Meu SciELO
Serviços Personalizados
Journal
Artigo
Indicadores
-
 Citado por SciELO
Citado por SciELO
Links relacionados
-
 Similares em
SciELO
Similares em
SciELO
Compartilhar
Podium. Revista de Ciencia y Tecnología en la Cultura Física
versão On-line ISSN 1996-2452
Rev Podium vol.19 no.1 Pinar del Río jan.-abr. 2024 Epub 13-Abr-2024
Original article
The vocational orientacion in the School Sport Initiation School
1Universidad de Las Tunas, Facultad de Cultura Física. Las Tunas, Cuba.
2Universidad de Holguín. Facultad de Cultura Física. Holguín, Cuba.
The research was aimed at resolving theoretical and methodological insufficiencies, related to the vocational orientation towards the Physical Culture career, in the training process of the pre-university student of the School Sports Initiation School, since the high school model in this type of centers establishes the need to achieve a solid comprehensive preparation in students, from teaching and sports training. The objective was to develop a strategy, supported by a pedagogical model, that contributes to the vocational orientation of pre-university students from the School of School Sports Initiation Schools towards the Physical Culture career. The population was made up of 102 tenth grade students and 72 teachers. Scientific methods and techniques were used such as historical-logical, analytical-synthetic, inductive-deductive, systemic-structural-functional, modeling, participant and structured observation, document analysis, evaluation by expert criteria, survey, critical opinion workshops and collective construction, in addition to mathematical-statistical methods. The foundations of the pedagogical model helped resolve the contradiction between the demands of the ideal model explicit in the Comprehensive Preparation Programs for Athletes and the limitations of teachers to develop vocational orientation towards this Career. The model and strategy were subjected to evaluation, through expert criteria and cycles of critical opinion and collective construction workshops, the results allowed confirming positive transformations in the treatment of the vocational orientation of the pre-university student towards the Physical Culture career.
Keywords: Physical Culture; strategy; pedagogical model; pre-university.
INTRODUCTION
Education constitutes a phenomenon that manifests itself in multiple forms of social practice and at very different levels. That is why sports educational institutions develop continuous improvement to enrich and transform, with the dynamics of society and the advances of science and technology, the incessant flow of progress; which means adopting a renewing and perennial attitude for the sake of multilateral and comprehensive training of the new generations, in order to preserve essential achievements such as sports and education (State Council, 2019).
In this aspect, the School Sports Initiation Schools (EIDE) are classified as a type of special institution with a dual function, the general polytechnic training of students and that aimed at the preparation and development of the sports reserve of the provincial and national teams. These schools have the mission of contributing to the comprehensive preparation of students, in coordination with other educational agents, so that they respond to social needs and interests, in correspondence with individual ones, in which vocational orientation is part of the pedagogical process and plays an important role in choosing a profession.
At EIDE, special attention is paid to the demands and expectations of the pre-university student model, for the comprehensive training of the athlete; hence, the development of basic motor skills and physical capacities that enhance sports preparation constitutes a strength. The above translates into a potential for transition to the Bachelor's degree in Physical Culture (hereinafter LCF).
From the observations made to training sessions and classes at the EIDE, manifestations related to the participation of educational agents in the process of vocational orientation towards the LCF, the pedagogical treatment of the vocational orientation of pre-university students toward this Career and their manifestations of disinterest towards this profile.
The above manifests a contradiction between the demands of the ideal model explicit in the Comprehensive Preparation Programs for Athletes (PIPD) referring to the harmonious, multilateral and comprehensive training of pre-university students of the EIDE and the limitations of teachers to develop the vocational orientation towards the LCF.
In the search for solutions to this contradiction, research by national and foreign authors was reviewed on ways to orient students towards university careers. In this direction, with different approaches and perspectives, Armas et al. (2018), Basto and Basto (2018) and Echevarría et al. (2017, 2018, 2018 and 2020)stand out, as Briones et al. (2018), Carpio and Guerra (2017), Corrales, et al. (2022), Erazo and Rosero (2022) and Herrera et al. (2018) do in the international level.
