the use of SPSS Ver.23, Minitab Ver.17, and AMOS Ver.23.
Research Questions
What are the behavioral factors in implementing the administrative system general policies?
What are the aspects of the administrative system general policies?
How is the status of the behavioral factors in implementing the administrative system general policies?
How is the status of the administrative system general policies?
Are there any relationships between the behavioral factors in the individual level and implementation of administrative system general policies?
Are there any relationships between the behavioral factors in the group level and implementation of administrative system general policies?
Are there any relationships between the behavioral factors in the organizational level and implementation of the general policies of the administrative system?
Are there any relationships between the behavioral factors in the environmental level and implementation of administrative system general policies?
How much is the reliability of the behavioral pattern related to the implementation of the administrative system general policies?
Results and discussion
Question 1: what are the behavioral factors in implementing the administrative system general policies?
Based on the conceptual model of the study, the behavioral factors variable in the current study includes 21 components in the individual, group, organizational, and environmental levels. The results of the behavioral factors questionnaire pattern fit are shown in the Figure 1, and regarding the provided indices in Table 1, it can be said that measurement models have a good fit. Thus, this model can be used for the determination of the behavioral factors.
Table 1 - The fit indices of behavioral factors model.
| Index | Acceptable limit | Reported value |
|---|---|---|
| Root Mean Square Error of Approximation (RMSEA) | Equal or lower than 0.08 | 077/0 |
| Minimum Chi-square divided by degree of freedom (CMIN/DF) | Equal or lower than 5 | 037/2 |
| Goodness of fit index (GFI) | Equal or greater than 0.9 | 927/0 |
| Adjusted goodness of fit (AGFI) | Equal or greater than 0.9 | 900/0 |
| Comparative fit index (CFI) | Equal or greater than 0.9 | 921/0 |
| Normalized fit index (NFI) | Equal or greater than 0.9 | 901/0 |
| Tucker Lewis Index (TLI) | Equal or greater than 0.9 | 903/0 |
| Incremental Fit Index (IFI) | Equal or greater than 0.9 | 923/0 |
Question 2: What are the aspects of general policies of the administrative system?
Based on the conceptual model of the study, the administrative system general policies variable in the current study includes 6 components which are religion-orientation, justice-orientation, and efficient organization, reverence of the client, development, and empowerment. The results of the administrative system general policies questionnaire pattern fit are shown in Figure 2, and regarding the provided indices in Table 2, it can be said that measurement models have a good fit. Thus, this model can be used for the determination of the general policies of administrative system.
Table 2 - The fit indices of the administrative system general policies model.
| Index | Acceptable limit | Reported value |
|---|---|---|
| Root Mean Square Error of Approximation (RMSEA) | Equal or lower than 0.08 | 061/0 |
| Minimum Chi-square divided by degree of freedom (CMIN/DF) | Equal or lower than 5 | 462/2 |
| Goodness of fit index (GFI) | Equal or greater than 0.9 | 922/0 |
| Adjusted goodness of fit (AGFI) | Equal or greater than 0.9 | 883/0 |
| Comparative fit index (CFI) | Equal or greater than 0.9 | 977/0 |
| Normalized fit index (NFI) | Equal or greater than 0.9 | 954/0 |
| Tucker Lewis Index (TLI) | Equal or greater than 0.9 | 960/0 |
| Incremental Fit Index (IFI) | Equal or greater than 0.9 | 977/0 |
Question 3: How is the status of the behavioral factors in implementing the administrative system general policies?
Based on the results obtained from Table 3, it can be said that in the studied population, the behavioral factors variable is at an optimal level (p<0.05). In other words, based on the obtained mean for this variable, it can be said that the status of the behavioral factors in the studied population is measured to be above the average.
Table 3 - The status of the behavioral factor in the studied population.
| Mean | Standard deviation | Theoretical mean=3.0 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| t-statistics | p-value | ||
| 63/3 | 39/0 | 38/37 | 001/0 |
Question 4: How is the status of the administrative system general policies?
As it is seen in Table 4, the religion-orientation, justice-orientation, efficient organization, reverence of the client, development, and empowerment components are at an optimal level, and the mean value of them is above average (p<0.05).
Table 4 Status of the administrative system general policies in the studied population.
| Component | Mean | Standard deviation | Theoretical mean=3.0 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| t-statistics | p-value | |||
| Religion-orientation | 65/3 | 78/0 | 46/19 | 001/0 |
| Justice-orientation | 46/3 | 77/0 | 82/13 | 001/0 |
| Efficient organization | 61/3 | 71/0 | 80/19 | 001/0 |
| Reverence of the clients | 53/3 | 77/0 | 08/16 | 001/0 |
| Development and empowerment | 51/3 | 76/0 | 47/15 | 001/0 |
Question 5: Are there any relationships between the behavioral factors in the individual level and implementation of the general policies of the administrative system?
