My SciELO
Services on Demand
Journal
Article
Indicators
-
 Cited by SciELO
Cited by SciELO
Related links
-
 Similars in
SciELO
Similars in
SciELO
Share
Podium. Revista de Ciencia y Tecnología en la Cultura Física
On-line version ISSN 1996-2452
Rev Podium vol.19 no.1 Pinar del Río Jan.-Apr. 2024 Epub Apr 03, 2024
Original article
Sport detraining in boxing
1Combinado deportivo Majibacoa, Las Tunas. Cuba.
2Universidad de Oriente. Santiago de Cuba, Cuba.
3Universidad de Holguín. Holguín, Cuba.
The preparation of the boxer entails physiological changes and adaptations to guarantee the physical, psychological and social loads to which its practitioners have been subjected. Once this stage is completed, sports detraining appears, the nature of which is eminently pedagogical and consists of uninstalling the components that guaranteed the accumulation of loads during his time as an active boxer, until reaching the levels of a normal systematic practitioner of Physical Culture. The objective of this work was to design a pedagogical strategy based on a model of the same nature for detraining enhanced with equine-interaction-prophylactics, based on the use of exercises with horses as an element of change. Observation of sports sessions, document analysis, a survey of former boxers, coaches, sports doctors, officials and selected experts, as well as critical opinion and socialization workshops among boxing coaches, were used as empirical methods and techniques. As results, a pedagogical model was obtained from which a strategy was derived. These contributions were verified through the partial application of the strategy in a sports complex in Majibacoa, Las Tunas and its feasibility to be generalized was demonstrated. The article offered aims to socialize results of the research carried out on sports detraining in boxing enhanced with equine-interaction-prophylaxis. Conclusively, the theoretical and practical contributions demonstrated the fulfillment of the research objective and the solution of the scientific problem.
Keywords: boxing; sports detraining; equine-interaction-prophylactic.
INTRODUCTION
Currently, a progress of training methods in boxing has been verified in multiple research carried out for this purpose. The authors Alarcón et al. (2023) corroborate that from this perspective the process being analyzed has a system character, made up of two subsystems: training and detraining. The first, aimed at the formation and development of sports skills and capacities in the training of the athlete; while the second, aims at their gradual and systematic detraining, reaching the level of a practitioner of Physical Culture.
Although, researches and the level of information about it are insufficient, as the researcher Marín, (2022) states "(...) researches (...) about sports detraining (...) are addressed, which are scarce in the literature".
The demands of the current level of boxing in the world cause a greater multiplication of efforts on the part of practitioners, boxers and trainers, since this level of training generates in all its social matrix the appearance of the sports detraining process, once the athlete's active life is over.
Detraining has not enjoyed the same research appeal as the training has had it; it is a pedagogical process that points to adverse physiological alterations, coronary risks and blood pressure problems, among others, as a result of the sudden total suspension of training.
Sports detraining can be considered, in a first approximation, as the process that should occur in the post-sport stage, initiated with the retirement of the athlete, where he/she is subjected to a system of influences to eliminate, in an intentional way, the highly specialized adaptations and learning acquired during high performance sports training (León. et al., 2021).
The researchers Hernandez et al. (2020) distinguish the phases related to sports training:
Basic preparation phase.
Phase of maximum realization of sporting potential.
Phase of sports longevity.
The sports longevity phase is organized in two stages, one of preservation of the achievements and the other of maintenance of the general training, in the latter the level of sports activity should be considerably reduced, ensuring a high general activity and the content of the training should have a reactive sanitation character, since it is about fixing the quality of the permanent qualities of the organism and everything valuable that the sports practice of previous years provided; this phase serves as a link between sports training and detraining and this stage is vital to make competent their condition of athlete in retirement.
Castellanos et al. (2020) point out the importance of the characterization of the sports retirement of young athletes in order to, from this, carry out the elaboration of individualization activities of detraining, so that it is truly effective.
The National Institute of Sports, Physical Education and Recreation (Inder in Spanish) and its network in the municipalities and provinces have assumed political will regarding the problem of sports detraining. The president of Inder entrusted the director of the Institute of Sports Medicine through resolution 82/2015 (Inder, 2015), the implementation and control of that process and the same mission to the Manuel Fajardo University of Physical Culture and Sports Sciences (UCCFD in Spanish) and the Faculties of Physical Culture of Cuba.