Despite the multiplicity of alternatives proposed by these authors, it is still not possible to propose solutions that objectively focus on the treatment of vocational orientation towards the LCF based on the specific approach to the contents of general polytechnic training and the of sports preparation. The above shows the existence of limitations in the general theoretical-methodological foundations whose systematized theoretical base does not contain the necessary arguments that support the vocational orientation towards the LCF, of the pre-university students of the EIDE.
The above made it possible to summarize as the main inconsistency the lack of theoretical-methodological foundations that reveal the structural and functional relationships of the vocational orientation towards the LCF of the pre-university students of the EIDE, and to pose as problematic the contribution to the vocational orientation of these students towards this profile; which favored the realization of the objective of developing a strategy, supported by a pedagogical model, that contributes to the vocational orientation of EIDE pre-university students towards the LCF career.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The research applies a mixed approach with the use of quantitative and qualitative methods. The dialectical-materialist approach was used as a general approach, along with the use of different methods and techniques of scientific research such as the historical-logical approach, used to facilitate the understanding and analysis of the background of the vocational orientation of the pre-university students of the EIDE towards the LCF, from its inauguration in 1977 to the present.
The analytical-synthetic one allowed the deepening of the contents of the object and field, in the treatment of the information derived from the solution of the tasks assumed in the study, in the realization of an approach to the foundations that support the research, in the interpretation of the empirical information obtained and in the preparation of the proposal.
The Inductive-deductive method made it possible to make inferences and generalizations of the vocational orientation towards the LCF in the analysis of the data obtained for the development of the pedagogical model, the strategy and the interpretation of the empirical information. The structural-functional systemic one allowed establishing the structure of the model, its components and the system of relationships between them, as part of the treatment of the vocational orientation of pre-university students from the EIDE towards the LCF, through the strategy derived from the model. pedagogical.
While modeling was used with the purpose of representing, from a theoretical perspective, the process of vocational orientation of these students towards the LCF and explaining its main characteristics.
On the other hand, participant and structured observation was used during the diagnosis phase to obtain information about the particularities and trends of the research object and to specify details in order to assess the feasibility of the pedagogical model and the functionality of the strategy.
The analysis of documents allowed to determine the level of orientation of the sports, education and authorized work commissions on the vocational orientation of pre-university students towards the LCF, in the context of sports centers, for which the exhaustive assessment of the PIPD, teaching programs, sports strategies in the province, official documents issued by INDER and the Ministry of Education (MINED) was carried out.
The evaluation by expert criteria was applied to search for consensus regarding the relevance of the pedagogical model, functionality of the strategy and the parameters to evaluate the vocational orientation of pre-university students from the EIDE towards the LCF.
The survey to diagnose the status of treatment for the vocational orientation of students towards this career; Consensus techniques were used to determine, together with the experts, the elements of the process in each of the components and indicators and the determination of the structural, functional and methodological specificities of the pedagogical model, as support for the strategy.
The pedagogical model and strategy were subjected to evaluation in the critical opinion and collective construction workshops, which allowed adjustments to be made and the feasibility and functionality of the proposal to be considered. The processing of the information obtained was carried out using mathematical-statistical procedures. The most used were: descriptive statistics, within it (the preparation of tables, the calculation of absolute and relative frequency), the calculation of the coefficient of expert competence (ka) and the Green procedure, to determine the points of cut in Delphi processing.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
In order to fulfill the proposed objective and be able to shape the strategy, based on a pedagogical model, an exploration of the current state of the treatment of the process under study was carried out, using the planned methods and instruments; the vocation of EIDE pre-university students for the LCF was defined as a research variable, which is understood as the harmonious relationship between knowledge, attitude, interest, motivation and personal disposition to opt for this future profession.
The definition of the variable made it possible to delimit the dimensions, indicators and measurement criteria for its evaluation and served as a starting point for its argumentation as a methodological contribution of this research, with its corresponding features, which were delimited from the interpretation of the operational definition. made.
To evaluate these indicators, the ordinal scale of Gamboa and Borrero (2019) was used in which each indicator shows a characteristic in the object of research and is measured with a scale of five travel points (1-5), to measure the presence of the characteristic, with the respective criteria to assess the level of execution of each dimension and each of these indicators, to grant the corresponding categories. It has validity, according to expert opinions. There is evidence of its content validity with exploratory factor analysis, criterion validity with Pearson's correlation coefficient in terms of linear association, and sensitivity to change, with analysis of variance for repeated measurements.