The results obtained from the correlation test in Table 5 shows that there is a significant relationship between the personal traits, motivation, job satisfaction, organizational commitment, citizenship behavior, positive approach, and organizational attachment components and the administrative system general policies (p<0.05). Regarding the fact that the calculated correlation coefficients are positive, these relationships are direct (incremental). In other words, with the increase in each of the behavioral factors components in the individual level, the implementation of the general policies of the administrative system is also increased. Based on the calculated correlation coefficients, it can be said that the relationship between organizational commitment and the general policies of the administrative system is more significant.
Question 6: Are there any relationships between the behavioral factors in the group level and implementation of the general policies of the administrative system?
The results obtained from the correlation test in Table 5 shows that there is a significant relationship between the teamwork spirit and organizational communications components and the general policies of the administrative system (p<0.05). Regarding the fact that the calculated correlation coefficients are positive, these relationships are direct (incremental). In other words, with the increase in each of the behavioral factors components in the group level, the implementation of the general policies of the administrative system is also increased. Based on the calculated correlation coefficients, it can be said that the relationship between organizational communications and the general policies of the administrative system is more significant. Based on the confirmatory factor analysis, the components as the political behavior, organizational conflict (inter-personal), and mutual trust between the employees and the managers have been omitted.
Question 7: Are there any relationships between the behavioral factors in the organizational level and implementation of the general policies of the administrative system?
The results obtained from the correlation test in Table 5 shows that there is a significant relationship between the organizational atmosphere, organizational justice, meritocracy, leadership style, job security, organization politicalness, organizational transparency, administrative corruption, organizational support, and change management components and the general policies of the administrative system (p<0.05). Regarding the fact that the calculated correlation coefficients are positive, these relationships are direct (incremental). In other words, with the increase in each of the behavioral factors components in the organizational level, the implementation of the general policies of the administrative system is also increased. Based on the calculated correlation coefficients, it can be said that the relationship between meritocracy and the administrative system general policies is more significant.
Question 8: Are there any relationships between the behavioral factors in the environmental level and implementation of the general policies of the administrative system?
The results obtained from the correlation test in Table 5 show that there is a significant relationship between economic conditions and political conditions components and the administrative system general policies (p<0.05). Regarding the fact that the calculated correlation coefficients are positive, these relationships are direct (incremental). In other words, with the increase in each of the behavioral factors components in the environmental level, the implementation of the general policies of the administrative system is also increased. Based on the calculated correlation coefficients, it can be said that the relationship between economic conditions and the general policies of the administrative system is more significant.
Table 5 - The relationship between the behavioral factors components and administration of administrative system general policies.
| Variable | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| General policies of the administrative system | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| behavioral factors in the individual level | 376/0** | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| behavioral factors in the group level | 274/0** | 510/0 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - |
| behavioral factors in the organizational level | 759/0** | 449/0 | 379/0 | 1 | - | - | - | - |
| behavioral factors in the environmental level | 345/0** | 161/0 | 034/0 | 383/0 | 1 | - | - | - |
**significant in 01/0، *significant in 05/0
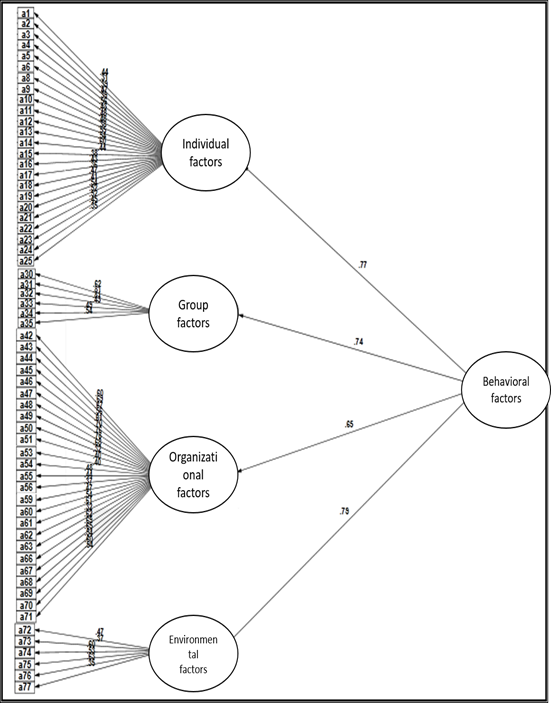
Fig. 1 -The results of confirmatory factor analysis of the factors effective on the behavioral factors (standardized factor loading).
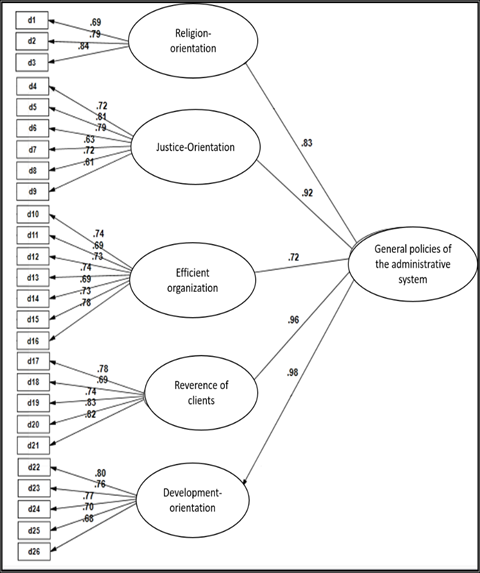
Fig. 2 -The results of confirmatory factor analysis of the administrative system general policies (standardized factor loading).