The above is supported by Title III, Article 32, paragraph e, of the Constitution of the Republic of Cuba (2015), which recognizes that the state "(...) guides, encourages and promotes physical culture, recreation and sport in all its manifestations" (p.13). The term detraining places the athlete at the center of the process.
The attraction for research on detraining has grown in the last five years and other studies that have coincided in signifying its importance for various sports, such as weightlifting, boxing, water polo, and models, strategies, methodologies, cardiological analysis and others have been designed. According to Alarcón, one of the authors of this article, there is still a gap, both in theory and in practice, which hinders the knowledge of this process, which leads to the need to generate other contributions that point towards the solution of the problem of sports detraining.
The bibliographic review evidences an epistemic gap related to the means and ways in which boxing detraining is carried out, as well as the insufficient culture on the part of athletes, coaches, family and community when taking a position on the process in this sport.
Despite the existence of a legal framework (Resolution 82-2015) that directs detraining as a responsibility of the aforementioned entities, the deaths of former boxers between the ages of 45 and 60 are regretted. These deaths are related, in some way, to the abrupt suspension of training. It can be cited the examples of Teófilo Stevenson Lawrence (60 years old), Arnaldo Mesa Bonell (45 years old) and José Aguilar Pulsan (55 years old), among others, who swell the sad list of those who died due to causes associated with detraining.
This process has been carried out in different ways and forms, including strategies, models, exercise systems and action plans, all of which have used physical exercise, games and other sports activities such as mountain climbing, dance therapy, aquatic activities, bicycle riding and have produced results in the various sports modalities that have used them. Each territory has implemented its experiences in related modalities, which demonstrates the openness and flexibility of the detraining process and its adaptation to different contexts with and from the community.
However, it is considered that the contributions and means used are not sufficient to reach a total understanding and phenomenal explanation of the detraining process in the retirement stage of boxers, so the constant search for solutions from science is a priority for the Cuban sports movement in its diverse character and the broad spectrum in which it develops.
The problematic situation is given in that the integral development of boxing practitioners in Cuba is guaranteed; however, the necessary efforts are not made, theoretically and practically, for the sustainable reinsertion into society of these athletes without health risks, once their active life as boxers is over. This determines the objective of this research, which is none other than to design a pedagogical strategy based on a model of the same nature for detraining enhanced with the prophylactic equine-interaction, from the use of the horse as an element of change.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Applied educational research was carried out, aimed at the solution of practical pedagogical problems, with a margin of generalization limited to boxing detraining in the province of Las Tunas.
The study was carried out in the province of Las Tunas. A diagnosis was initiated with the population and sample shown in the table below Table 1 and Table 2.
Table 1. - Population and sample used in the diagnosis of the research
| Population and sample | |||
| Participants | Population | Sample | % |
| Ex-boxers | 24 | twenty | 83.3% |
| Youth | 8 | 7 | 87.5% |
| Schoolchildren | 11 | 9 | 81.5 |
| Social | 5 | 4 | 80.5 |
| Coaches | 16 | 14 | 87.5% |
| Families | 24 | 20 | 83.3% |
| Sports doctors | 4 | 4 | 100% |
| Officials | 16 | 12 | 75% |
| Total | 84 | 70 | 83.33% |
Table 2. - Socializing entities
| Socialized Entities | |||
| Schools | Two primary schools | Two primary schools | 100% |
| A secondary school | A secondary school | 100% | |
| Family doctor office | 2 | 1 | 50% |
| Agro livestock cooperative | 1 | 1 | 50% |
Among the socializing entities, the schools had 100 % of the sample of athletes and in their sports areas are located the detraining centers used. The family doctor's offices were diagnostic centers of the primary health system of the ex-athletes. The agricultural production cooperative provided the horses and favored the diagnosis of hygiene and epidemiology, this knowledge allowed to declare them suitable to be used in the detraining of the ex-boxers.
Measuring tapes, markers, whistles, stopwatches, implements, muzzles and sweatshirts used in the work with horses were used.
For the diagnosis, the following indicators were determined.
Culture of ex-boxers and their families on the importance of the sports detraining process.
Activities carried out for detraining.
Individual character of sports detraining.