The categories were defined, in a gradation that goes from excellence to lower levels, which are listed below: excellent ( 4,75<x ̅≤5), very good ( 3,75<x ̅≤4,75), good ( 2,75<x ̅≤3,75), average ( 1,75<x ̅≤2,75) and poor ( x ̅≤1,75), depending on the intervals that from a qualitative point of view, they assessed the level of execution of said particularity in the students' training process. Likewise, the assumption of continuity was shared due to its long breadth, based on the criteria of Gamboa and Borrero (2019) for whom it is legitimate to analyze ordinal data parametrically and, due to its usefulness, reach valuable results.
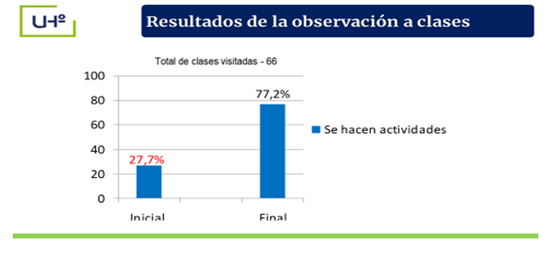
The observation was carried out covertly and directly in 66 classes, 33 of them in the teaching area and 33 in the sports areas. It was found that only in 22.7 %, (15) of them, there was an attempt to take advantage of the potential acquired by pre-university students in order to create knowledge, feelings, interests and motivations for the LCF; while in 77.2 % (51) it did not occur.
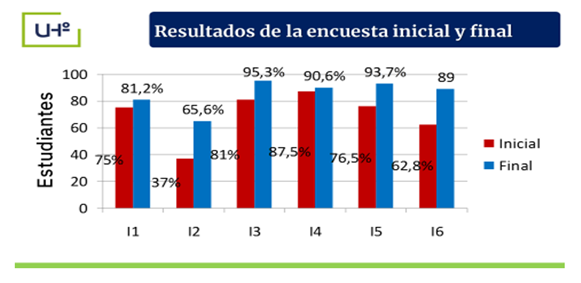
The survey applied to the students showed that 75 % (48) had not yet established immediate professional goals and objectives, 37 % (38) made isolated voluntary efforts, characterized by pessimism and insecurity in achieving the goals set to access the Career, 81.2 % (52) showed ignorance of its particularities, 87.5 % (56) stated that they were not interested or motivated by it, 76.5 % (49) considered insufficient the vocational orientation provided towards this profile and 82.8 % (53) requested it in the fourth option.
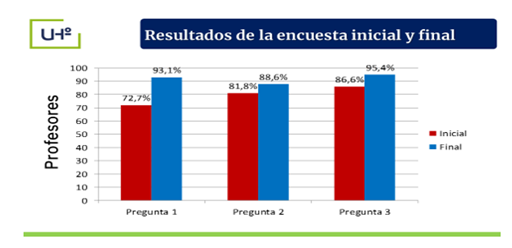
The initial survey applied to EIDE teachers revealed that 72.7 % (32) of them expressed ignorance about the four spheres of action of Physical Culture, 95.4% recognized the need for the integration of educational agents to raise the interest and motivation of EIDE pre-university students for the LCF from the curricular, extracurricular and socio-political aspects and 88.6% (39) stated the need to develop topics related to the vocational orientation of students, from the linking of the content of the subjects and the PIPD in the curricular, extracurricular and sociopolitical aspects of the training process in the methodological preparations of the center.
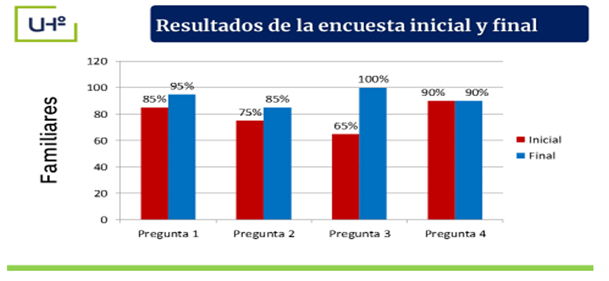
The survey applied to 20 relatives of EIDE pre-university students showed that 85 % (17) of them do not know what types of help the school provides to their children to orient them so that they can choose a career at the end of the twelfth grade, 75 % (15) were unaware of the particularities of the LCF, 65 % (13) stated that they were unaware of the activities carried out by the school related to vocational orientation towards this specialty and 90 % (18) stated that they motivate their children so that they are recognized athletes in their sport.