Question 9: How much is the reliability of the behavioral pattern related to the implementation of the administrative system general policies?
The software output is indicative of the proposed model’s fit, as the Root Mean Square Error of Approximation (RMSEA) value is 0.067, the CMIN/DF value is 2.65, and GFI value is 0.881. Other indices for the study’s proposed model fit are shown in Table 6.
Table 6 - Fit indices of the proposed model.
| Index | Acceptable limit | Reported value |
|---|---|---|
| Root Mean Square Error of Approximation (RMSEA) | Equal or lower than 0.08 | 067/0 |
| Minimum Chi-square divided by degree of freedom (CMIN/DF) | Equal or lower than 5 | 2/65 |
| Goodness of fit index (GFI) | Equal or greater than 0.9 | /8810 |
| Adjusted goodness of fit (AGFI) | Equal or greater than 0.9 | 883/0 |
| Comparative fit index (CFI) | Equal or greater than 0.9 | 977/0 |
| Normalized fit index (NFI) | Equal or greater than 0.9 | /9540 |
| Tucker Lewis Index (TLI) | Equal or greater than 0.9 | 960/0 |
| Incremental Fit Index (IFI) | Equal or greater than 0.9 | 977/0 |
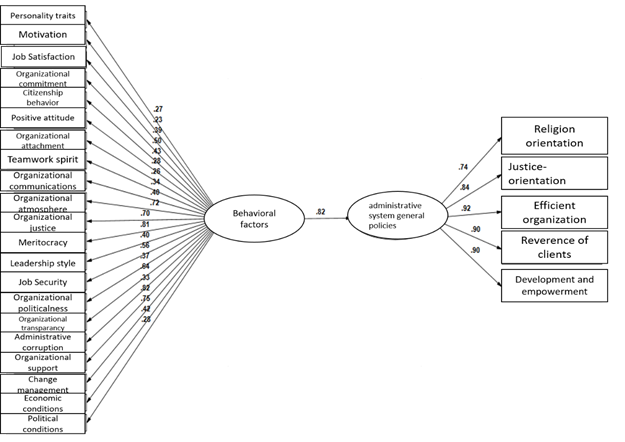
Fig. 3 - The results of the structural equations for evaluation of the proposed model (standardized factor loading).
The results obtained from the correlation test in Table 7 show that there is a significant relationship between the behavioral factors variable and the administrative system general policies (p<0.05). Regarding the fact that the calculated correlation coefficients are positive, these relationships are direct (incremental), i.e. with the increase in the behavioral factors levels in the studied population, the implementation of the administrative system general policies are also improved and increased (Fig.3).
Conclusions
The results of the testing of the behavioral factors status with implementation of the general policies of the administrative system and also, testing the model, besides confirming the proposed model, showed that these factors are effective on the implementation of the administrative system general policies. Based on the theoretical models, the behavioral factors can be categorized under individual, organizational group, and environmental levels. Also, in terms of the administrative system general policies variable, from among the components of this variable, the religion-orientation, justice-orientation, efficient organization, reverence of the clients, development, and empowerment are in an optimal level. Among these components, the religion-orientation has ranked the highest followed by the efficient organization and reverence of the client as second and third. Since the recognition of the past behavior and prediction of the future behavior play an important role in the behavior guidance, investigation of the employees behaviors in three individual, group, and organizational levels is of a great importance. The findings showed that the status of the behavioral factors is measured to be above the average. The problems related to this area, which are in two general frameworks including the destructive personality and behavioral traits of the employees, and dissemination of the negative norms in the intra-organizational interactions and in dealing with the clients, would lead to provoking the problems and difficulties of the bureaucracy system in the country, such as dissemination of the negative political behaviors in the governmental organizations, inclination to the maintenance of the existing situation and resisting the transition and renovation, dominance of nepotism over the rules, treating the clients with ingratitude, and consequently, employees indifference to the organizational goals, which are directly related to the human resources. Therefore, one of the factors effective on the successful implementation of the administrative system general policies and related to the human resources, is that of behavioral factors, which are according to Tehrani & Maleki (2016), in a study titled ‘the administrative system of development plans’, among the harmful factors within the administrative system, and accordingly, identification of such factors and the factors affecting them, can be useful for the successful implementation of the country’s policies, objectives, and plans, since the content or material poured into the organization container is the very human behavior. Therefore, the main content of the organization consists of the human behavior and human activities and behaviors are also exhibited to achieve the predetermined organizational goals. The result of human’s work and energy and the organizational structures and structures are manifested in the main functions or tasks of the organization. In this regard, Khanifar, et al. (2004), in a study, investigated the behavioral and structural factors effective on the well-being of the administrative system. In addition, in lines with the results of the current study, the results of Salehi Amiri & Shadaluei (2013); and Rizkallah (2015).