Specifically, in the diagnosis, structured observation was applied, with the involvement of the researcher, for a previous analysis of the object of study; and non-participant observation, in which the researcher observed from outside, without being part of the group under investigation. In both cases, an observation guide was prepared by the researcher. The following indicators were taken into account in the guide:
Object of the observation.
Objective of the observation.
Total time and frequency of the observations.
Number of observers.
Type or types of observation used.
The use of observation allowed the deepening of the knowledge of other elements related to sports detraining in boxing, which were summarized in the following table (Table 3).
Table 3. - Application of observation
| Observations made to the sports detraining sessions | |||
| Structured | Non-participating | Time total | Frequency weekly |
| 10 | 8 | 18 hours | 3 |
Document analysis was employed for the review of:
Resolution 82/15. Sports detraining procedure for high-performance athletes linked to the Cuban Sports Movement. 2015.
Resolution No. 25/14. Admission policy for athletes, coaches and sport specialists. Legal norms. 2014.
Program of activities for the detraining of young tennis players in Villa Clara. 2019.
Surveys were applied to ex-boxers, coaches, sports doctors, officials and selected experts with the objective of obtaining information from these subjects about the object of study. Interviews were also conducted with ex-boxers.
Microsoft Word for word processing, Microsoft Excel for the elaboration of tables and Microsoft PowerPoint for the elaboration of presentations were used as computer tools.
In relation to the social and pedagogical variables of sports detraining, the following dimensions were determined:
According to these dimensions, the following were specified as indicators:
Involvement in the detraining process.
Participation in the activities carried out.
Modalities of participation.
Data in terms of percentages represented with the help of the SPSS package were used. Version 14. The diagnosis showed the need to offer the contributions of the research in order to fulfill its objective.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
As results two contributions were elaborated, one theoretical: Pedagogical model for sports detraining in ex-boxers enhanced with the equine-interaction-prophylactic, and from the practical point of view a strategy of the same nature that minimizes the problems caused by the lack of an adequate detraining.
The modeling method was put in function of the theoretical and comparative conception between the current situation of the sports preparation model and the ideal pedagogical model of detraining with its categories, higher order qualities, dimensions and internal contradiction. Therefore, a pedagogical model for sports detraining in ex-boxers was elaborated, conceived from the components that can be appreciated in this process of load liberation that had a sociological, biological, psycho-pedagogical and equine-interaction-prophylactic character that conferred its essential nature. The most significant characteristics of each of them are presented below.
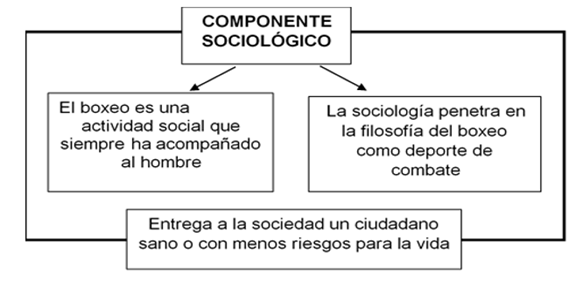
Sociological component
A sociological review of sports detraining in boxing made it possible to assess, from the qualitative point of view, that it establishes tasks aimed at the transition period, from one stage to another, but should not miss its social, humanistic and prophylactic character, declared as the main objective of detraining in this post-sports stage, with a view to delivering to society a healthy citizen, or with less risk to life. Sociology made it easier to penetrate into the philosophy of boxing, as a combat sport, to scrutinize its essence, not only pedagogical, but also social.
The general objectives of modern boxing, established by the International Amateur Boxing Association, become social advances in a sport discipline that has been maintained for 2600 years in the social program of the Olympic Games. In Cuba, the selection of the best boxers in history demonstrates the social significance that this sport has always had, among them Eligio Sardinas, Cid Chocolate (1910-1988); Teófilo Stevenson, the Great Champion (1952-2012) and Félix Savón, the Boxer History (1967).
Sociology gives it a holistic character by considering detraining as a consequence of the social matrix that generates training, with a purely social and prophylactic objective; on the other hand, from the scientific-technical development, detraining is a product of the development achieved by the pedagogical sciences and of one of the oldest and most popular social activities developed by man as a social being: sport (Figure 1).