The main causes that generated these limitations focused on the insufficient work of vocational orientation towards the LCF, based on the potential acquired by the pre-university students of the EIDE and the integration of the training contexts of school, family, community, in addition to the weak integration of educational agents and their influence on pre-university students from the curricular, extracurricular and socio-political perspectives, as well as the insufficient use of the potential of the environment for solving problems with the benefit of vocational orientation.
The results obtained from the applied instruments revealed that the activities related to the vocational orientation of pre-university students in the EIDE training process are limited, they lack an interdisciplinary, methodological, improvement and research character aimed at training educational agents from the curricular, extracurricular and socio-political to strengthen feelings, interests and motivations from the four spheres of action towards the LCF.
The assessment, critical and reflective analysis carried out, concerning the characterization, allowed to reveal as the cause of the problem: the insufficiencies in the theoretical-methodological order of the process of vocational orientation of the pre-university students of the EIDE towards the LCF that are manifested in the limitations of teachers, to take advantage of the possibilities and training potential of the contexts and of the students, to integrate the contents of general polytechnic training with the PIPD in a harmonious and comprehensive orientation of the vocation towards the LCF.
The results of the historical study, the systematized theoretical foundations and the elements exposed during the initial diagnosis confirmed the insufficiencies in the vocational orientation towards the LCF detected in the students, teachers and family members at the beginning of the research, which made it possible to select a strategy based on a pedagogical model to solve the research problem.
Pedagogical model of vocational orientation towards a career in Physical Culture
The pedagogical model of vocational orientation towards the LCF, of the EIDE pre-university student, was developed from the study of the theoretical-methodological foundations carried out, the diagnosis of the initial situation, the evaluations of the general polytechnic training in sports schools and the expert judgment.
From these elements, the model is built from the representation, interpretation, theoretical-methodological construction of the training process whose function is to explain, with a pedagogical approach, the vocational orientation towards the LCF, of these students and serves as a project and guide for its implementation, through a strategy that guarantees its practical realization.
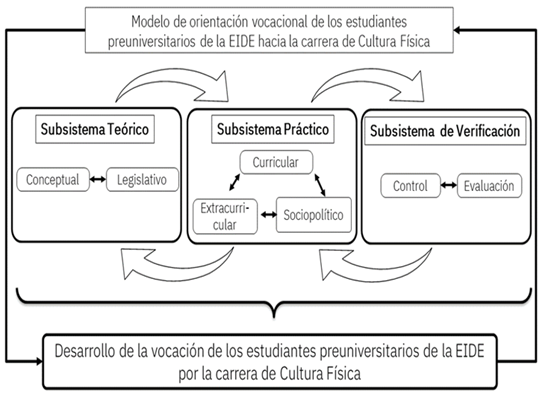
The pedagogical model has a systemic approach due to the mode of interaction and organization that exists between the subsystems and components that make it up; each component presents a high degree of specialization due to the functions they fulfill, an issue that enables its integrity and stability, despite the qualitative changes that may occur within its limits. It is structured in three subsystems, the theoretical subsystem, the practical subsystem and the verification subsystem.
The theoretical subsystem has the function of theorizing the vocational orientation of pre-university students at the EIDE; it is understood as the system of categories and legal norms that theoretically support said vocational orientation, it is what guarantees the theoretical basis that supports the pedagogical model and allows obtaining a system of knowledge that facilitates the preparation of those involved for its implementation, acts as a regulatory and normative aspect of the process that is modeled and constitutes the highest hierarchy subsystem within the structure, composed of two dialectically interrelated components that fulfill specific functions separately: the conceptual and the legislative.
The conceptual component is defined as the conceptualization of the model that emanates from the systematized theoretical foundations. This component has an argumentative function, given its multidisciplinary sociocultural approach, which is based on the theories and principles that define the theoretical possibility of modeling the vocational orientation of pre-university students from the EIDE towards the LCF.
While the legislative component is defined as the regulations and standards that support the legality of the vocational orientation of pre-university students of the EIDE towards the Career. This component has a legalization function by delimiting the legal basis on which the proposed model is based, favoring the training of educational agents in charge of implementing it and arguing the rules that regulate the vocational orientation of pre-university students from the EIDE towards the LCF.
The conceptual and legislative components reveal a close relationship of coordination, given that both complement each other and condition the theoretical basis of the model, as well as the knowledge system for its execution, while at the same time they constitute the core of the theoretical preparation of the teachers for its implementation.
On the other hand, the practical subsystem is defined as the design, planning and control of the methodological work for the vocational orientation of pre-university students from the EIDE towards the LCF. It has an explanatory function that is expressed in the theoretical-methodological conception of the ways and forms of organization to condition its implementation in practice.
The practical subsystem is structured by the curricular, extracurricular and sociopolitical component of vocational orientation. These make up the structure of the Cuban curricular model of Pre-University Education. In a close dialectical relationship, the training process of EIDE pre-university students is developed, but it differs from the pedagogical model in the dynamics, relationships and functions, based on the role that each one plays.
The curricular component is defined as the preparation for the physical-academic training of these students, its function is cognitive, since it favors the appropriation of knowledge, habits and behaviors, as well as the training and development of motor and intellectual skills in accordance with the demands social and the exercise of competition. This component is based on three interrelated elements: academic, sports and research.
The extracurricular component is defined as the promotion and development of vocational orientation towards LCF in the community. It has a complementary function by coordinating the vocational orientation towards the Career, initiated in the curricular component, through the different training and cultural actions of the academic, sports and research elements, which are now expanded with specific actions of a specialized cultural nature, aimed at the transmission of practical knowledge as a way to maintain, preserve and enrich the identity of physical culture and sport.
The sociopolitical component fulfills the cultural axiological function in which the treatment of vocational orientation towards the LCF and the level of involvement of educational agencies and agents in this task turns them into moral paradigms, as they are bearers of values that influence training. political-ideological of the student. It is made up of the educational project of each grade, year, group, sports team and curricular strategies.
Coordination relationships are established between the curricular, extracurricular and sociopolitical components, since vocational orientation requires interdisciplinary work that conditions the integration between them, which are also dimensions of the training process of the EIDE pre-university student. In the same way, the extracurricular and sociopolitical components become in a relationship of subordination with the curricular, as this is responsible for guiding, from the contents of the subjects and sports disciplines, the activities to be developed related to the four spheres of action of culture. physics and the exit to the different educational projects.
Finally, the verification subsystem is where the assurance of what is planned, organized and executed in the theoretical and practical subsystems is guaranteed; it has an evaluative function, which is expressed in guaranteeing compliance with the proposed objectives and the implementation of the actions corresponding to each of the components of these subsystems as well as allowing the analysis, comparison, correction and issuance of value judgments on the effectiveness of the vocational orientation of pre-university students from the EIDE towards the LCF.
The control and evaluation mechanisms are specified in the review of documents, visits to activities, verifications and observation, which are implemented in correspondence with the processes and results that will be controlled and evaluated. This subsystem is made up of two components, control and evaluation, which fulfill specific functions that complement each other within the subsystem.
The control component has an applicative function, since it requires the application of research techniques, procedures and instruments to personal (individual and collective) and non-personal sources, which are directly related to the processes, structures and functions involved in vocational orientation such as surveys, minutes of management and technical bodies, visits to activities of the teaching-educational process, training units, reports on the results of visits at the center, province and nation level, verification of official documents and others. The function of this component is expressed in planning, organizing, executing and concluding control.
The evaluation component allows determining the quality parameters and the level of compliance with the objectives and functions of each of the components and elements that intervene in the vocational orientation of pre-university students from the EIDE towards the LCF. Between the subsystems, a dialectical relationship of coordination occurs between the objectives, content, organizational forms, mechanisms and procedures for control and evaluation of the vocational orientation of pre-university students from the EIDE towards the LCF (Figure 1).
Pedagogical strategy for the treatment of vocational orientation of pre-university students of the EIDE towards the Bachelor's Degree in Physical Culture
The proposed pedagogical intervention strategy has a coherent, flexible and feasible structure to be modified, but it is suggested that no essential changes be introduced that affect its correspondence with the pedagogical model. Its objective is to contribute to the vocational orientation of pre-university students towards the LCF, in the EIDE training process.