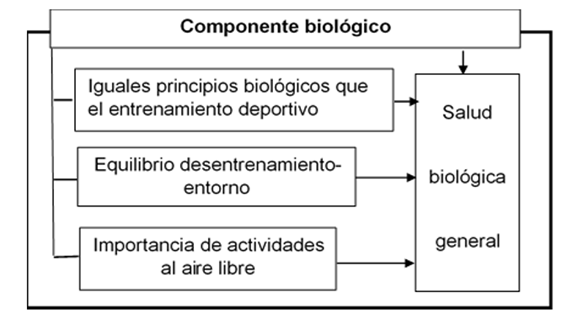
Biological component
The detraining process takes place under the same biological principles present in sports training (Law of bioadaptation), the exercises present in any of the stages of detraining (transit, adaptation and maintenance) are subject to irritability mechanisms capable of creating, internally or externally, the necessary reflexes to trigger motor actions.
Physical exercises are the motor acts of voluntary character that are executed to fulfill the different tasks of the sport; this characteristic (use of the same means) between training and sports detraining makes them accomplices of the same motor acts, of the degree of voluntariness and of the reflex mechanisms, sustained in an eminently pedagogical development process.
The biological effect, provoked by the motor acts on the organism depends, to a great extent, on the equilibrium relations between this one and the environment; the environmental conditions also play a role in the adaptation process and can define the particularities of the tempering. Observations show that systematic trainings carried out in modern indoor sports facilities, with constant microclimatic conditions, cause distempering phenomena in athletes, this is reflected in the defense mechanisms, with an abrupt decrease in health levels that alter homeostasis and affect the training sections. The importance of outdoor activities favors tempering and the general state of the organism (Figure 2).
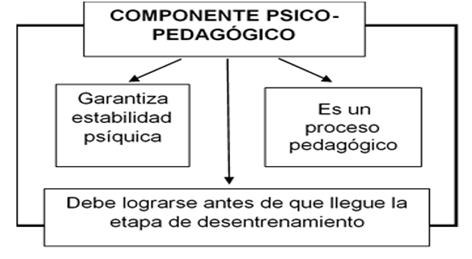
Psychopedagogical component
This component guarantees a psychic and decisive stability in the retirement stage, which is multi-causal. An instability in this direction may be caused by poor sports performance, injuries, indiscipline and longevity, all of which point to a new stage: detraining, for which the main setback may be in their lack of preparation.
For this reason, pedagogy and psychology must contribute to instruction, prevention and orientation before the detraining stage arrives in order to avoid the appearance of psychic phenomena capable of modifying the living conditions of former athletes, such as stress, responsible for favoring the appearance of behavioral changes in the personality, which affects athletes, families and communities.
The detraining is a pedagogical process whose main objective is to treat the retirement stage, to face it with pedagogical and psychological orientation, it favors the zone of proximal development that the ex-athlete has reached, this orientation and help contributes more when it is supervised by a specialist trained under the profile of the career of the Bachelor in Physical Culture and Sport and not of an outsider personnel, incapable of facing the challenges in this area of knowledge.
The retirement stage, with its psychological characteristics very different from the training period, must be prepared in advance, where the levels of psychic tension rise and the negative emotional conditions appear so that stressful processes arise as a negative pressure very often linked to painful and worrying external events, or caused by situations that modify the conditions of life.
The athlete, in this case the boxer, has prepared for the result, not achieving it is seen and analyzed as a failure, the fact of training with eagerness to improve sports performance, under a methodological and scientific control of training involves a level of physical and psychological stress. In the retirement stage, the main task of the psychological preparation changes, here the objective is the progressive reduction of the indicators of the loads (volume, intensity, density, frequency) that allow the formation, in the athlete, of the maximum psychic and physical disposition to overcome the negative emotional states that arise until they are brought to optimal processes (Figure 3).
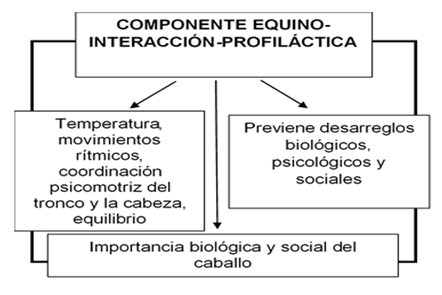
Equine-interaction-prophylactic component
The proposed model is based on the equine-interaction-prophylactic component that considers the biological and social importance that exercise with horses represents as a factor of change in detraining classes.