The strategy is aimed at EIDE teachers and pre-university students. It considers the work developed in previous degrees related to vocational orientation and the preparation of promoters. The execution of its actions favors the dynamics of vocational orientation towards the LCF, in a flexible framework, since its adaptation is recommended, based on the diagnosis of the insufficiencies and potentialities related to vocational guidance in this process.
It is structured in phases and actions that are distributed in four stages: preparation, planning, development and verification, all dialectically interrelated, a process in which the performance of pre-university students becomes the protagonist of the dynamics of this movement, from the development of actions that lead to perfecting their vocational orientation towards the LCF.
The preparation stage aims to achieve socialization, familiarization, alignment, preparation and updating with the relevant actions to achieve levels of theoretical preparation regarding the vocational orientation of pre-university students from the EIDE towards the LCF. It has an awareness phase whose purpose is to achieve the identification and commitment of the factors involved and the training phase whose purpose is the theoretical-methodological preparation of the faculty based on the aspects contained in the pedagogical model. In the diagnosis and familiarization phase, the initial state of vocational guidance is characterized.
The planning stage aims to project and organize the actions, purposes, aspirations and goals based on the vocational orientation of the pre-university students of the EIDE; for this, structures, functions and relationships of human resources and structures that intervene in the process are established. The projective phase of this stage conceives the strategic planning of the actions in the different components of the pre-university training process, their functions and interactions, and the organizational phase has the purpose of determining functions, relationships, responsibilities, tasks and resources to guarantee compliance with the objectives projected, in each component of the vocational orientation towards the LCF.
The implementation stage aims to put into practice what was previously planned and organized. The executive phase is responsible for applying, in an exploratory manner, what is planned in each component of the vocational orientation towards the LCF in the training process of the pre-university students of the EIDE and collecting the initial and final results of this process for verification and comparison of strategy implementation.
Finally, the purpose of the verification stage is to verify the state of the vocational orientation of the pre-university students of the EIDE towards the LCF and to consider the value judgments based on the predetermined objectives.
Its main objective is to establish the degree of effectiveness of the actions implemented in the pedagogical strategy for the development of vocational orientation towards this Career, in the training process of pre-university students of the EIDE. How the strategy affects the process is evaluated by comparing the results with the proposed goals, and the pertinent actions are carried out in such a way that its objective is achieved and may include the rethinking of the actions, objectives, goals.
The planning, organization of control and evaluation phase of this stage aims to design and organize the control and evaluation of the system of actions for the vocational orientation of pre-university students from the EIDE towards the LCF and is carried out through the implementation of the actions: define the objectives of control and evaluation, determine the variables, dimensions and indicators to control and evaluate, select the methods, techniques and instruments for control and evaluation.
The objective of the analysis phase of the processing and conclusions of control and evaluation is to collect and process the information received by the controllers and evaluators to draw up the conclusions of both processes and is carried out through the collection and processing of data, the analysis, synthesis and preparation of the final report.
Assessment of the level of relevance and functionality of the pedagogical model and the strategy for the treatment of vocational orientation of pre-university students of the EIDE towards the Bachelor's Degree in Physical Culture
The assessment of the level of relevance and functionality of the model and strategy was carried out through the analysis and interpretation of the consultation of expert criteria on its feasibility, which contributed important elements in the verification of qualitative and quantitative results. Another important tool applied was the application of critical opinion and collective construction workshops that allowed the proposal to be submitted, comprehensively, to validation in educational practice.
The consultation of the experts was carried out through the Delphi method, with the objective of collecting their predictive criteria on the relevance of the pedagogical model and the strategy, which constituted an assessment and consultation prior to the partial implementation of the indicators (Table 1).