This component refers to the equine-interaction-prophylactic as a set of activities where horses are used, aimed at preventing biological, psychological and social disorders caused by high performance training in harmony with the environment. The biological, psychological and social dimensions integrate the athlete as a biopsychosocial being, in equilibrium (homeostasis) with the environment where the activity takes place, which implies the term health and constitutes, in its multiple meanings, the final objective of this activity.
One of the physiological indicators of the approached process is the elevation of the body temperature, activity that is achieved at the beginning of the classes with the warm-up and is complemented with the temperature of the horse 38.80 higher than that of the human body, this thermal superiority acquires importance when constituting a calorific instrument of biological character, present in the equine that can be located and used in any part of the community: guardrails, mountain areas, parks, stadiums, etc. Its multiple benefits come from the ability to achieve muscle and ligament relaxation. With work, the temperature of the equine can rise up to 400°C, a characteristic used to achieve greater muscle relaxation and facilitate, with a few warm-up exercises, an optimal state of physical and psychological disposition for the activity and a high degree of relaxation of the lower bioclimatic chains and the buttocks.
The temperature generated by the horse (back and sides) favors, to the extent of the increase, the processes of balance by facilitating biological adjustment mechanisms, greater blood circulation, which benefits the physiological function of the internal organs. The regulation of the contact is achieved with the use of implements such as saddles, poles or hair and even shorts, the closer the interaction of the ex-sportsman with the horse, the greater the heat transmission process and its benefits.
The horse in its first breath (step) generates between 90 to 110 rhythmic movements per minute, these movements are captured by the pelvic belt and transmitted throughout the spine to the head and from there to the anatomy, which is an excellent training of psychomotor coordination of the trunk and head, with the stimulation of rhythmic movements are activated muscle and bone tissues, which favors the processes of neurotoxicity to be stimulated their associated neural areas. Also, when analyzing the organism as a whole, other processes are activated that favorably affect the lower limbs, stimulating balance, coordination, postural control and trunk straightening.
When walking, the horse generates multidirectional oscillations (up and down, right to left, front and back) that favor the mechanics of movements related to human locomotion patterns. These oscillations have a pendular character for the trunk and are in the same biomechanical line as the equally pendular phenomena of conventional human gait. This characteristic is characteristic of the horse, which cannot be imitated by any man-made equipment to achieve such vibrations, which places exercises with horses as an essential means in detraining centers.
The possibility of riding favors the detraining process, in correspondence with locomotion limitations, motivated by variables such as age and the aging process that can be limiting, where the use of exercises with horses enters to play a dynamizing role in the process. The equine-interaction-prophylactic has shown positive results, it is a treatment that includes activities and an equestrian environment to achieve physical, occupational and emotional improvement (Figure 4).
The following figure shows the use of the horse in sports detraining by means of the equine-interaction-prophylactic (Figure 5).
The systemic nature of the components that were part of the model is highlighted, each of which has its essential elements, but they form a unitary, holistic and complex whole, in this case boxing detraining and, in turn, these components are interdependent and have close links between them through the relationships or links that they establish and that allow them to be seen as subsystems (components) of a more complex system (boxing detraining).
This contribution supported the strategy offered by the research and can be used for the elaboration of new theoretical and practical contributions on the topic addressed. At the same time, it can be a way to increase the proposals on sports detraining to increase its validity in relation to training.
The results obtained in the diagnosis of the research are as follows:
Poor level of preparation to face the retirement stage on the part of coaches, athletes, families and the community.
Scarce general culture in the knowledge of the detraining process (involving coaches, athletes, officials, families and the community).
Lack of correspondence between the necessary exercises to carry out the process and the ex-athlete's own characterization (appeals to empirics).
Insufficient degree of motivation to comply with the objectives of the detraining process.
Insufficient use of complementary activities in the maintenance stage.
Presence of chronic pathologies such as psychic dysfunctions and neuromotor and functional disorders, which was the main cause for the sudden suspension of the training.
The poor culture of the main actors-athletes and coaches-which hinders the consolidation of the detraining process in the withdrawal stage.
Existence of a goal program for the detraining of ex-elite athletes that does not contemplate ex-athletes at another level in the high-performance pyramid.
The article presented here shares the idea that the biological sacrifices made by athletes to maintain their adaptive responses reach their limits and it is appropriate to carry out a sports detraining process, so the biological component was taken into account and a process was proposed with the use of equine-interaction-prophylactic with the use of exercises with horses as an element of change.
For Mena (2020) "(...) the planning of sports detraining is a process aimed at preserving the health of high-performance athletes who reach longevity and culminate their active sports life", which was also considered in the model proposed by the research conducted.
Very important is the consideration of the authors Frómeta et al. (2022) when they state: The scarce knowledge of the theoretical-methodological procedures on the retirement stage of athletes and the poor systematization of the ideas arising around detraining hinder the realization of effective actions for the reincorporation of former high-performance athletes to their communities with optimal post-sports health.
It has been taken into account that detraining, at the end of the sports life, brings benefits for the physical and mental health of the high-performance athlete. The research carried out has had the implicit purpose of preserving the physical and mental health of the athlete who begins the retirement stage and starts a sports detraining process.
The proposed model contributes to alleviate the epistemological gap that exists on detraining to increase the knowledge of athletes, coaches, families and the community related to this process. In general, it is recognized how this model provides a solution to the scientific problem and objective of the research, which is generated from insufficiencies in the detraining process in boxing. The proposal gives a novel and different answer to the exposed problem and the model, as a scientific result, was motivated by the use of exercises with horses, as the element that breaks with traditionalism in this process.
CONCLUSIONS
The proposed elements agreed with the mentioned authors, but with the significance of the equine-interaction-prophylactic in sports detraining. This theoretical proposal had its practical application in the strategy provided by the research, but it can be used in others.
The strategy can be applied to practically any area, as long as it is the implementation of a plan designed to take the greatest possible advantage of the given conditions and resources, and can be classified according to different criteria.
In this research, a pedagogical strategy was elaborated for the sports detraining of ex-boxers reaching their retirement stage. However, the author of the research suggests to continue working on other ways for this detraining that favors the process in athletes, families and communities.
REFERENCIAS BIBLIOGRÁFICAS
Alarcón-Ramírez, B. J., Ramos-Romero, G., & Frómeta-Moreira, N. (2023). El desentrenamiento deportivo en el boxeo como problemática social. EduSol, 23(83), https://edusol.cug.co.cu:443/index.php/EduSol/article/view/492 [ Links ]
Asamblea Nacional del Poder Pupular. (2019). Constitución de la República de Cuba. Editora Política. https://www.parlamentocubano.gob.cu/index.php/sites /default/files/documento/2022-01/Nueva%20Constituci%C3%B3n%20240%20KB-1_0.pdf [ Links ]
Castellanos, S. M. H., Garcias, E. O., Matos, J. L. F., & Piperski, M. (2020). El desentrenamiento deportivo en atletas jóvenes del Atletismo de alto rendimiento en Villa Clara. Ciencia y Actividad Física, 7(1), 30-47. http://revistaciaf.uclv.edu.cu/index.php/revista/article/view/100 [ Links ]
Frómeta-Moreira, N., Padilla, R., Alarcón-Ramírez, B. J., & Romero-Frómeta, E. (2022). El desentrenamiento deportivo: Una garantía básica para la salud postdeportiva. Revista DeporVida, 19(51). https://deporvida.uho.edu.cu/index.php/deporvida/article/view/814 [ Links ]
INDER. (2015). Procedimiento de desentrenamiento deportivo para los atletas de alto rendimiento vinculados al Movimiento Deportivo Cubano. Resolución 82/15. INDER. [ Links ]
Pérez, O. M. (2020). Modelo para la planificación del proceso de desentrenamiento deportivo. Revista Conrado, 16(75), https://conrado.ucf.edu.cu/index.php/conrado/article/view/1380 [ Links ]
Reyes, B. B. L., Cardero, D. D. H., Arias, G. J. H., & León, M. C. (2021). Control pedagógico del desentrenamiento deportivo: Pedagogical control of sports training. Cumbres, 7(2), https://doi.org/10.48190/cumbres.v7n2a4 [ Links ]
Received: February 27, 2023; Accepted: October 14, 2023











 text in
text in