Table 1. - Absolute frequency
| Indicators | I | B.A. | A | PA | NA | TOTAL |
| I1 | 3 | 14 | 13 | 0 | 0 | 30 |
| I2 | 9 | 12 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 30 |
| i3 | 1 | 10 | 16 | 3 | 0 | 30 |
| I4 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 30 |
| i5 | 11 | 18 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 30 |
| i6 | 15 | 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 30 |
Legend: Fairly Adequate (BA), Adequate (A), Poorly Adequate (PA), Not Adequate (NA)
Ninety percent (27) of the experts believed that the theoretical coherence between the principles, premises and indicators for the implementation of vocational orientation is in the category of excellent, 76 % (23) stated that the structure of the strategy is evaluated as excellent, 83.3 % (25) evaluated the aspects related to the indications for the implementation of the strategy as excellent, 73.3 % (22) evaluated the aspects identified with the categories and definitions of excellent and 86.6 % (26) expressed that the aspects aimed at the feasibility and functionality of the strategy were excellent.
Together with the favorable criteria derived from the assessment, suggestions were made that enriched the proposed instrument, these suggestions include: preparing teachers in the use of the model in order to achieve greater motivation towards the LCF, with emphasis on the importance of same; Sstarting from the diagnosis of needs, analyze the proposed dimension and indicators to gain clarity and be able to take into account the criteria provided; prepare a guide for evaluating the model and develop training actions with teachers.
In the conclusions of the workshop, interventions were made in recognition of the novelty, the relevance of the proposal and the depth of the scientific results submitted to the analysis; it was heighted the theoretical, methodological and practical preparation of the EIDE teachers to develop the vocational orientation towards the LCF, the relationships established between the subsystems and the need to integrate the contents of the general polytechnic training subjects and those of the sports discipline, depending on the vocational orientation. They consider the treatment of vocational orientation of pre-university students from the EIDE to the LCF to be feasible.
Observation of classes and training units after applying the proposal confirmed an increase in the development of activities identified with the LCF compared to the results obtained in the initial characterization (Figure 2).
On the other hand, the results of the final survey carried out on the students showed an improvement related to the vocation, professional interests, the goals set and the immediate professional objectives, in addition to showing greater confidence in the selection of the LCF as they were more familiar with its particularities; which meant a development of the vocation for the Career (Figure 3).
Likewise, the final results of the survey applied to the EIDE teachers showed greater knowledge of the methods, techniques and ways to treat vocational orientation towards the LCF in the students' training process; they recognized the need for the integration of educational agents from the curricular, extracurricular and sociopolitical component, where the school, family, community link is established that allows the development of the vocation; the majority approved the content related to the treatment of the vocational orientation of the pre-university student towards the LCF, in the methodological preparations at the center level (Figure 4).
The final survey administered to family members revealed an improvement in the help from the school to guide their son about the opportunities offered by the Career; they recognize its particularities and social importance, in its four spheres of action; they propose to know the activities that the school develops with the aim of promoting their children's vocation, motivation and interest in it and the majority of those surveyed recognized the importance and need to train teachers in the four spheres of action of Physical Culture (Figure 5).
The final results obtained coincide with the studies of Carpio and Guerra (2017) that recognize in the activities related to vocational orientation a methodological, improvement and research character aimed at training educational agents, hence the context of the LCF and its impact on the training process of the pre-university students of the EIDE is justified.
This process, in accordance with the ideas of Erazo and Rosero (2022), considers the comprehensive conception of vocational guidance; the characterization of the development of vocational and professional interests of students; the integration of the system of influences exerted by different educational contexts with the participation of the school, family and community to motivate students for the LCF.
Briones and Trivino (2018) and Basto and Basto (2018) constitute theoretical references with which it is coincided and that support the potential of the contents that are the object of appropriation by students, during classes and training units, in order to develop vocational orientation towards LCF.
The identification and solution of the main limitations in the training process of EIDE pre-university students, related to vocational orientation towards the LCF, has points of contact with the work of Herrera et al. (2018) who, from the perspective of medical vocational training, transcends the use of the potential acquired by students, as well as the integration of school, family, community and the influences of educational agents from the curricular, extracurricular and sociopolitical aspects, based on activities identified with the Career that allow students to develop their vocation, motivation and professional interests.
CONCLUSIONS
The dialectical integration of different concepts assumed in the research allowed the development of a pedagogical model of vocational orientation of pre-university students towards the LCF that allowed promoting the vocation, interest and motivation for the profession.
The theoretical perspective assumed allowed structuring the strategy for the treatment of the vocational orientation of pre-university students towards the LCF, from the dialectical relationships between the subsystems of the model, expressed in its components, which grant it objectivity and effectiveness.
The assessment of the level of relevance and functionality of the pedagogical model and the strategy allowed to corroborate the solution to the problem, from the qualitative and quantitative analyzes obtained by the application of the instruments, which supported its reliability and viability in the LCF training process.
REFERENCIAS BIBLIOGRÁFICAS
Basto, R. M., & Basto, M. A. (2018). Tendencias históricas del proceso de formación continua de la orientación profesional en la educación preuniversitaria. Maestro y Sociedad, 27-41. https://maestroysociedad.uo.edu.cu/index.php/MyS/article/view/3375 [ Links ]
Briones, Y., & Triviño, J. (2018). Factores que intervienen para elegir carreras universitarias. Enfermería global, 1(37), 200-207. https://www.adayapress.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/04/20.pdf [ Links ]
Corrales Castro, O., Valdés Pedroso, M., & Monteagudo Soler, J. F. (2022). Acciones para el fortalecimiento de la formación laboral en profesores noveles de Educación Física/Actions to strengthen job training in novice Physical Education teachers. PODIUM - Revista De Ciencia Y Tecnología En La Cultura Física, 17(1), 41-56. https://podium.upr.edu.cu/index.php/podium/article/view/1064 [ Links ]
Carpio, A., & Guerra, L. (2017). La Orientación Profesional de los Alumnos que Ingresan a la Educación Superior. Revista Brasileira de Orientação Profissional, 11-24. https://www.redalyc.org/pdf/2030/203016901003.pdf [ Links ]
Consejo de Estado. (2019). Constitución de la República de Cuba. Editorial Política. [ Links ]
de Armas, N., Lunar, F. J., Echevarría, O., & Tamayo, Y. S. (2018). Orientación para el desarrollo de motivos profesionales del estudiante-atleta hacia la carrera de Cultura Física. En REDIPE (Ed.) Apropiación, generación y uso del conocimiento IV (pp. 211-222). Sello Editorial REDIPE. ISBN: 978-1-945570-50-6 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/336749042_ORIENTACION_PARA_EL_DESARROLLO_DE_MOTIVOS_PROFESIONALES_DEL_ESTUDIANTE _ATLETA_HACIA_LA_CARRERA_PEDAGOGICA_DE_CULTURA_FISICA [ Links ]
Echevarría, O., & Tamayo, Y. S. (2017). La Cultura Física como medio de orientación y educación para el desarrollo comunitario. Revista Innovación Tecnológica, 23. Número Especial dedicado a Evenhock. [ Links ]
Echevarría, O., Tamayo, Y. S. & Bader, F. (2018). La orientación vocacional deportiva: un proceso de ayuda para la selección de talentos. En REDIPE (Ed.) Serie: Educación y Pedagogía de la Comprensión Edificadora (pp. 211-224). Editorial Redipe, ISBN 978-1-945570-44-5. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/336749036_LA_ORIENTACION_VOCACIONAL_DEPORTIVA_UN_PROCESO_DE_AYUDA_PARA_LA_SELECCION_DE_TALENTOS [ Links ]
Echevarría, O., Tamayo, Y. S., & Jeffers, B. (2020). Talento deportivo: reorientación vocacional. Mundo FESC, 10(S1), 7-13. https://www.fesc.edu.co/Revistas/OJS/index.php/mundofesc/article /download/389/466/835 [ Links ]
Erazo, X. F., & Rosero, E. del R. (2022). Orientación vocacional y su influencia en la deserción universitaria. Horizontes. Revista De Investigación En Ciencias De La Educación, 5(18), 591-606. https://doi.org/10.33996/revistahorizontes.v5i18.198. [ Links ]
Gamboa, M. E., & Borrero, R. Y. (2019). Recursos estadísticos para investigar sobre coherencia didáctica. Ejemplos de su implementación. Editorial Académica Española. http://roa.ult.edu.cu/handle/123456789/4322 [ Links ]
Herrera, V., Tejeda, I., Quintana, M., Pérez, M. N. & Sosa, I. (2018). Formación vocacional y motivación: su incidencia en el estudio de la carrera de Medicina. EDUMECENTRO, 10, 111-125. http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S207728742018000200009. [ Links ]
Received: December 23, 2023; Accepted: January 10, 2024











 texto em
texto em